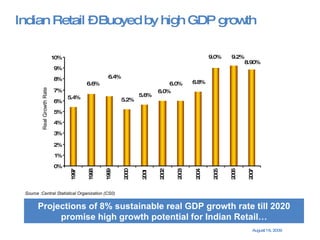
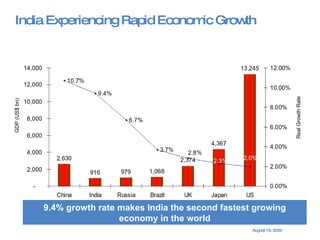
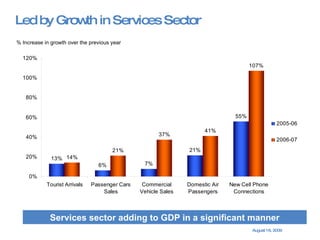
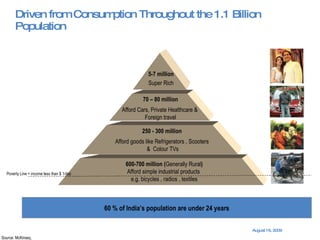
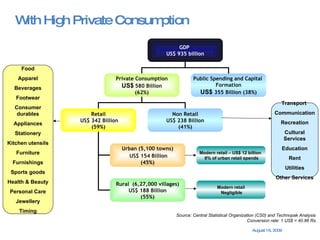
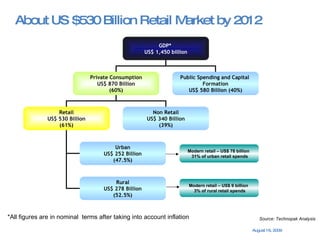
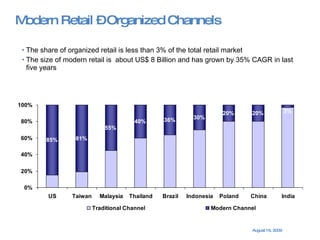
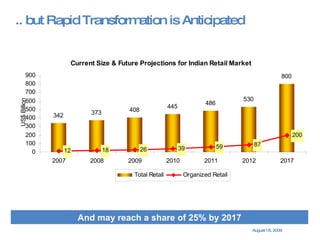
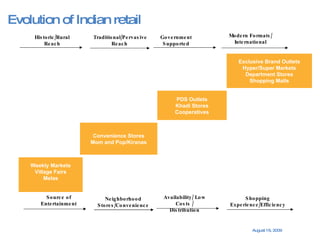
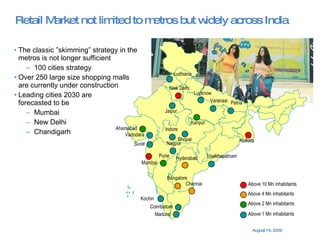
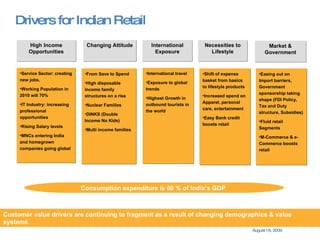
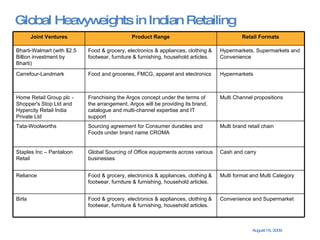
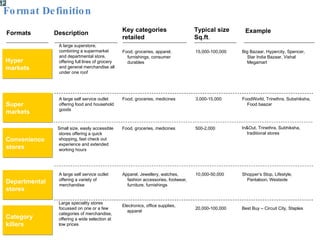
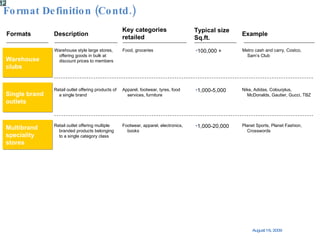
The document summarizes the changing retail landscape in India. It notes that India is experiencing rapid economic growth driven by a high GDP growth rate and rising private consumption. This is fueling growth of the retail sector, though modern retail currently makes up a small portion. Various formats of retail are discussed including hypermarkets, convenience stores, and brand outlets. Global retailers are entering the Indian market through joint ventures.