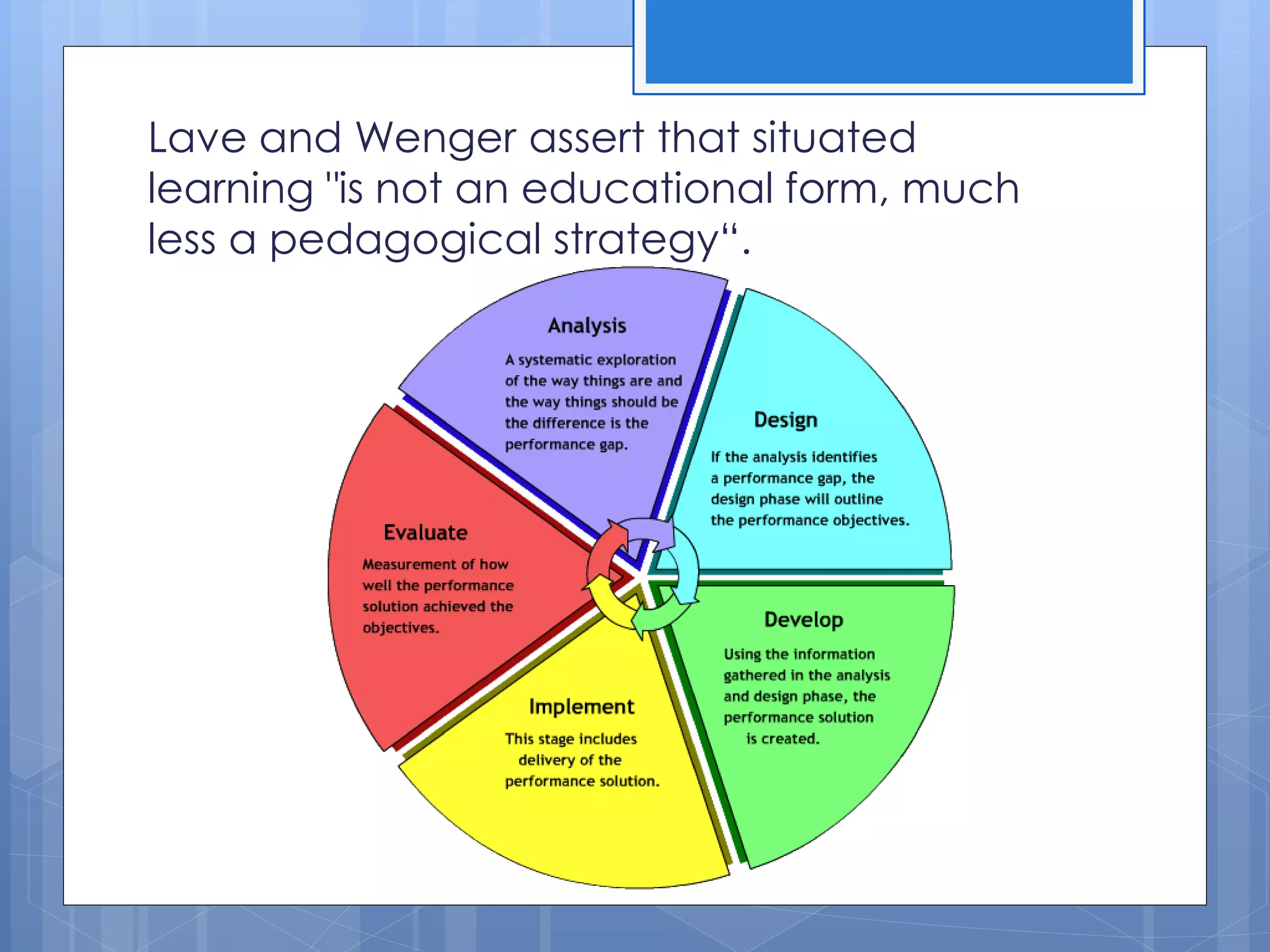
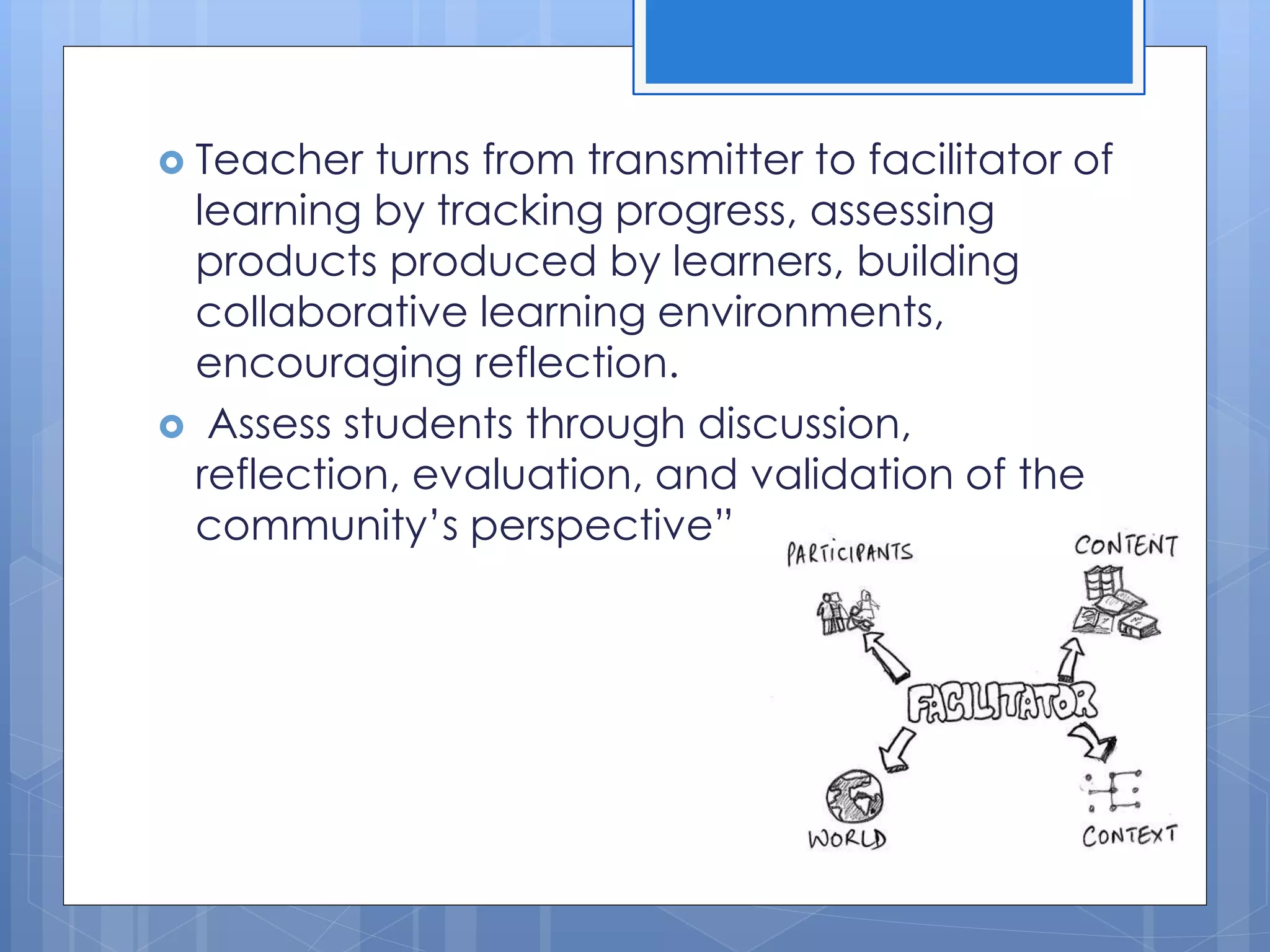
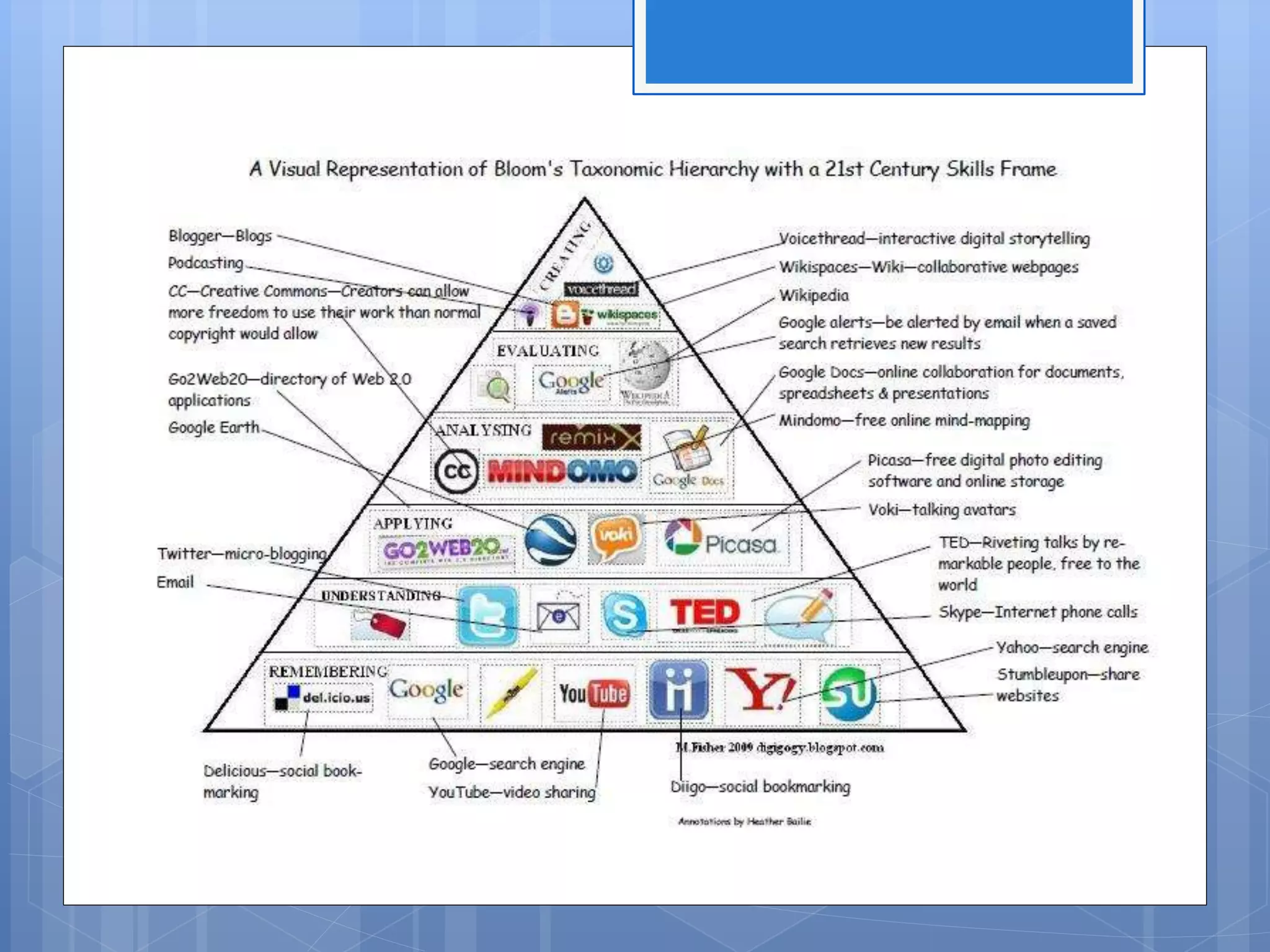
Situated learning is an instructional approach where learning occurs through authentic experiences such as field trips, internships, labs, and other activities that reflect real-world situations. It focuses on active participation over passive learning and involves students in collaborative activities that challenge them to solve complex problems. Traditional learning occurs through abstract lessons, while situated learning connects prior knowledge to contextual learning experiences.