Embed presentation
Download to read offline



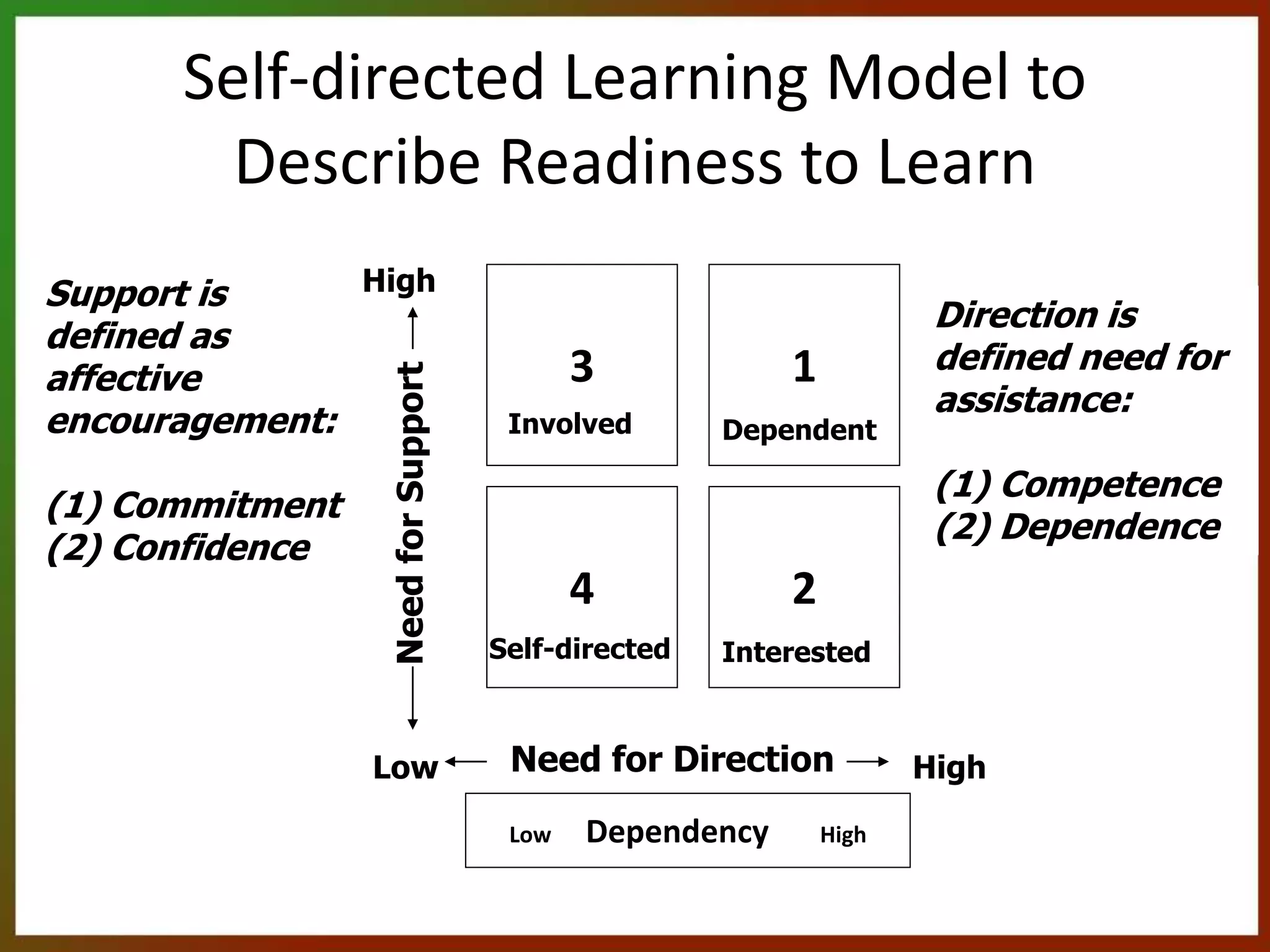
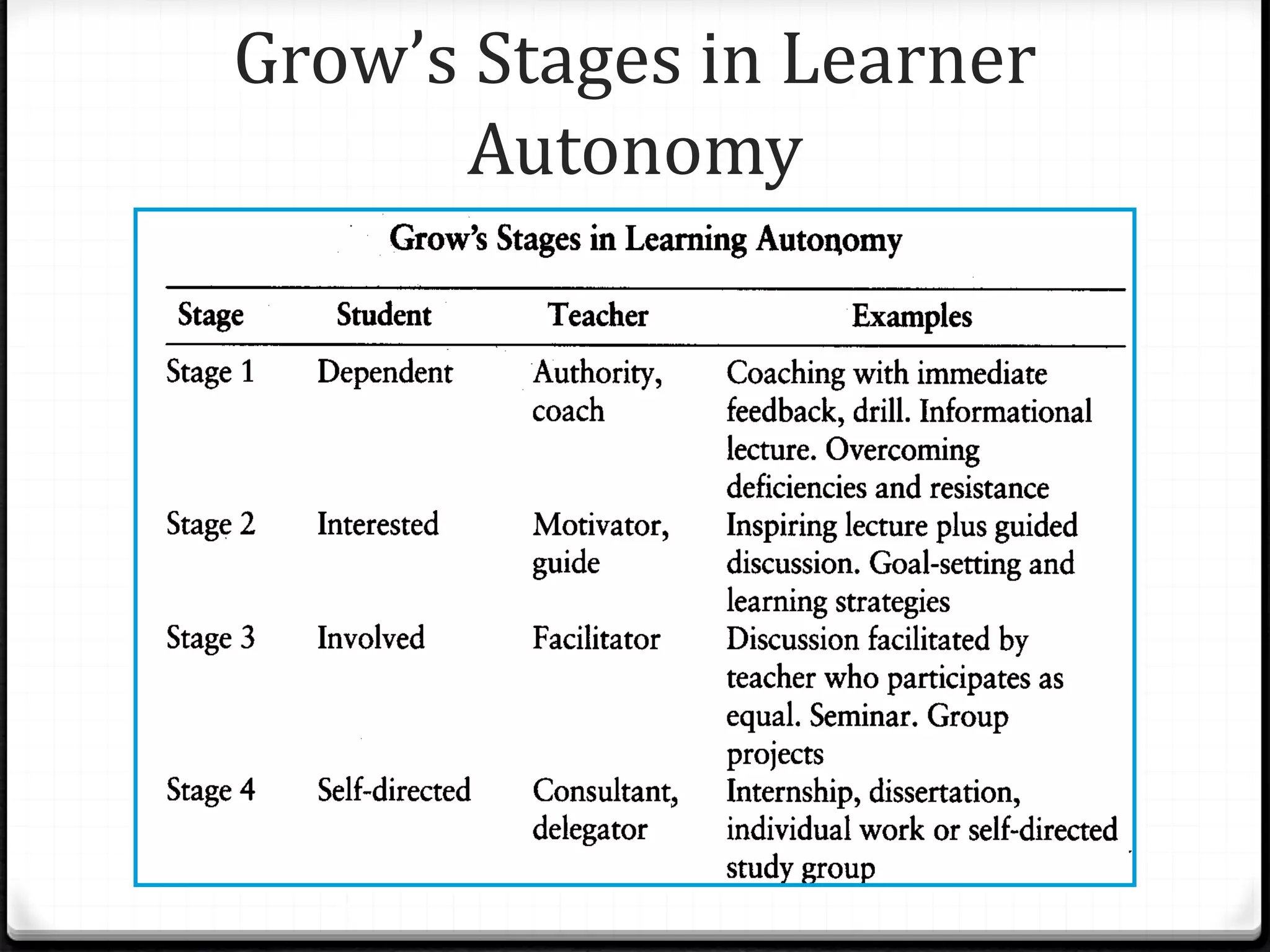



The document provides an agenda for a meeting that includes: 1) Discussing highlights from assigned textbook readings on student development, learning climate, and becoming self-directed learners. 2) Identifying competencies learners need for self-directed learning and which can be taught or selected in hiring. 3) Debating whether self-directed learning is innate or can be taught, and how it can be taught. 4) Reviewing models of readiness to learn and developing their own model for different learner levels in their setting. 5) Discussing what they know about adult learning principles.







