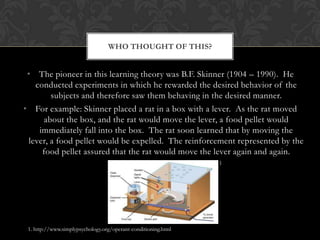
Operant conditioning is a learning theory developed by B.F. Skinner that uses reinforcement to shape behavior. It works by rewarding desired behaviors, making them more likely to reoccur. For example, Skinner conditioned rats to press a lever by rewarding them with food each time. Teachers can apply this by rewarding students for good test scores or homework with classroom rewards like prizes or computer time. This motivates students to achieve in order to receive the reinforcement, benefiting their learning.