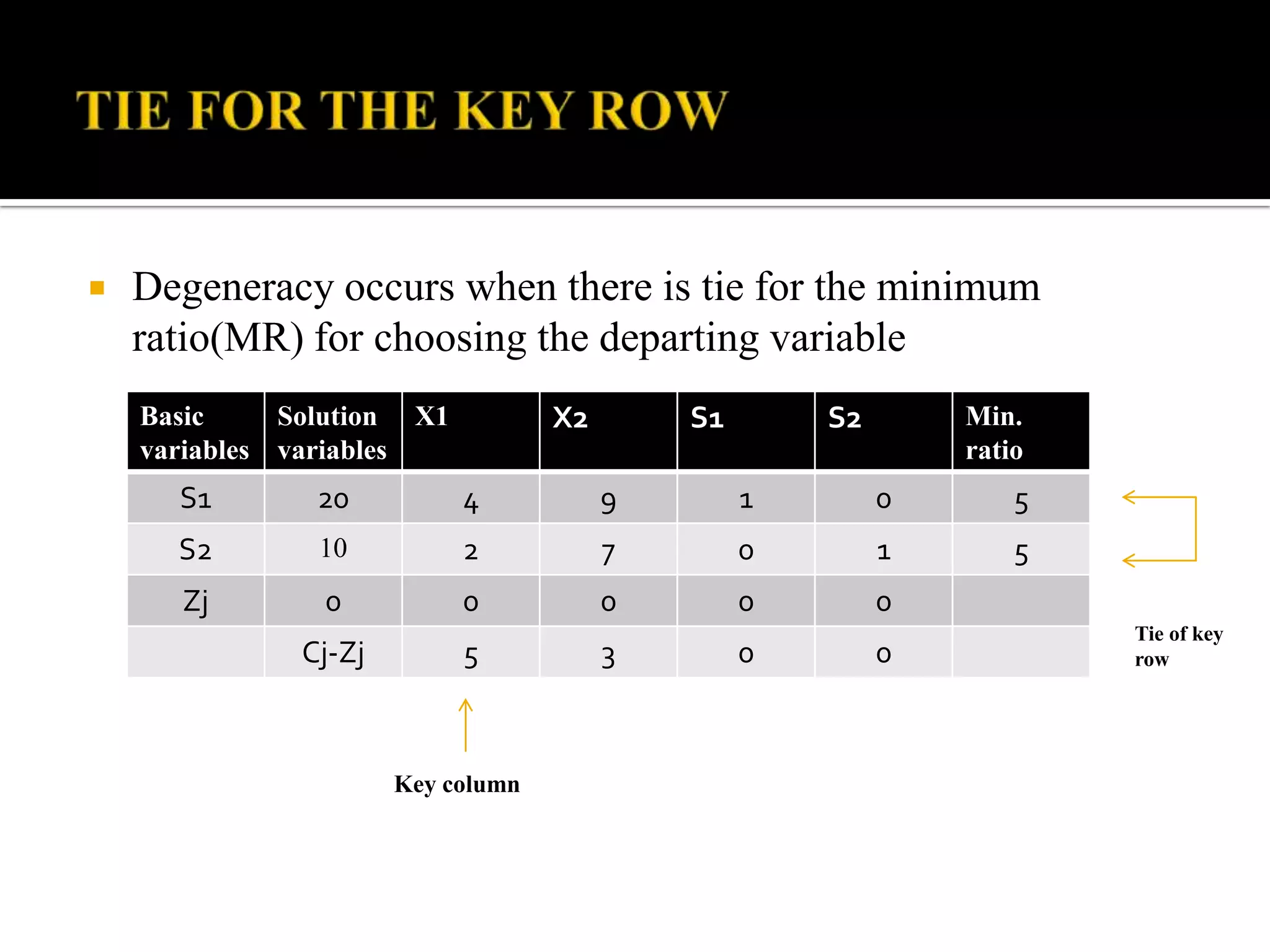
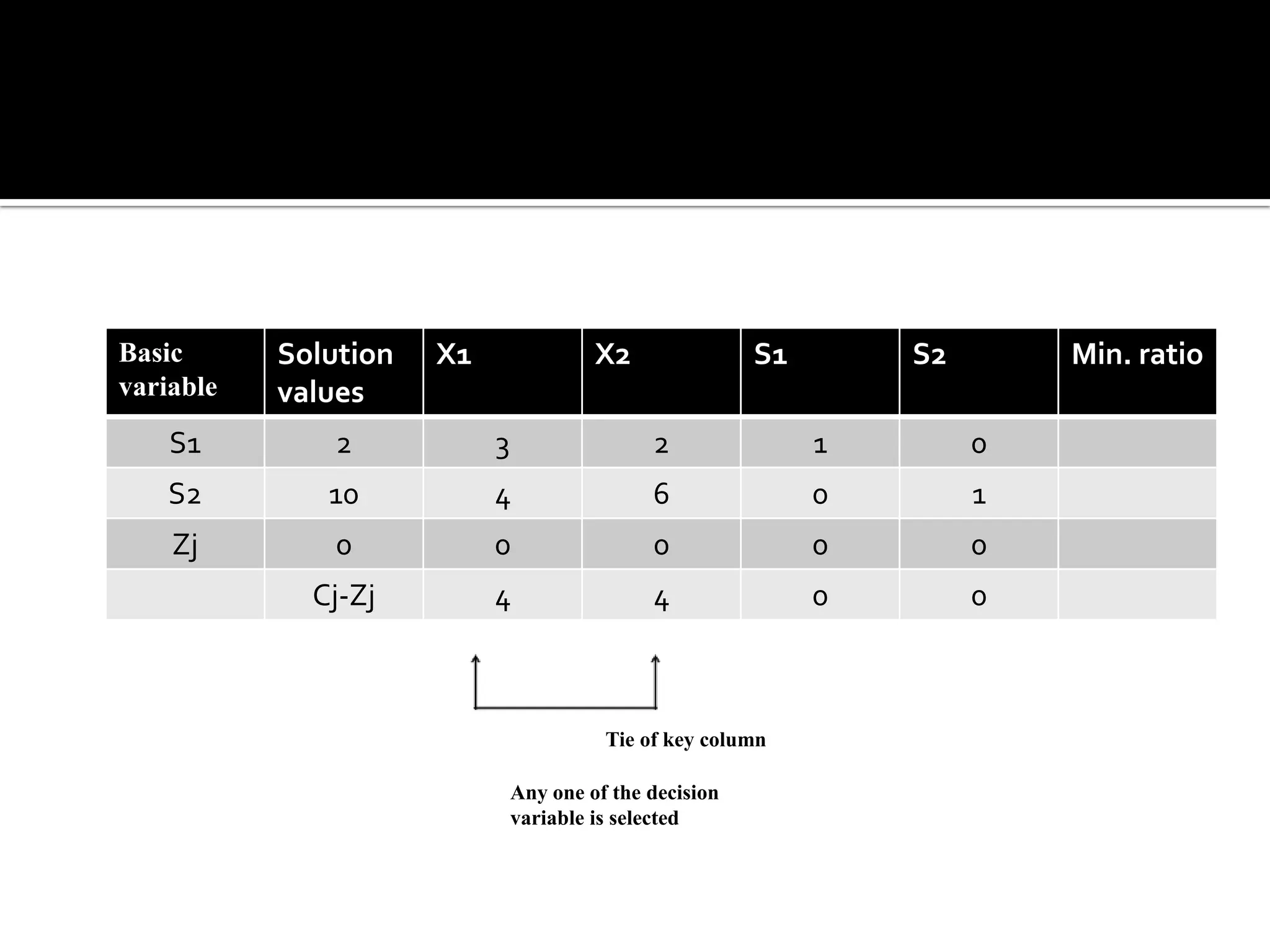
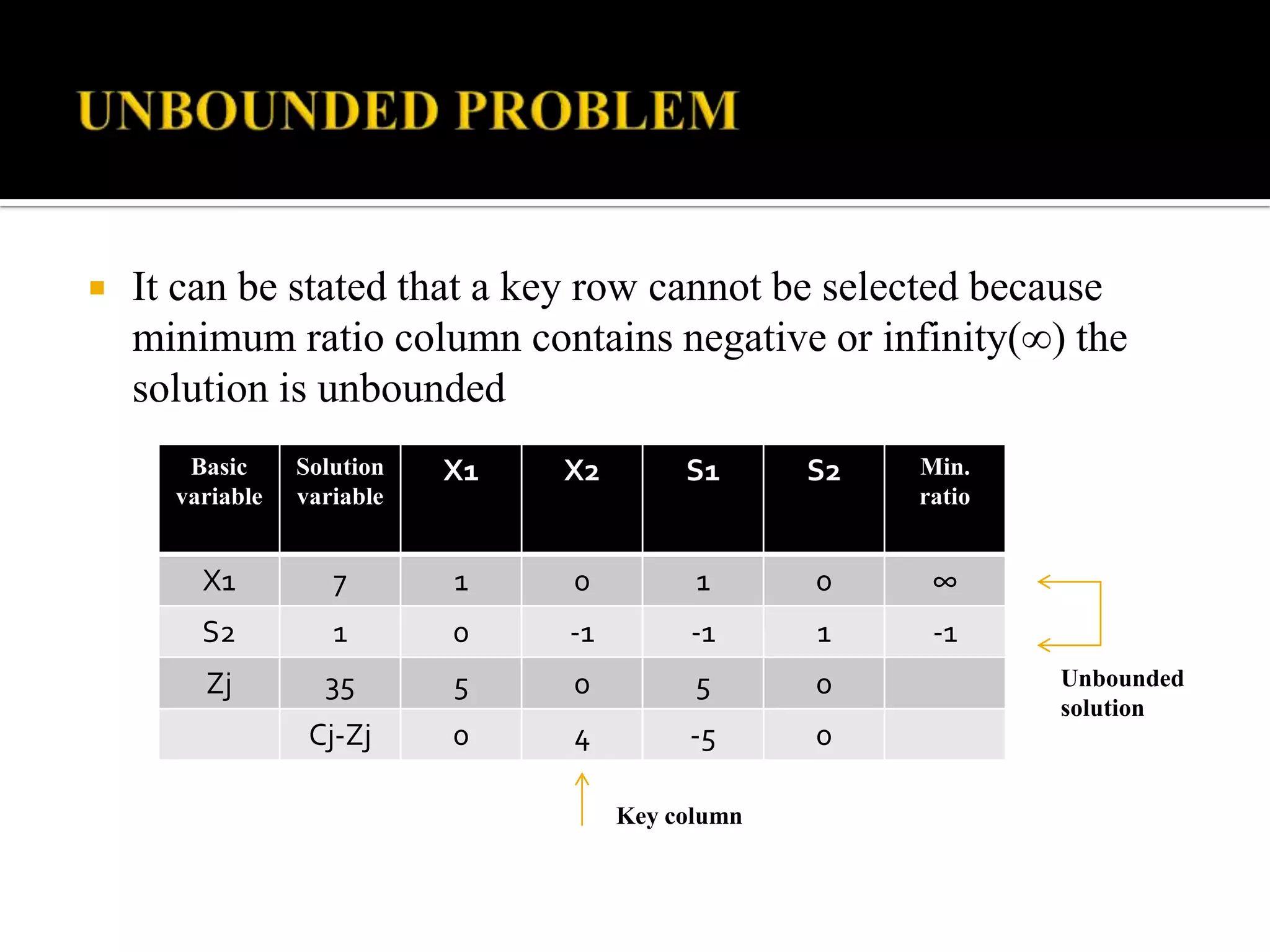
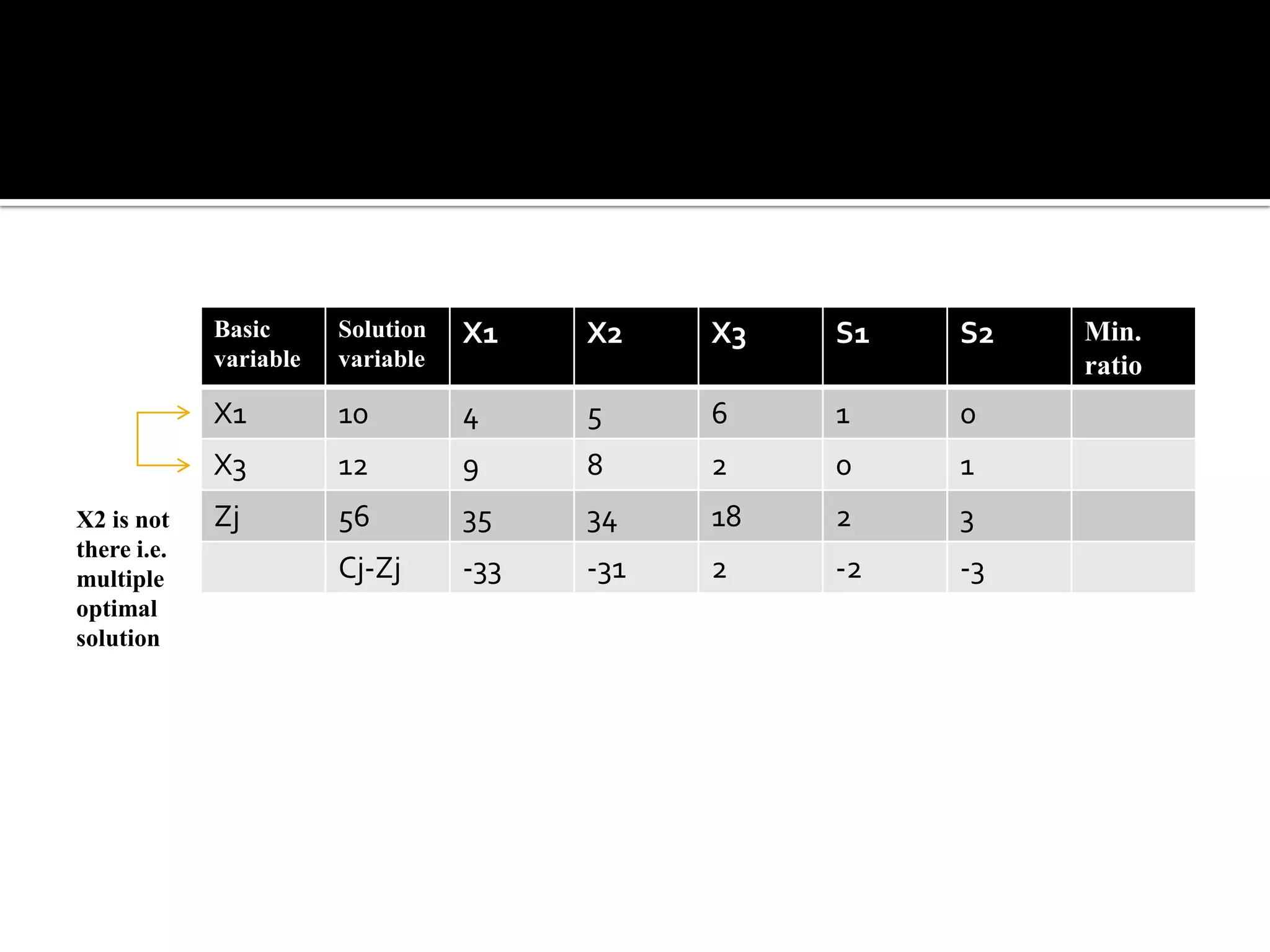
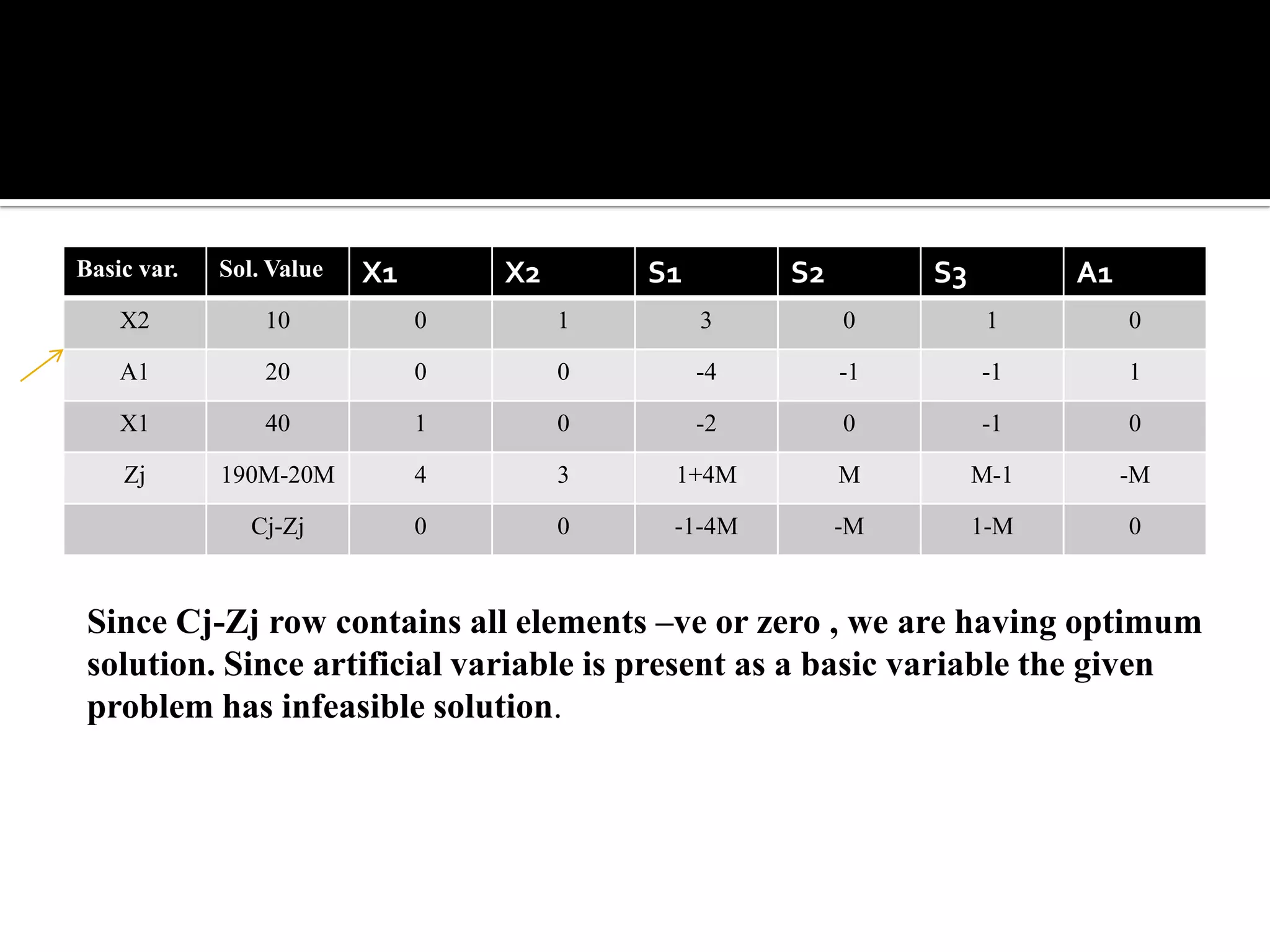
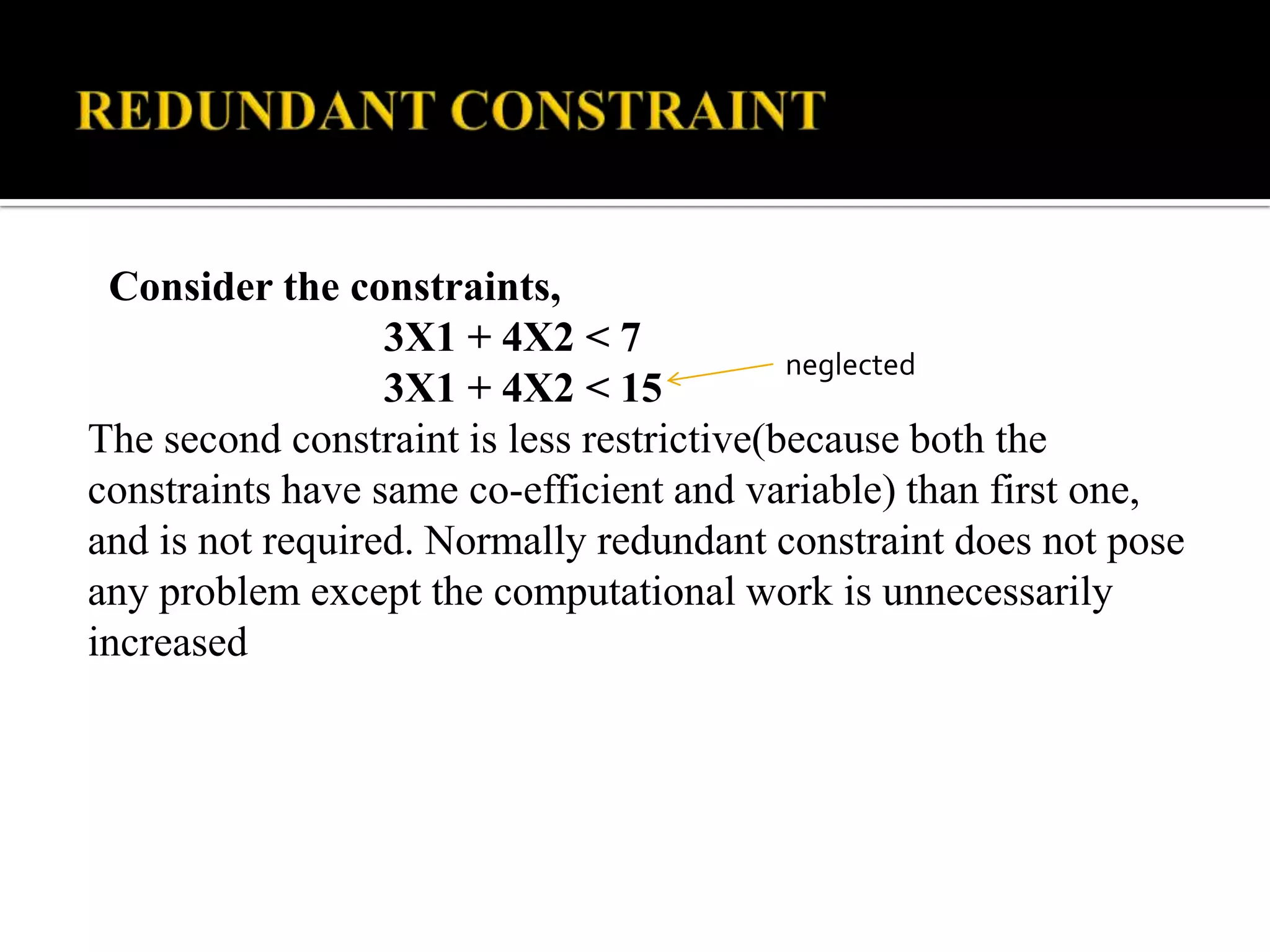
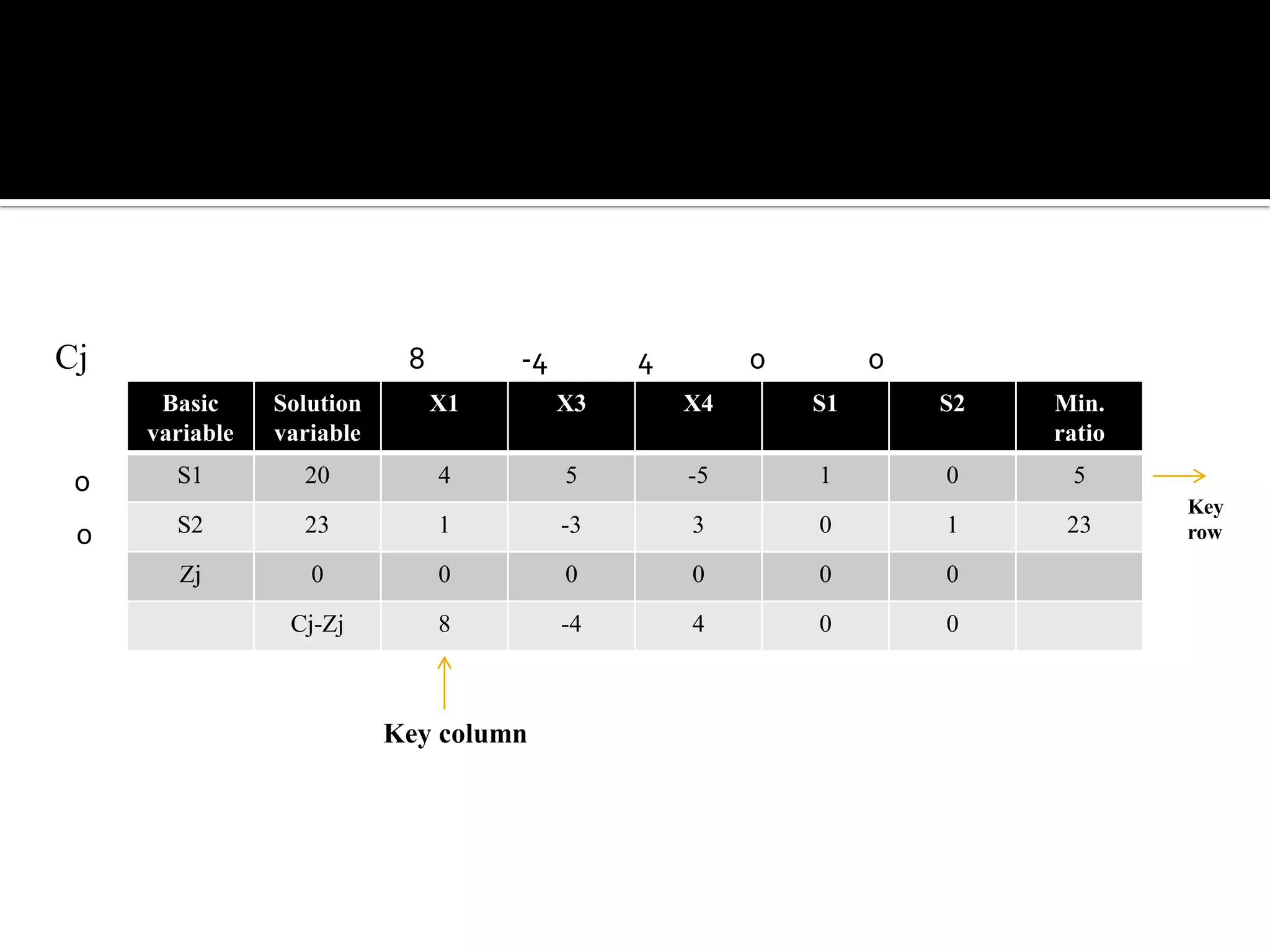
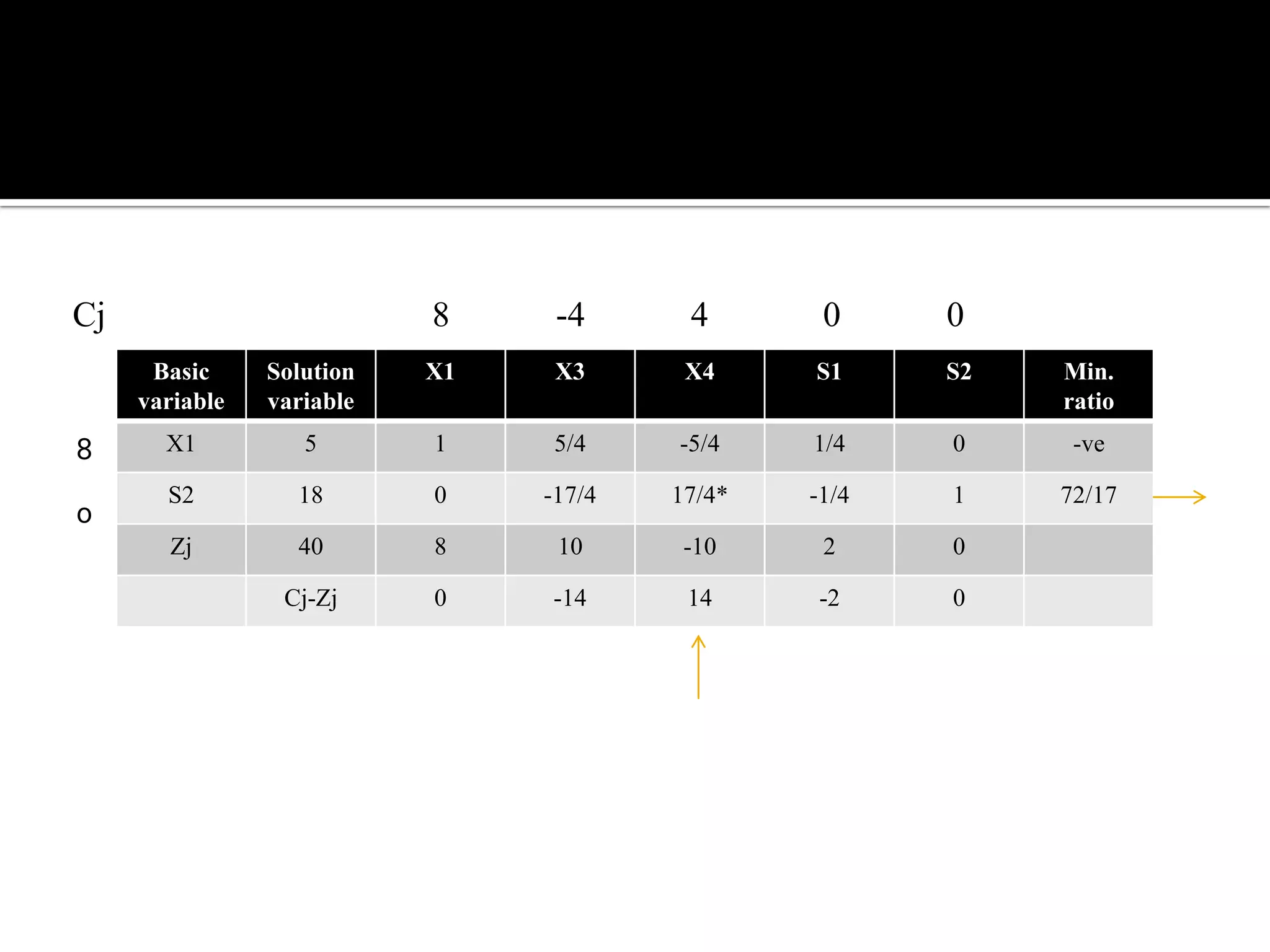
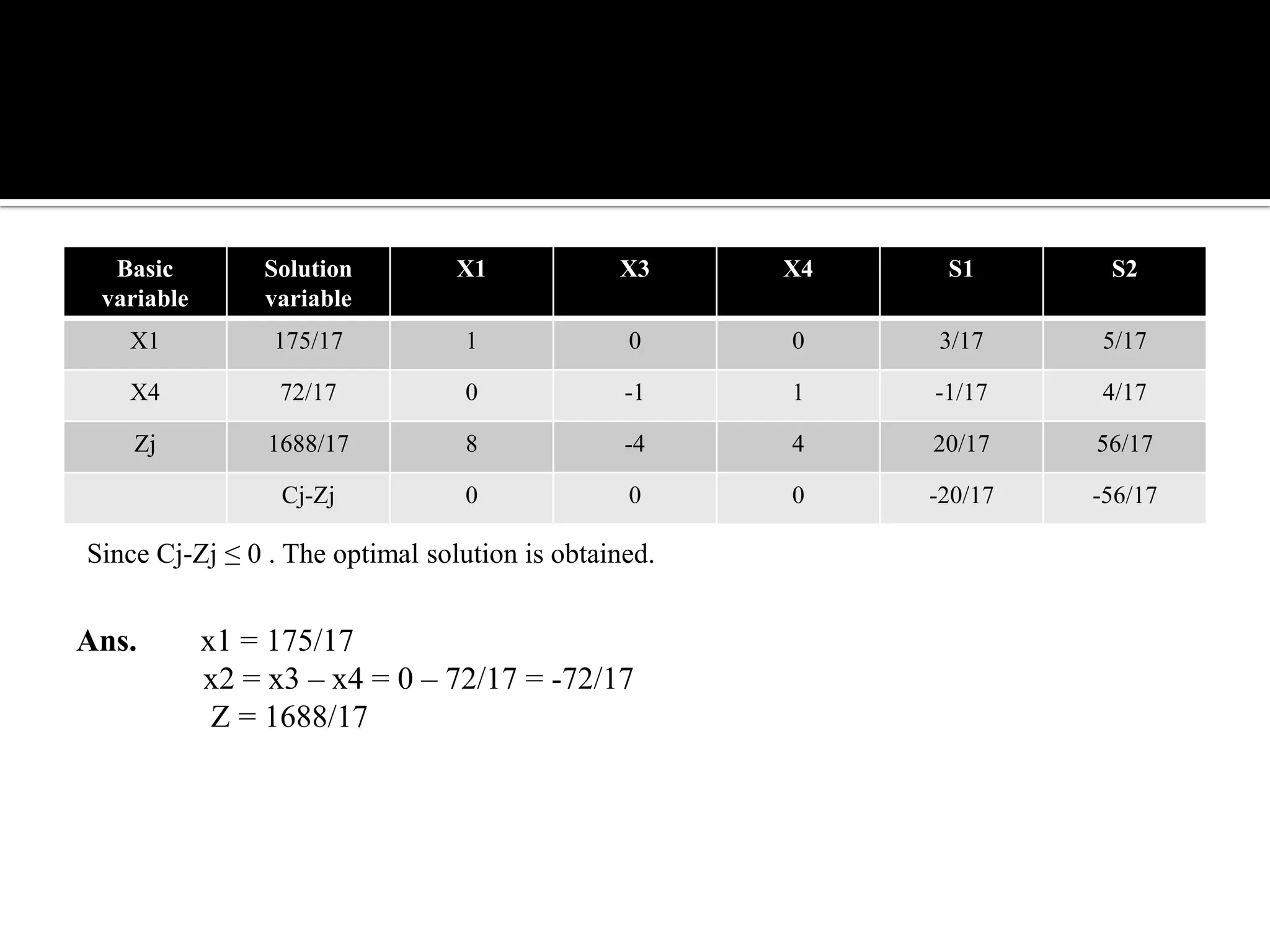
This document discusses several types of complications that can occur when solving linear programming problems (LPP), including degeneracy, unbounded problems, multiple optimal solutions, infeasible problems, and redundant or unrestricted variables. It provides examples and explanations of how to identify each type of complication and the appropriate steps to resolve it such as introducing slack or artificial variables, breaking ties, or setting unrestricted variables equal to the difference of two non-negative variables.