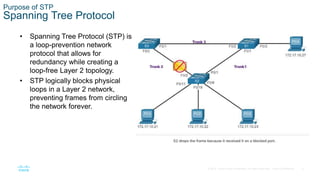
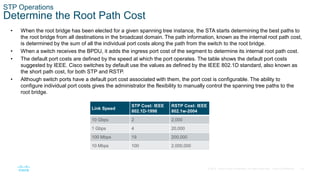
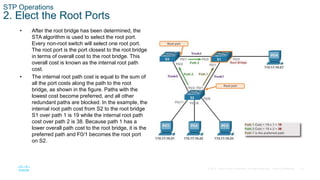
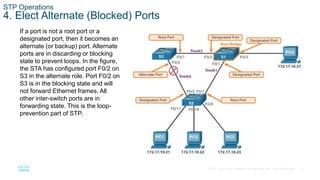
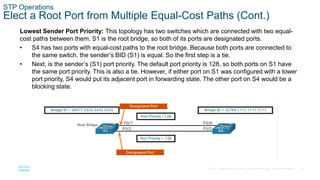
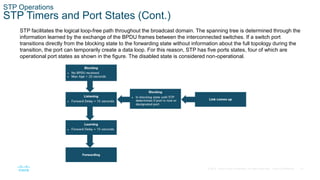
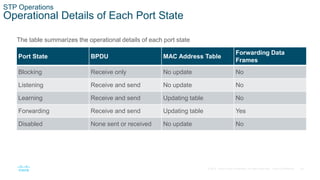
The document discusses spanning tree protocol (STP) and how it creates a loop-free layer 2 network topology. STP works by electing a single root bridge as a reference point. It then selects root ports, designated ports, and alternate/blocked ports on each switch to ensure only one path exists between any two switches, preventing loops. This is done by exchanging BPDUs and selecting ports based on criteria like bridge ID, port priority, and port ID for ports with equal path costs. STP allows for redundancy while avoiding broadcast storms caused by loops.