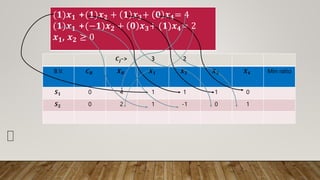
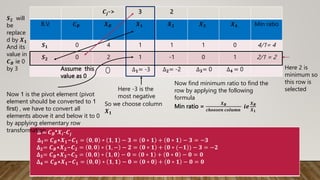
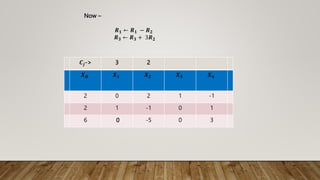
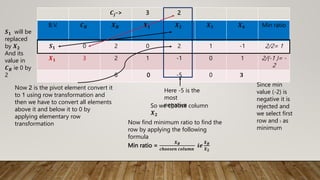
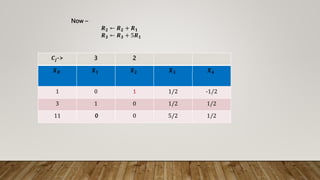
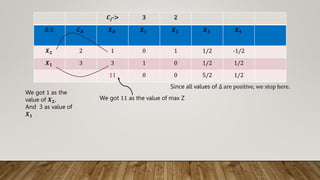
The document details the simplex method applied to a linear programming problem with the objective of maximizing the function z = 3x1 + 2x2 under specific constraints. It outlines the steps involved in incorporating slack variables, performing row transformations, and identifying pivot elements to arrive at the optimal solution. The final result indicates that the maximum value of z is 11, achieved with x1 = 3 and x2 = 1.