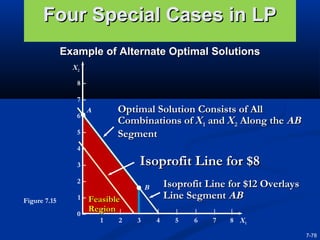
This document provides an overview of linear programming models and techniques. It discusses the basic assumptions and requirements of linear programming problems, including having an objective function to maximize or minimize, constraints, alternative courses of action, and linear expressions. The document then covers how to formulate a linear programming problem by understanding the problem, identifying the objective and constraints, defining decision variables, and writing mathematical expressions. It provides an example problem involving determining the optimal product mix for a furniture company. Finally, it discusses solutions methods for linear programming problems, including graphical methods of analyzing the feasible region and using isoprofit lines or analyzing corner points to find the optimal solution.