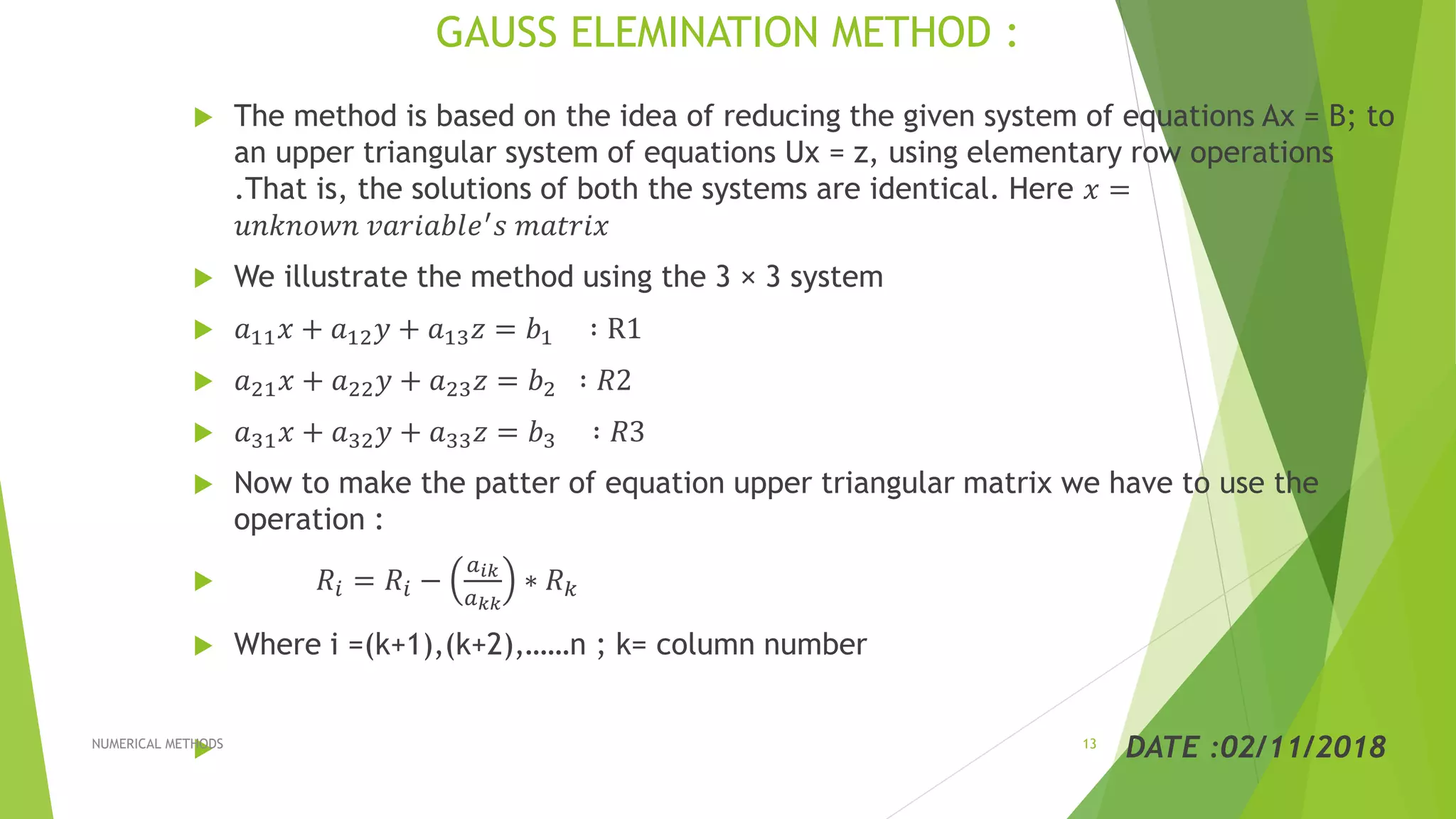
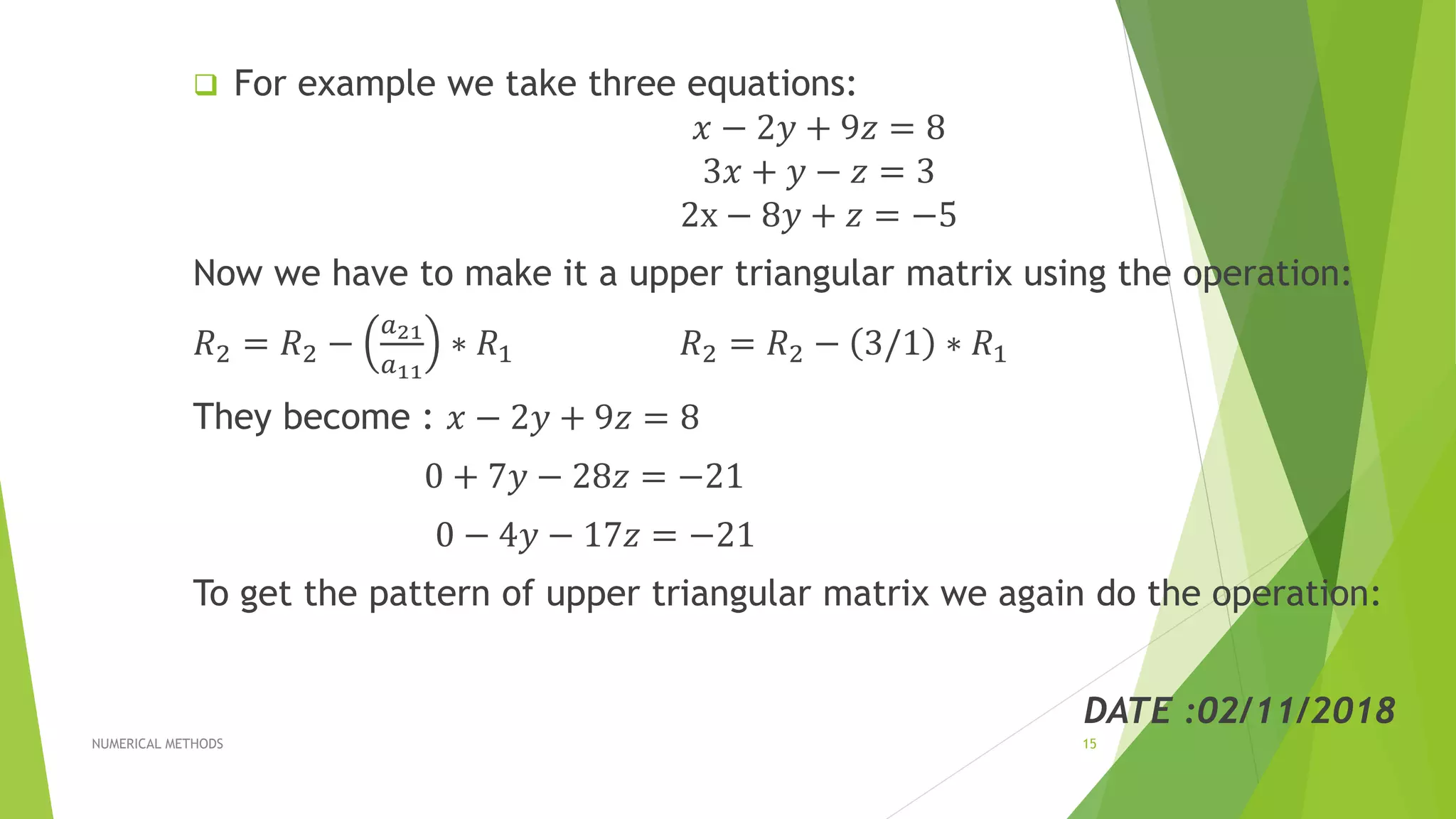
The document presents methods for solving systems of linear equations, specifically focusing on the LU factorization method and the Gauss elimination method. It describes the process of using triangular matrices to find solutions and illustrates the techniques with examples. The conclusion highlights the efficiency of triangular systems over more complex methods like matrix inversion.


![LU Factorization Method :
This method is based on the fact that every square matrix can be represented as a
product of lower and upper triangular matrix; i.e. [A]=[L]*[U]
[L]=Lower triangular matrix; [U]=Upper triangular matrix
Provided all the principle minors are non singular .
Let us consider we have : 𝑎11 𝑥 + 𝑎12 𝑦 + 𝑎13 𝑧 = 𝑏1
𝑎21 𝑥 + 𝑎22 𝑦 + 𝑎23 𝑧 = 𝑏2
𝑎31 𝑥 + 𝑎32 𝑦 + 𝑎33 𝑧 = 𝑏3
the system of equation can be represented as : [A]*[X]=[B]
now matrix A can be represented as [A]=[L]*[U]
DATE :02/11/2018NUMERICAL METHODS 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-5-2048.jpg)
![[A]=[L]*[U]=
𝑙11 0 0
𝑙21 𝑙22 0
𝑙31 𝑙32 𝑙33
*
1 𝑢12 𝑢13
0 1 𝑢23
0 0 1
From here we have to find the values of the elements of lower & upper triangular
matrix.
Then : [A]*[X]=[B];
[L]*[U]*[X]=[B]; As : [A]=[L]*[U]
Now we have to consider that [U]*[X]=[Y] ----------(i)
So that [L]*[Y]=[B]---------------------(ii)
Now using the (ii) equ. We have to find the elements of matrix [Y];where [L],[B]
Is known to us.
Then using the matrix [Y] in equ. (i) we can find the unknown variable matrix
[X] & get the set of solution of the given equation.
DATE :02/11/2018
NUMERICAL METHODS 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-6-2048.jpg)
![ For example we have three equation given bellow and find the sol. By LU method :
8𝑥 − 3𝑦 + 2𝑧 = 20
4𝑥 + 11𝑦 − 𝑧 = 33
6x + 3𝑦 + 12𝑧 = 36
The given equ. Can be represented as : [A]*[X]=[B];
A=
8 −3 2
4 11 −1
6 3 12
,B=
20
33
36
,X=
𝑥
𝑦
𝑧
A=L*U;
𝑙11 0 0
𝑙21 𝑙22 0
𝑙31 𝑙32 𝑙33
*
1 𝑢12 𝑢13
0 1 𝑢23
0 0 1
=
8 −3 2
4 11 −1
6 3 12
Leading to : 𝑙11 = 8 ; 𝑙11 𝑢12 = −3 𝑢12 = −(
3
8
)
DATE :02/11/2018
NUMERICAL METHODS 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-7-2048.jpg)
![ 𝑙11 𝑢13 = 2 𝑢13 =
1
4
;
𝑙21 = 4; 𝑙21 𝑢12 + 𝑙22 = 11 𝑙21 = 11 − 𝑙21 𝑢12 = (
25
2
)
𝑙21 𝑢13 + 𝑙22 𝑢23 = −1 𝑢23 = −
4
5
𝑙31 = 6; 𝑙31 𝑢12 + 𝑙32 = 3 6 ∗ −
3
8
+ 𝑙32 = 3 𝑙32 = (
21
4
)
𝑙31 𝑢13 + 𝑙22 𝑢23 + 𝑙33 = 12
𝑙33= (
567
50
) [using the values ]
Hence [L]=
8 0 0
4 (
25
2
) 0
6 (
21
4
) (
567
30
)
& [U]=
1 −(
3
8
) (
1
4
)
0 1 (−
4
25
)
0 0 1
Thus the equation A*X=B i.e. L*U*X=B
Now consider L*Y=B ------------(I)
where U*X=Y-------------(II)
DATE :02/11/2018
NUMERICAL METHODS 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-8-2048.jpg)
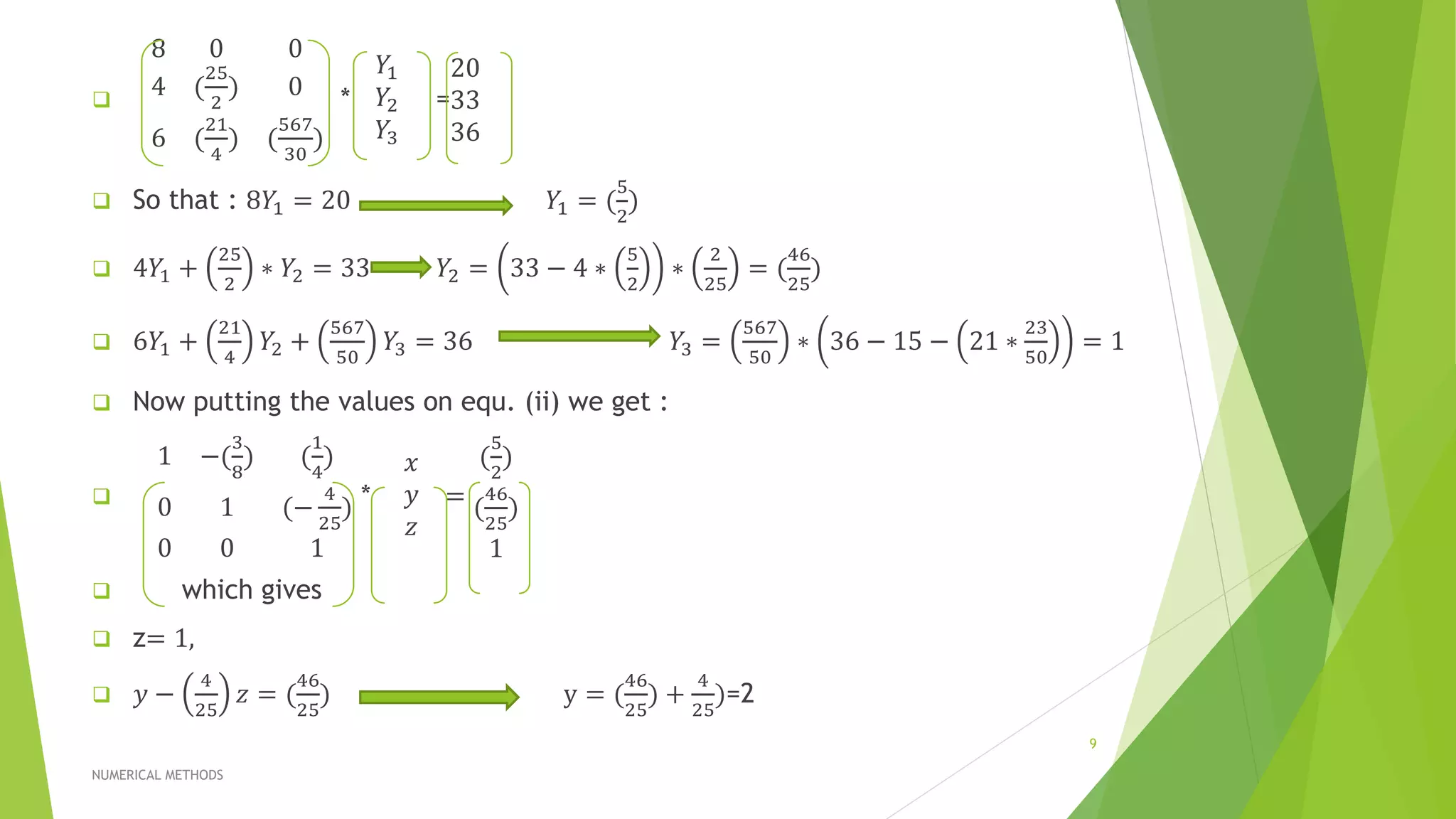



![So after applying the operation the equation becomes :
𝑎11 𝑥 + 𝑎12 𝑦 + 𝑎13 𝑧 = 𝑏1
0+𝑎′12 𝑦 + 𝑎′13 𝑧 = 𝑏′2 [𝑅′2 = 𝑅2 −
𝑎21
𝑎11
∗ 𝑅1 ]
0+𝑎′12 𝑦 + 𝑎′13 𝑧 = 𝑏′3 [ 𝑅′3 = 𝑅3 −
𝑎31
𝑎11
∗ 𝑅1 ]
then after that we have to apply the same process to make that pattern
to a upper triangular matrix.
𝑎11 𝑥 + 𝑎12 𝑦 + 𝑎13 𝑧 = 𝑏1
0+𝑎′22 𝑦 + 𝑎′23 𝑧 = 𝑏′2
0 + 0 + 𝑎′′33 𝑧 = 𝑏′′3 [ 𝑅′′3 = 𝑅′3 −
𝑎32
𝑎22
∗ 𝑅2 ]
the successively we can find the values Z, Y, X.
DATE :02/11/2018NUMERICAL METHODS 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-14-2048.jpg)



![INVERSSION OF MATRIX :
Let us consider we have a matrix [A] & we have to find the inverse of that
matrix . Let [x] be the inverse of matrix [A].
we know that : A ∗ 𝐴−1 = [𝐼]
now : [A]*[X]=[I] as we considered that : [X]= 𝐴−1
Then we convert the system into an augmented matrix
in the form of [A|I ].
then we have to use elementary row operation on the
augmented matrix to get upper triangular matrix by using
Gauss Elimination Method.
DATE :02/11/2018NUMERICAL METHODS 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-19-2048.jpg)
![Let us consider we have a matrix like this :
A=
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
𝑎21 𝑎22 𝑎23
𝑎31 𝑎32 𝑎33
& the inverse of [A] is [x] (say).
Let x is : x=
𝑥11 𝑥12 𝑥13
𝑥21 𝑥22 𝑥23
𝑥31 𝑥32 𝑥33
: A ∗ 𝐴−1 = [𝐼]
now : [A]*[X]=[I] as we considered that : [X]= 𝐴−1
The augmented matrix looks like : [A| I ]
=
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
𝑎21 𝑎22 𝑎23
𝑎31 𝑎32 𝑎33
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
=
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
0 𝑎′22 𝑎′23
0 𝑎′32 𝑎′33
1 0 0
𝑔21 𝑔22 0
𝑔31 0 1
=
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
0 𝑎′22 𝑎′23
0 0 𝑎′′33
1 0 0
𝑔21 𝑔22 0
𝑔′31 𝑔′32 1
DATE :02/11/2018
NUMERICAL METHODS 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-20-2048.jpg)
![Then we can get the equivalent system of three equ.
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
0 𝑎′22 𝑎′23
0 0 𝑎′′33
*
𝑥11
𝑥21
𝑥31
=
1
𝑔21
𝑔′31
from here we can calculate the values of 𝑥11; 𝑥21; 𝑥31 .
Similarly :
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
0 𝑎′22 𝑎′23
0 0 𝑎′′33
*
𝑥12
𝑥22
𝑥32
=
0
𝑔22
𝑔′32
From here we can calculate the values of 𝑥12; 𝑥22 ; 𝑥32
Similarly :
𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13
0 𝑎′22 𝑎′23
0 0 𝑎′′33
*
𝑥13
𝑥23
𝑥33
=
0
𝑔22
𝑔′32
from here we can calculate the values of 𝑥13; 𝑥23 ; 𝑥33.
so that we have the elements of inverse matrix [X] ; which is our required solution.
DATE :02/11/2018
NUMERICAL METHODS 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-21-2048.jpg)
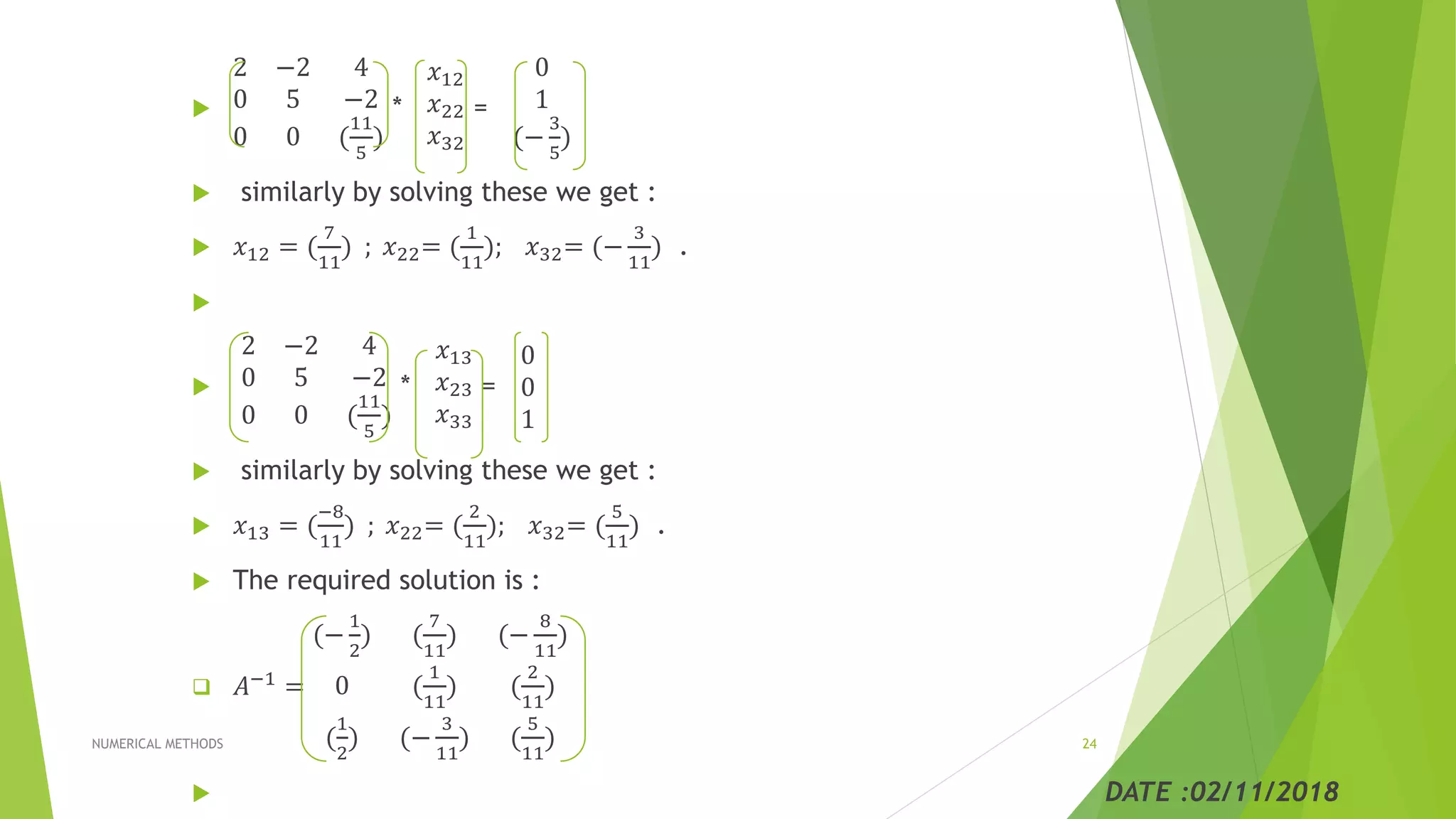
![ For example we take a matrix and try to find it’s inverse :
A =
2 −2 4
2 3 2
−1 4 −1
consider the augmented matrix is :
2 −2 4
2 3 2
−1 4 −1
: 1 0 0
: 0 1 0
: 0 0 1
=
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 3 1
: 1 0 0
: −1 1 0
: (
1
2
) 0 1
[using 𝑅′2 = 𝑅2 −
2
2
∗ 𝑅1; 𝑅′
3 = 𝑅3 − (
1
2
)𝑅1]
DATE :02/11/2018NUMERICAL METHODS 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-22-2048.jpg)
![ =
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 0 (
11
5
)
: 1 0 0
: −1 1 0
: (
11
10
) −(
3
5
) 1
[using 𝑅′′3 = 𝑅3 −
3
5
∗ 𝑅2]
The inverse matrix is given as : X=
𝑥11 𝑥12 𝑥13
𝑥21 𝑥22 𝑥23
𝑥31 𝑥32 𝑥33
Thus we have an equivalent system of three equation :
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 0 (
11
5
)
*
𝑥11
𝑥21
𝑥31
=
1
−1
(
11
10
)
which gives :2𝑥 − 2𝑦 + 4𝑧 = 1;
5𝑦 − 2𝑧 = −1;
11
5
∗ 𝑧 = (
11
10
)
Solving by back substitution method we get ;
𝑥 = −
1
2
; 𝑦 = 0; 𝑧 = (
1
2
)
DATE :02/11/2018NUMERICAL METHODS 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalsolutionofsystemoflinearequations-181103022514/75/Numerical-solution-of-system-of-linear-equations-23-2048.jpg)