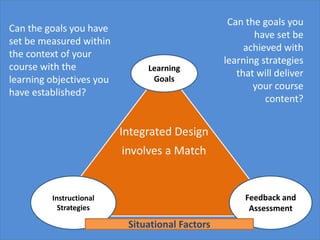
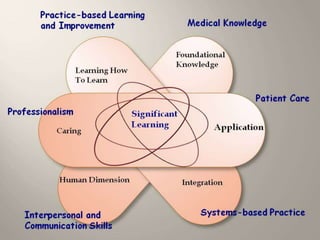
This document provides an agenda and overview for a class session on designing and implementing curricula. It discusses integrating course design using backward design by beginning with learning goals and aligning objectives, instructional strategies, and assessment. The document also covers establishing significant learning goals in different domains, writing measurable objectives, considering situational factors, anticipating barriers to implementation, and the difference between audit-ive and educative assessment. Students are asked to consider how to best implement their curricular projects and self-assess their performance in the course.