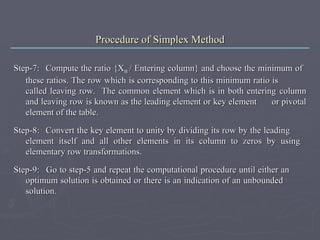
The steps of the simplex method for solving a linear programming problem are:
1) Convert the problem to one of maximization and make the right-hand sides of constraints non-negative.
2) Introduce slack/surplus variables to convert inequalities to equations.
3) Obtain an initial basic feasible solution and compute net evolutions.
4) If a negative net evolution exists, select the most negative column and row ratios to identify a new basis.
5) Iterate steps 5-8 until an optimum solution is found or the problem is determined to be unbounded.