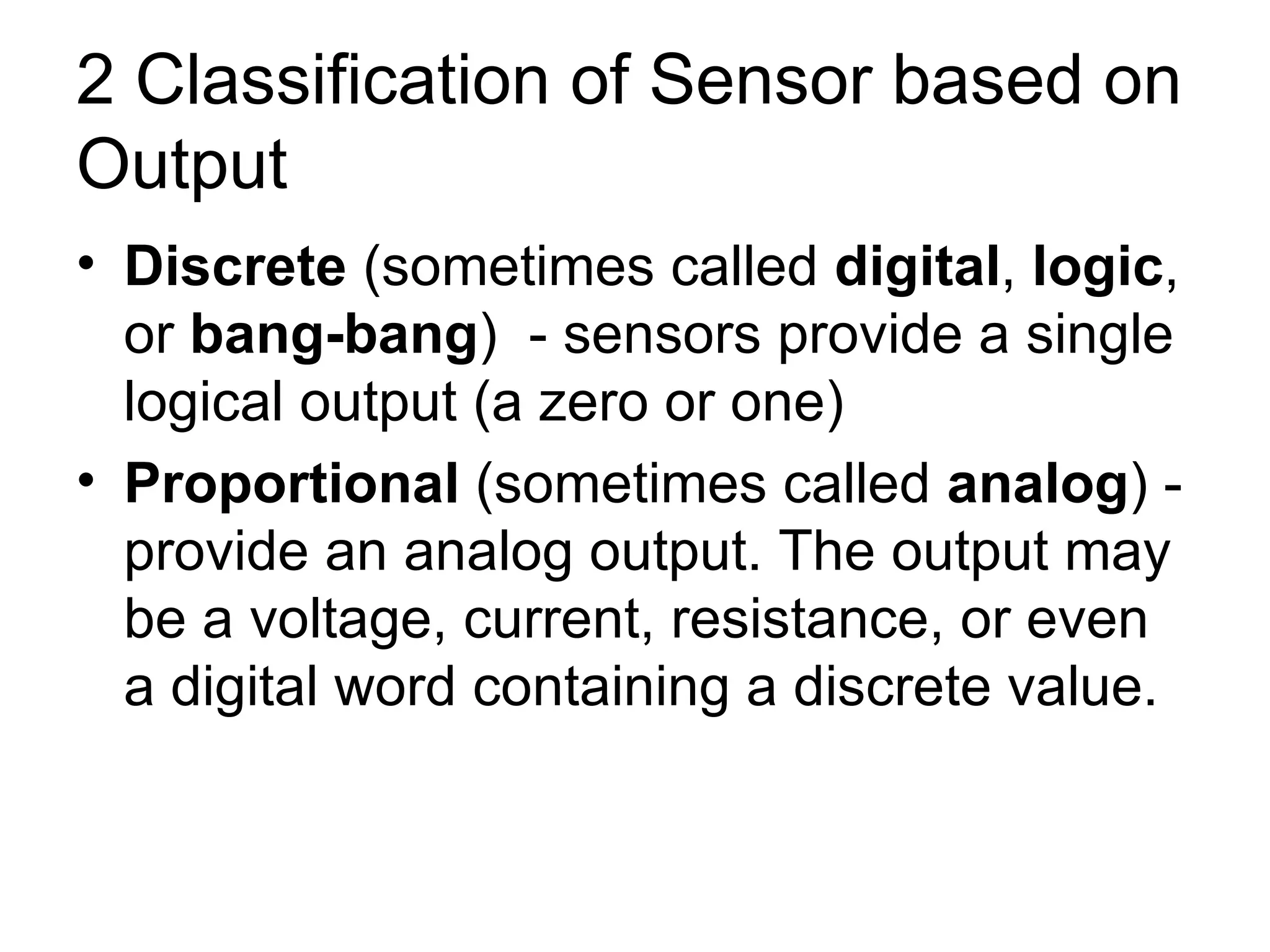
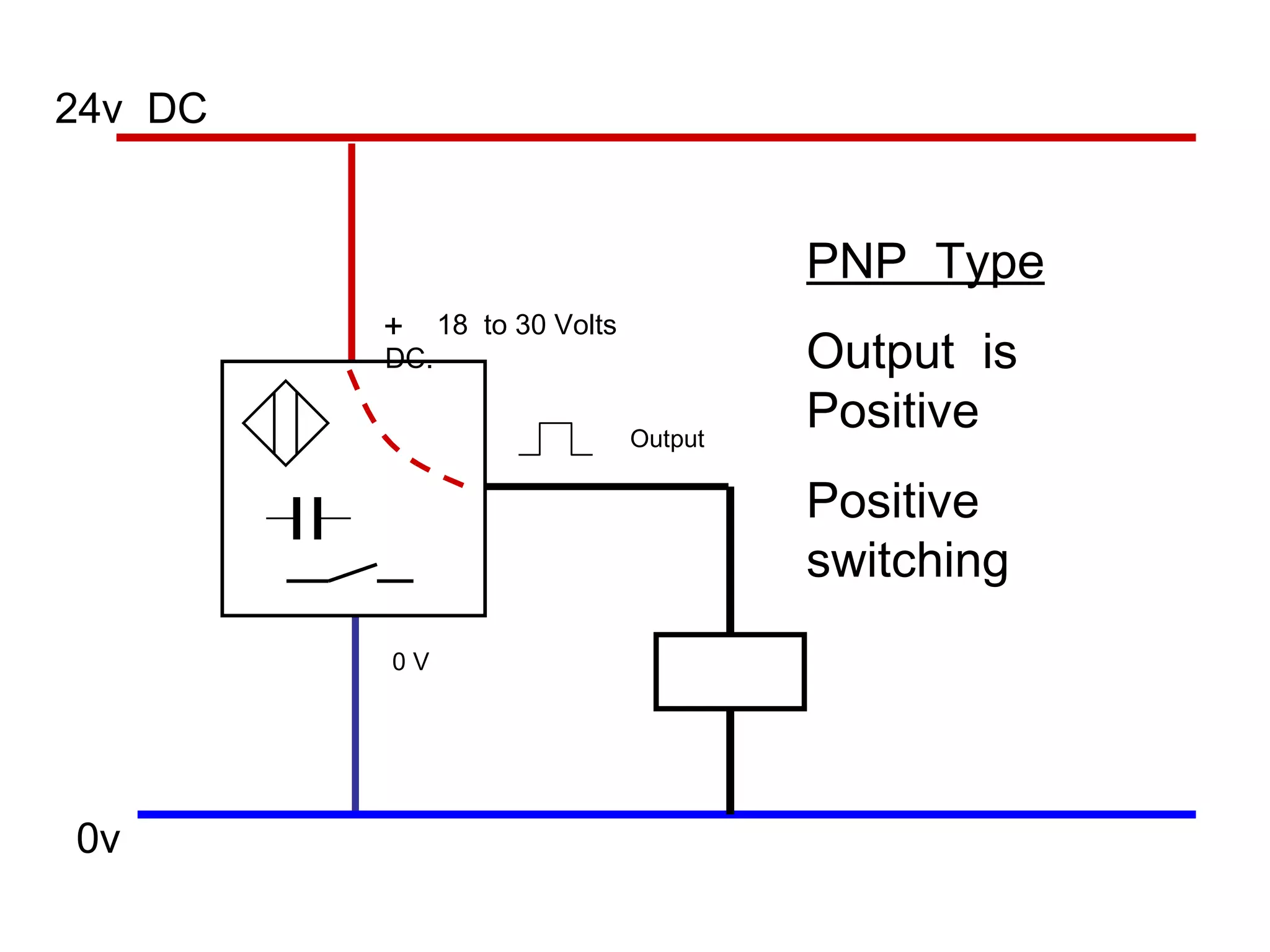
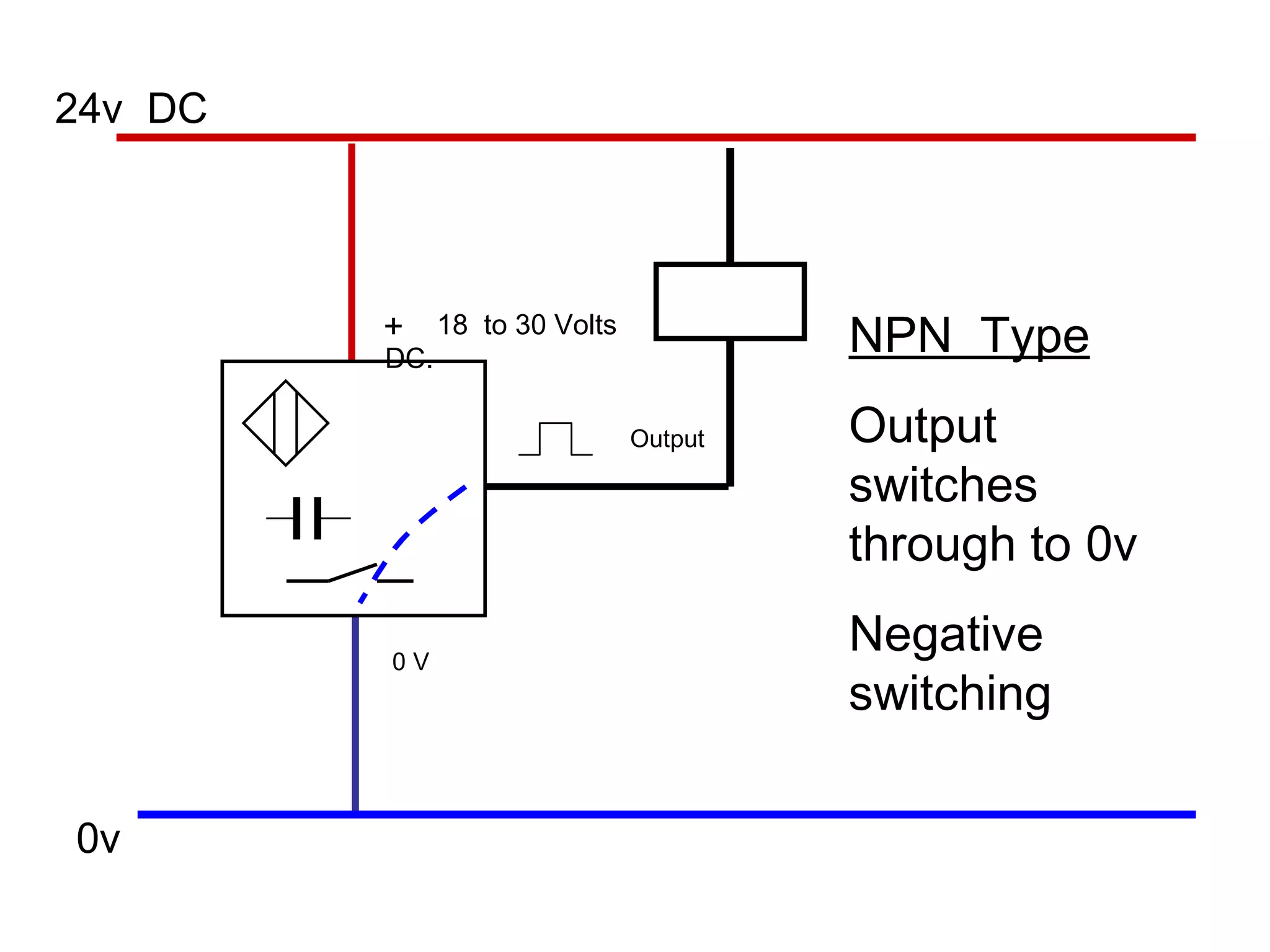
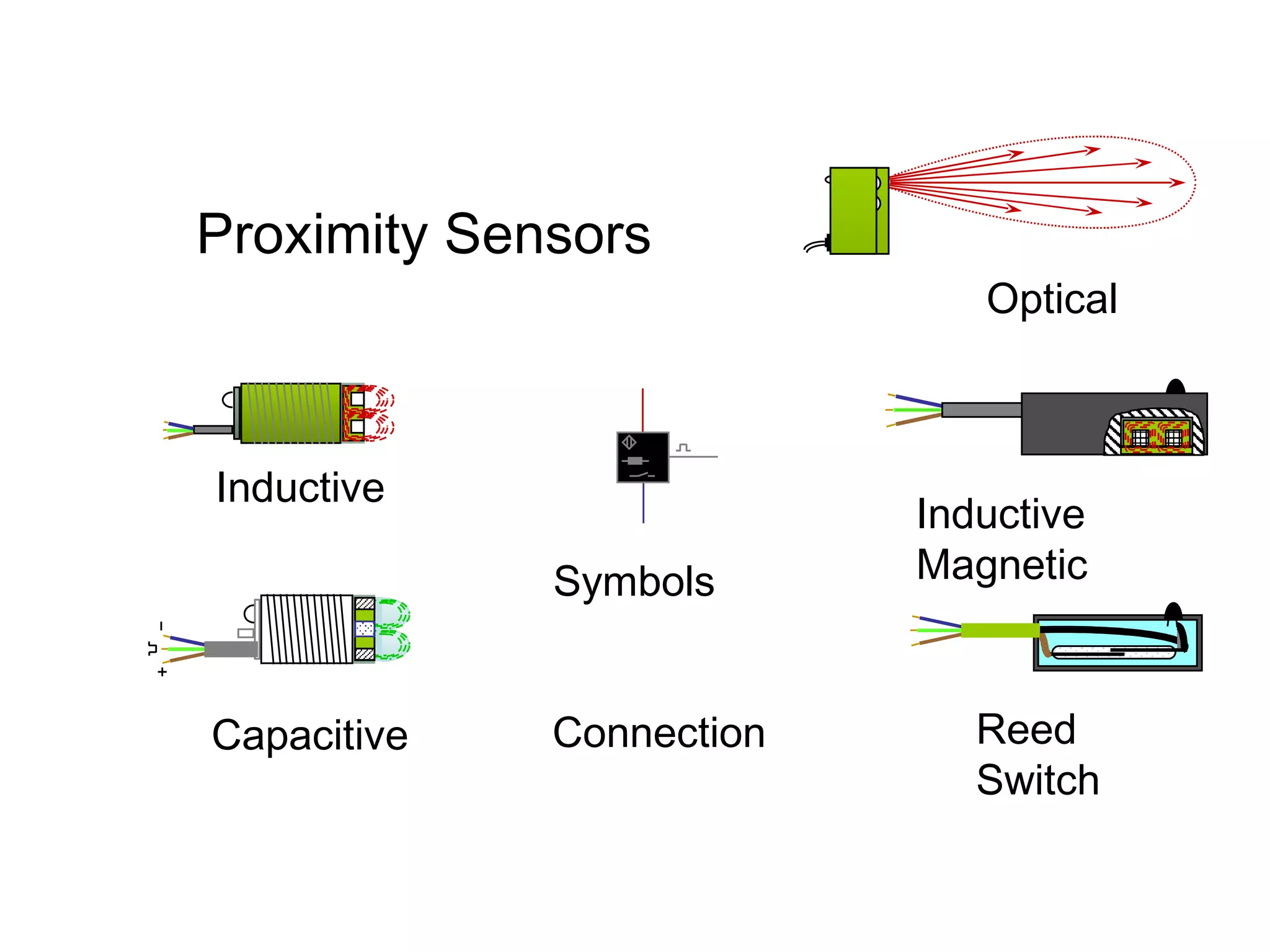
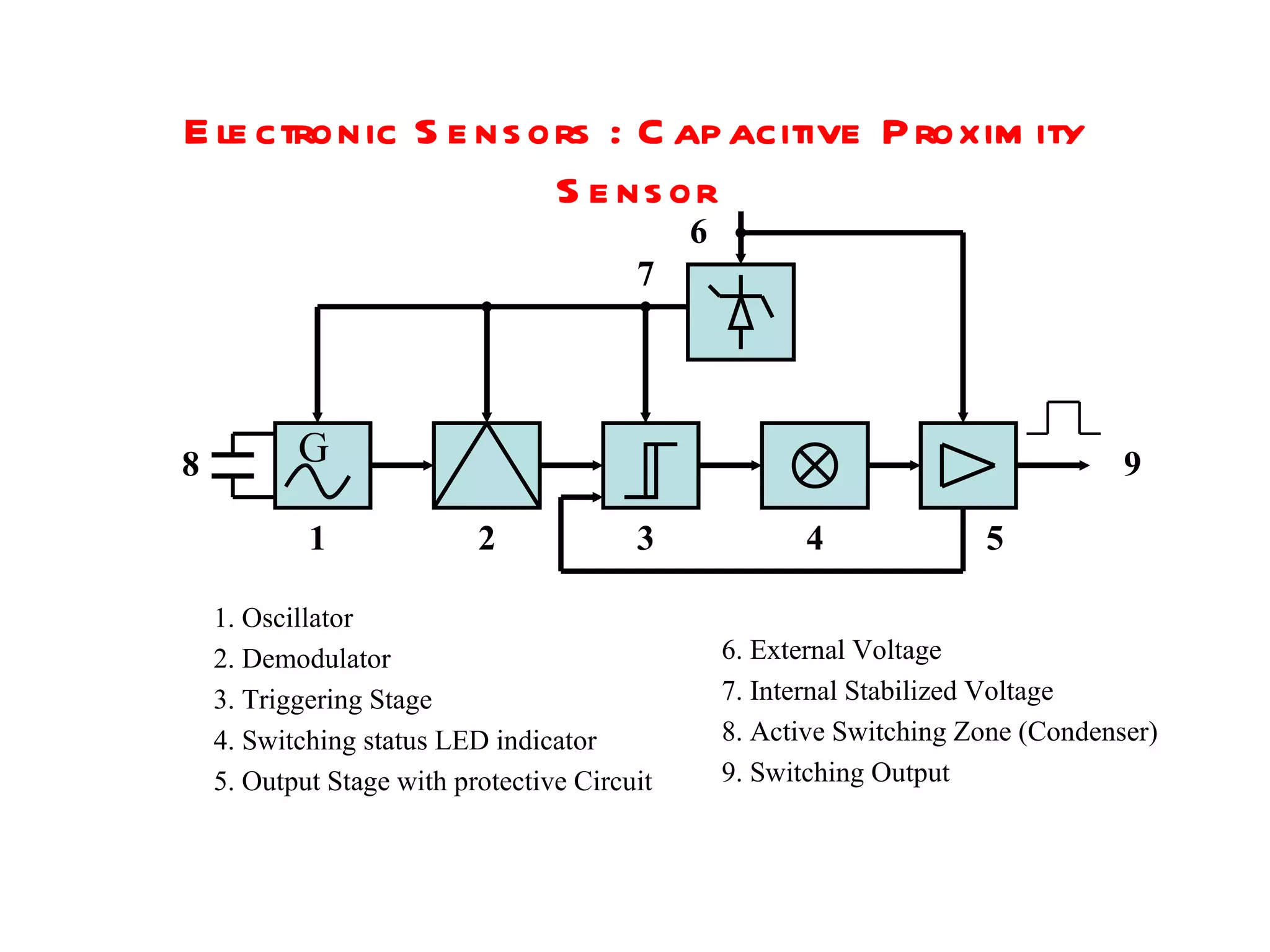
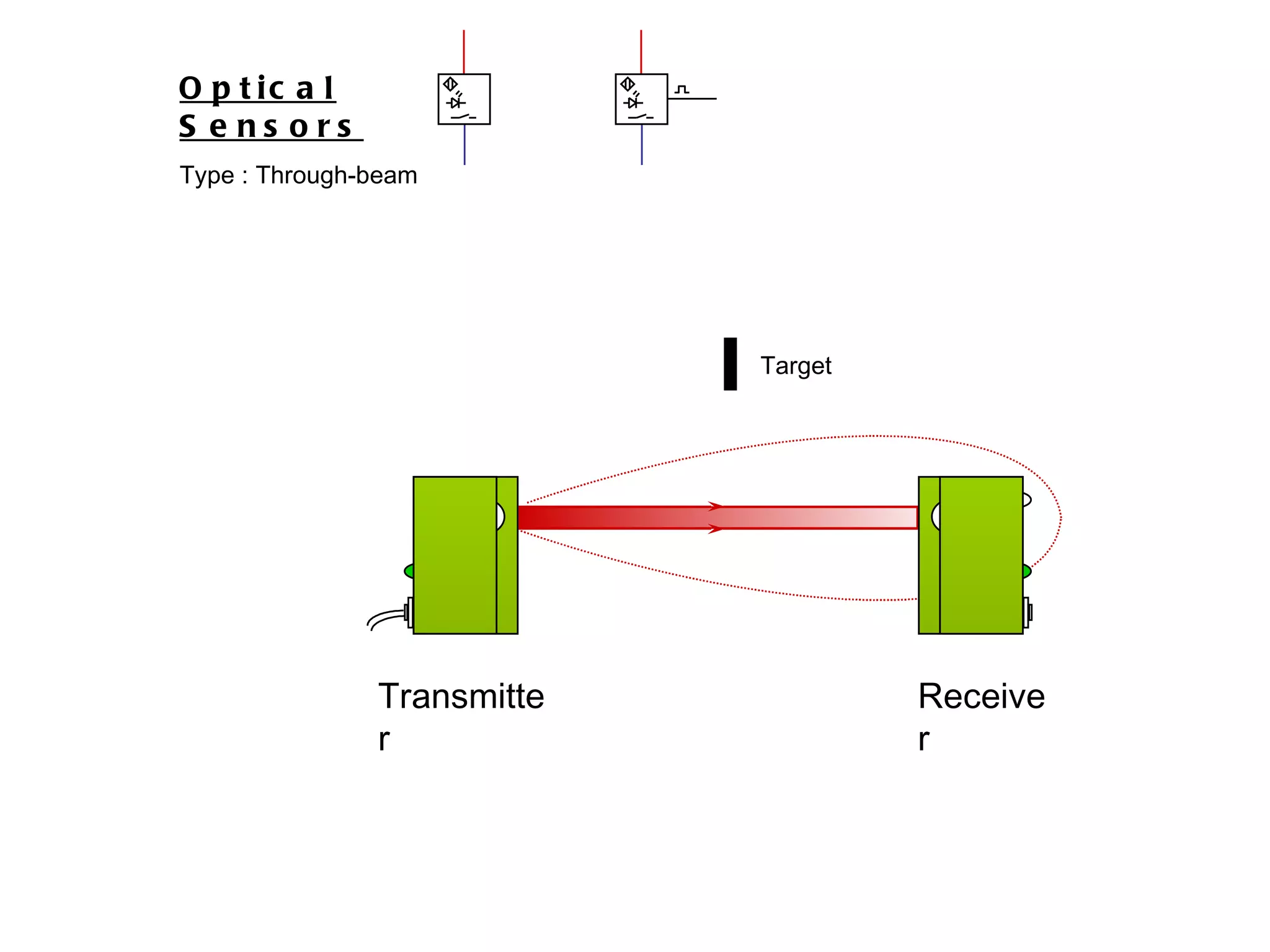
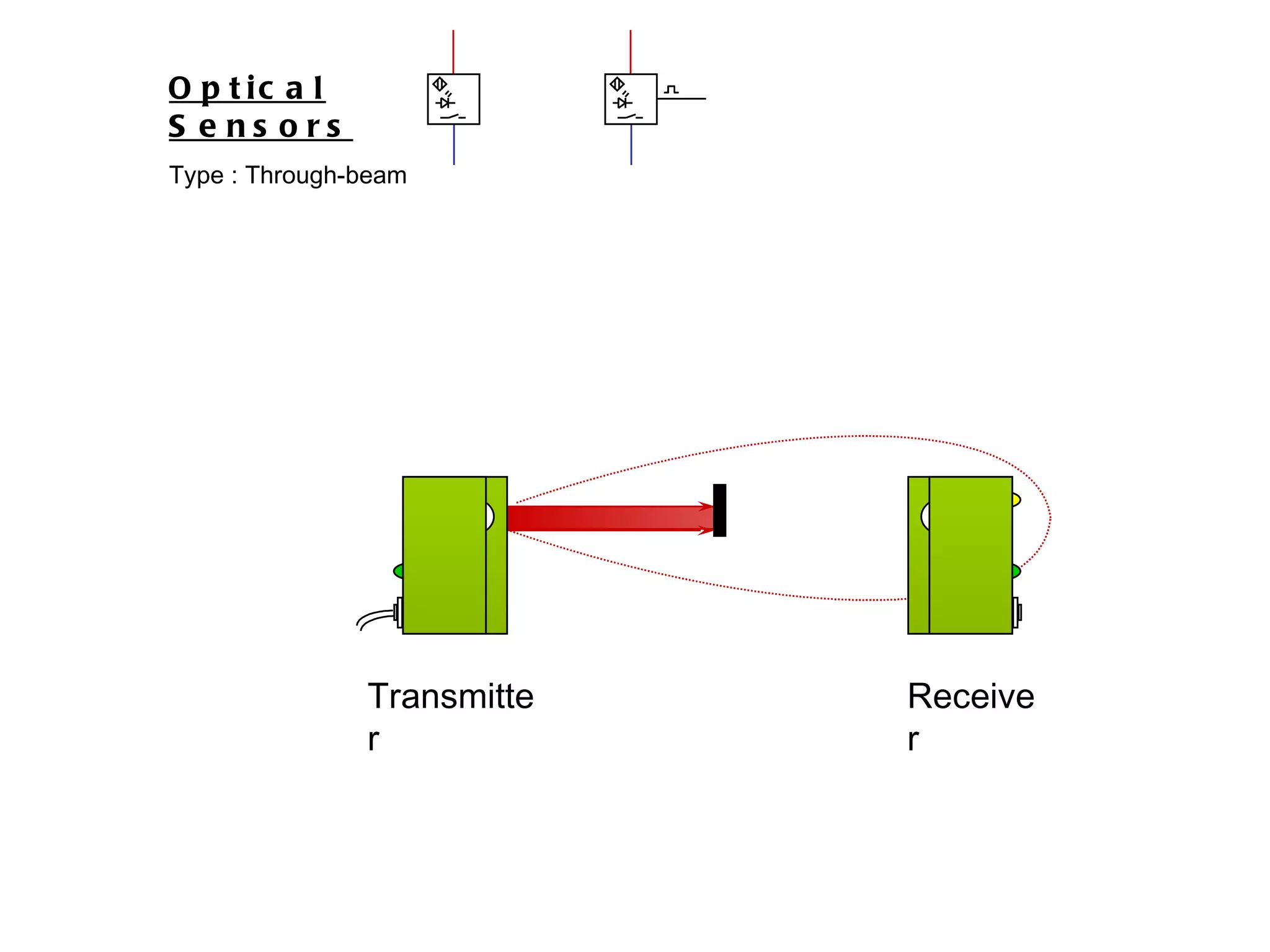
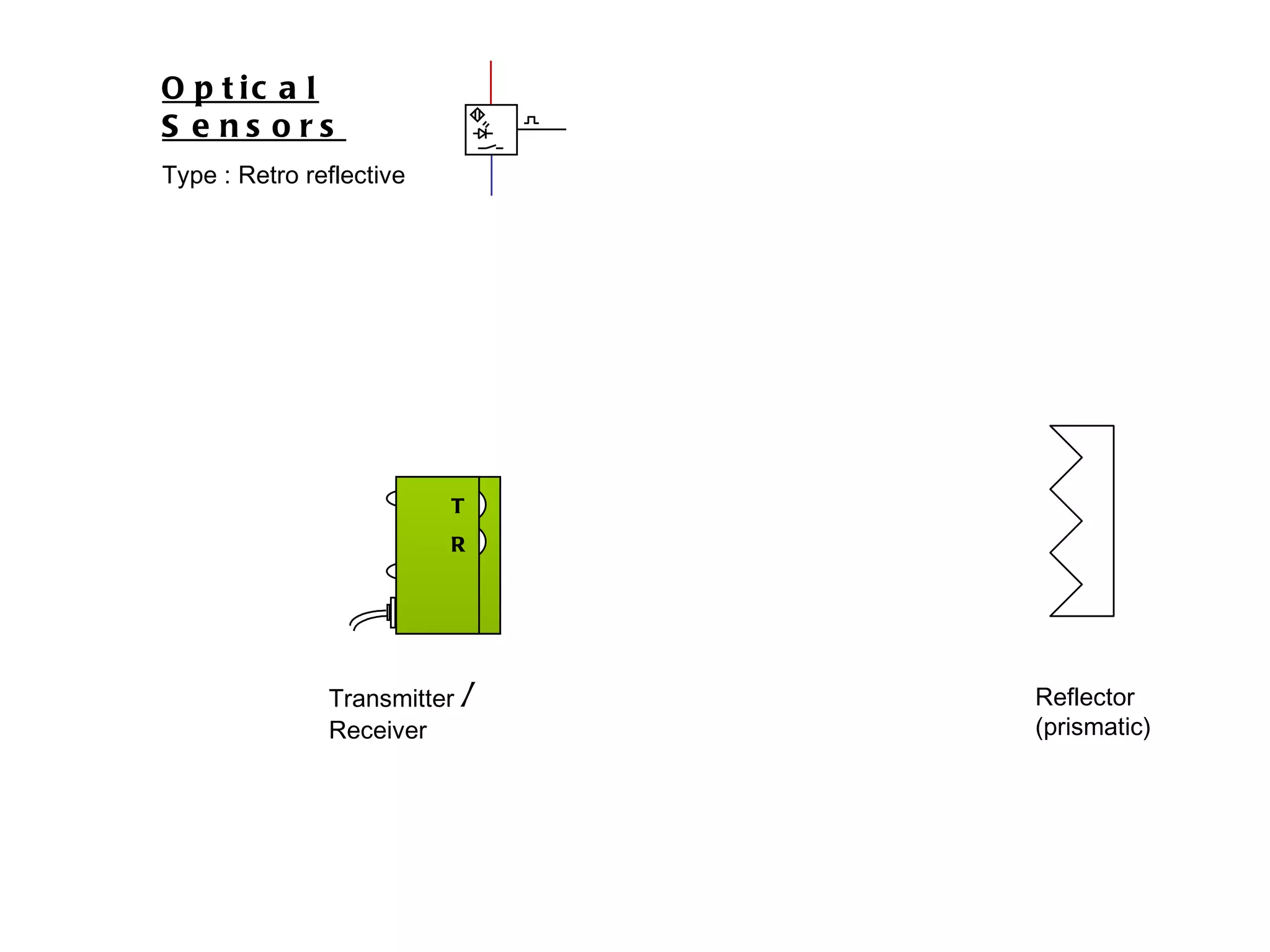
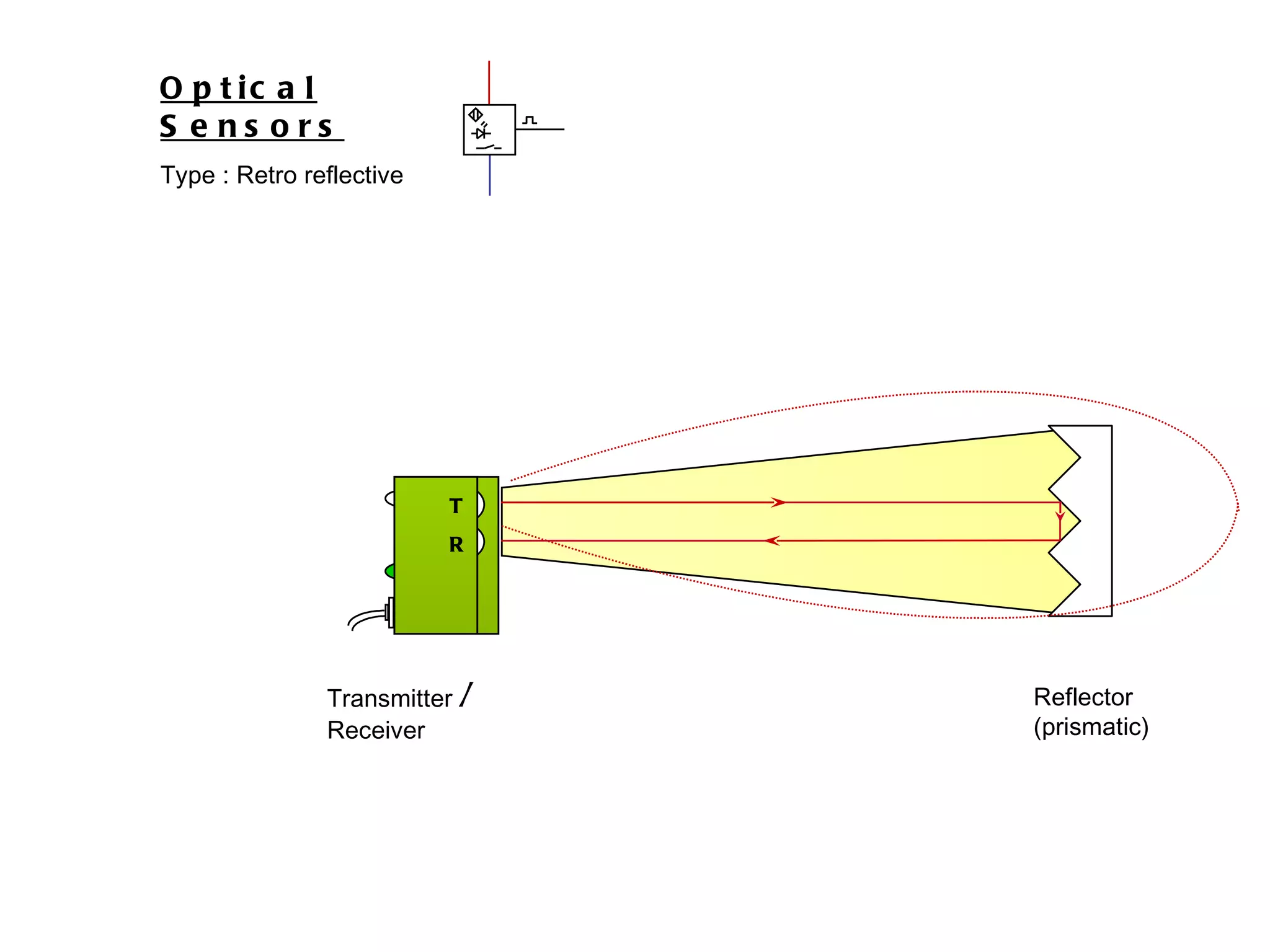
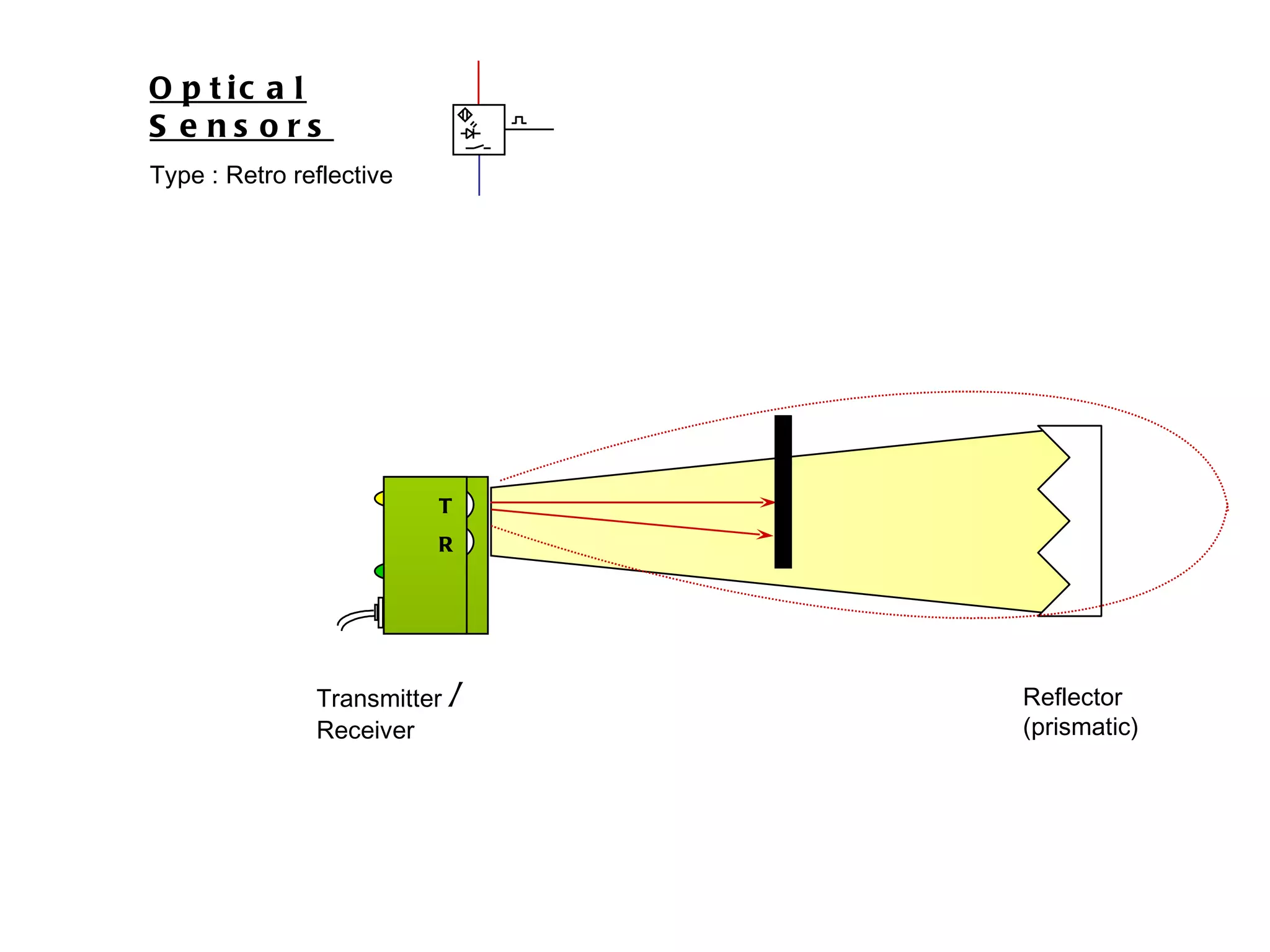
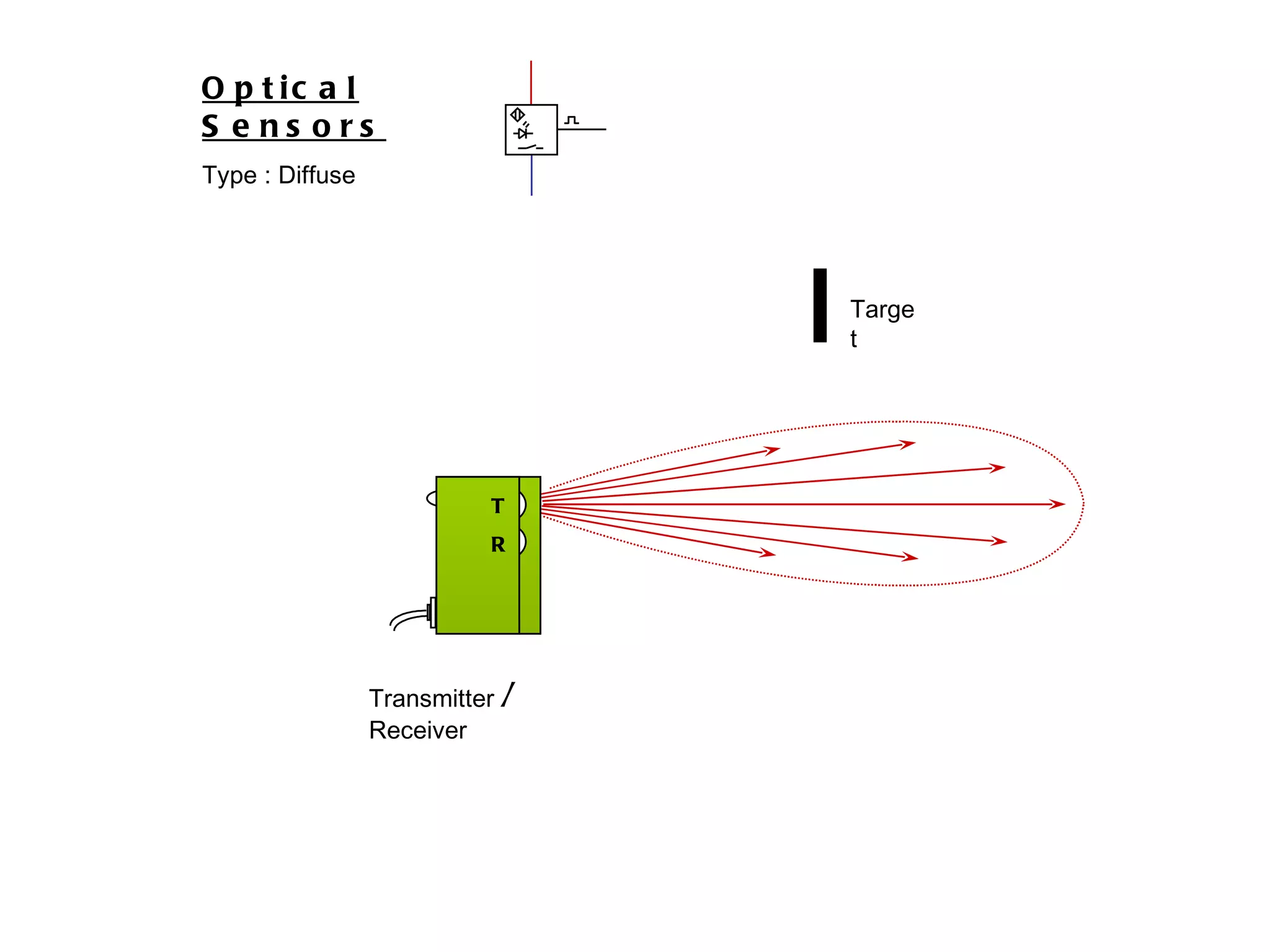
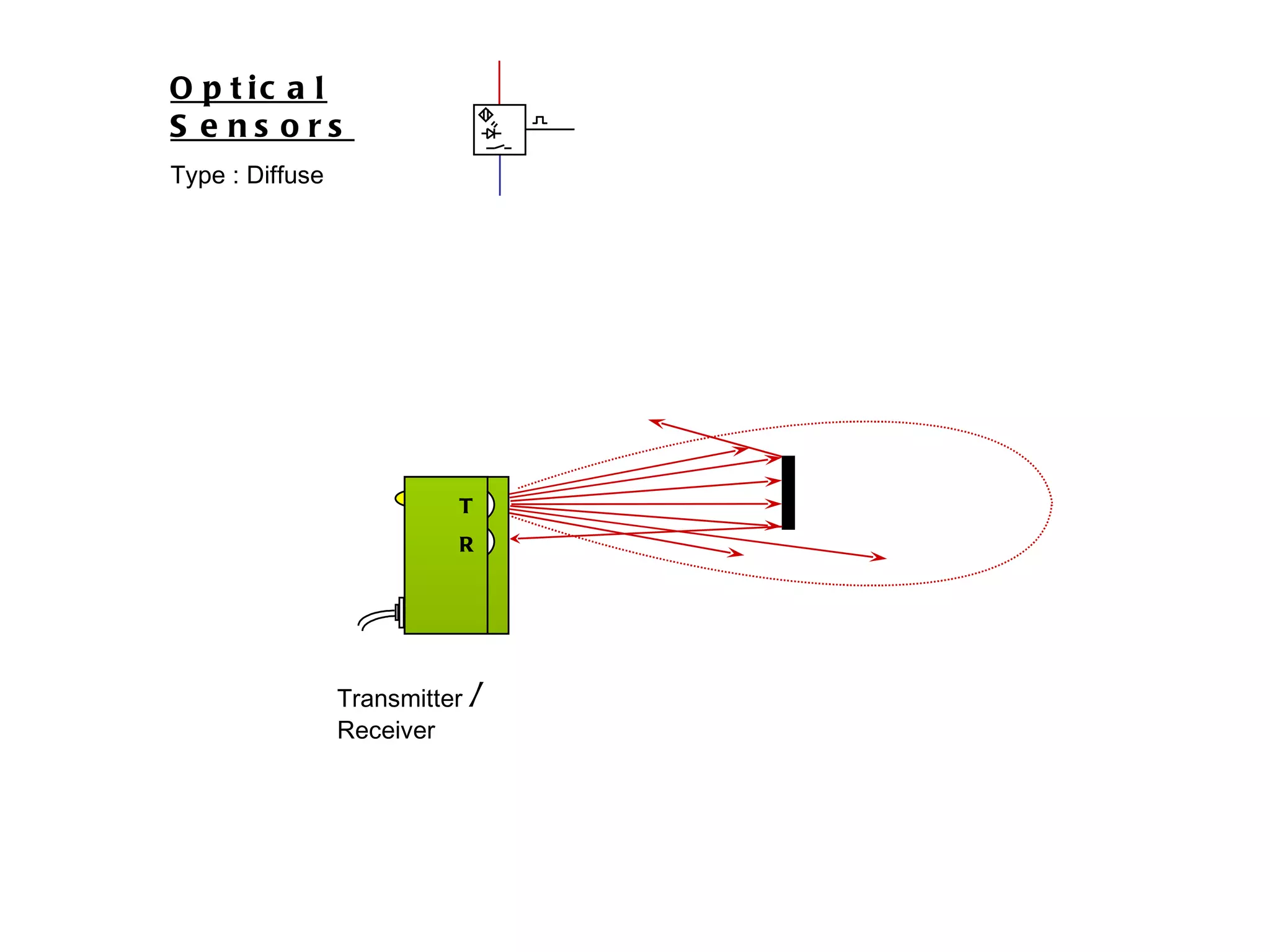
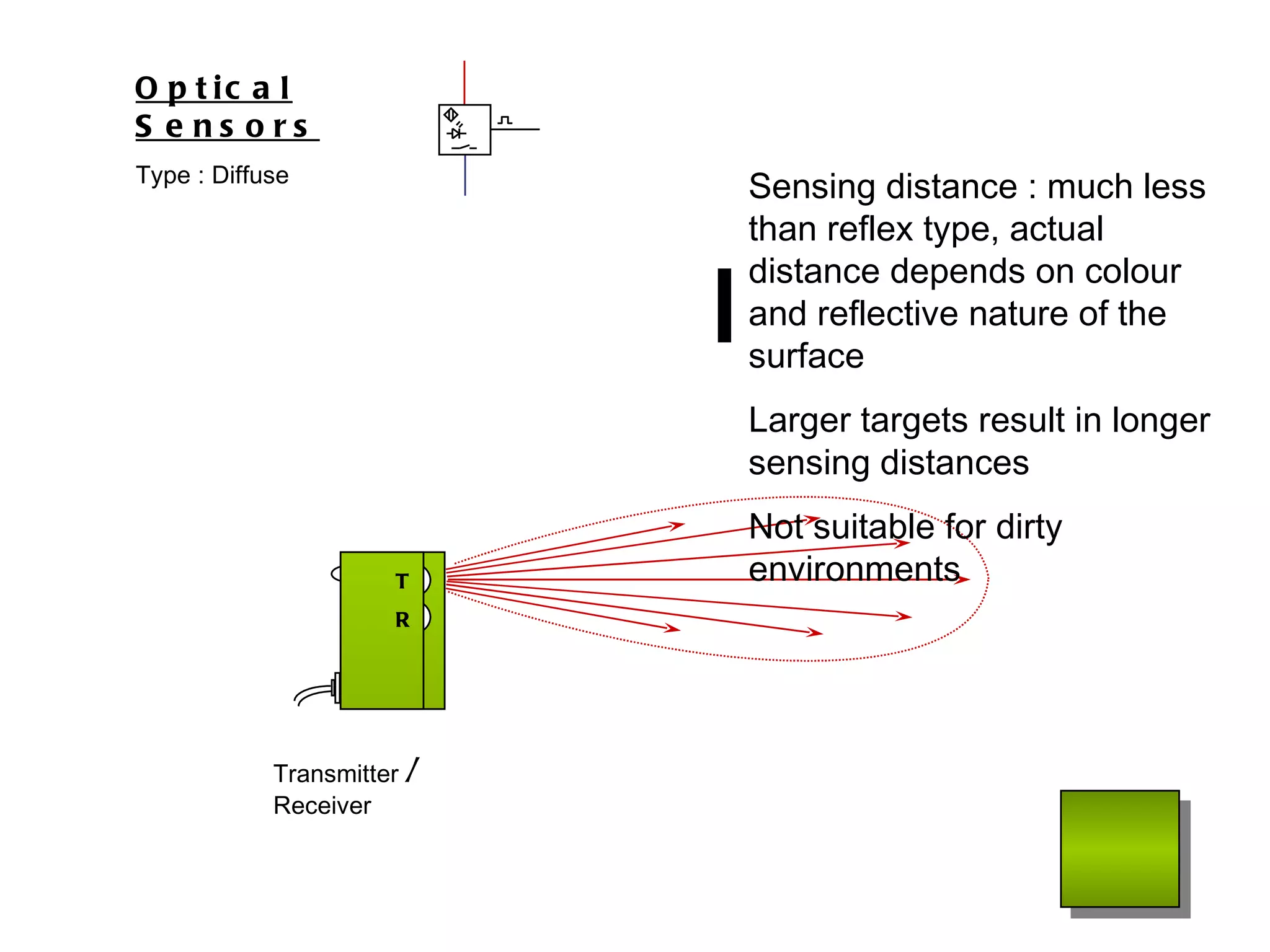
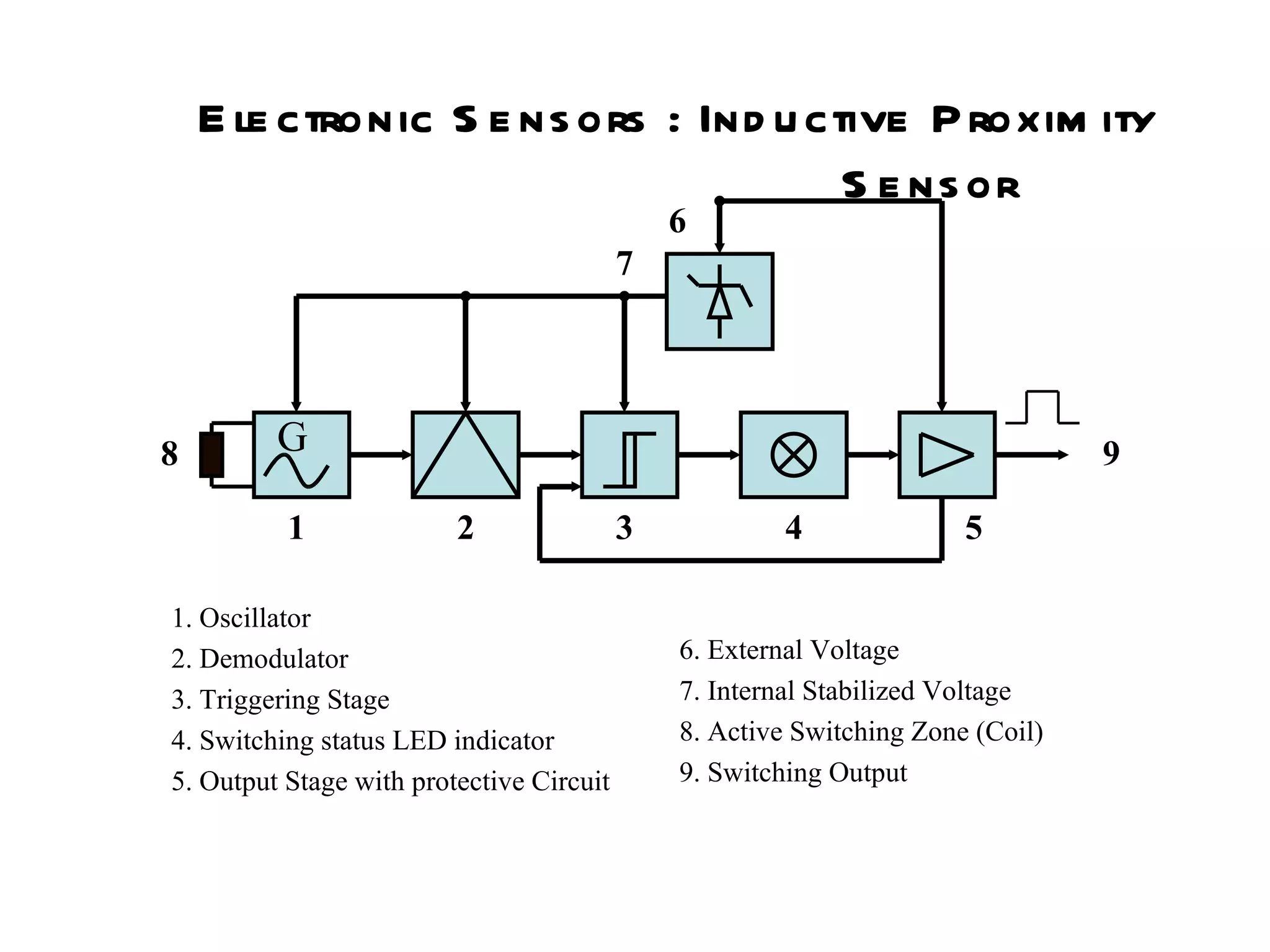
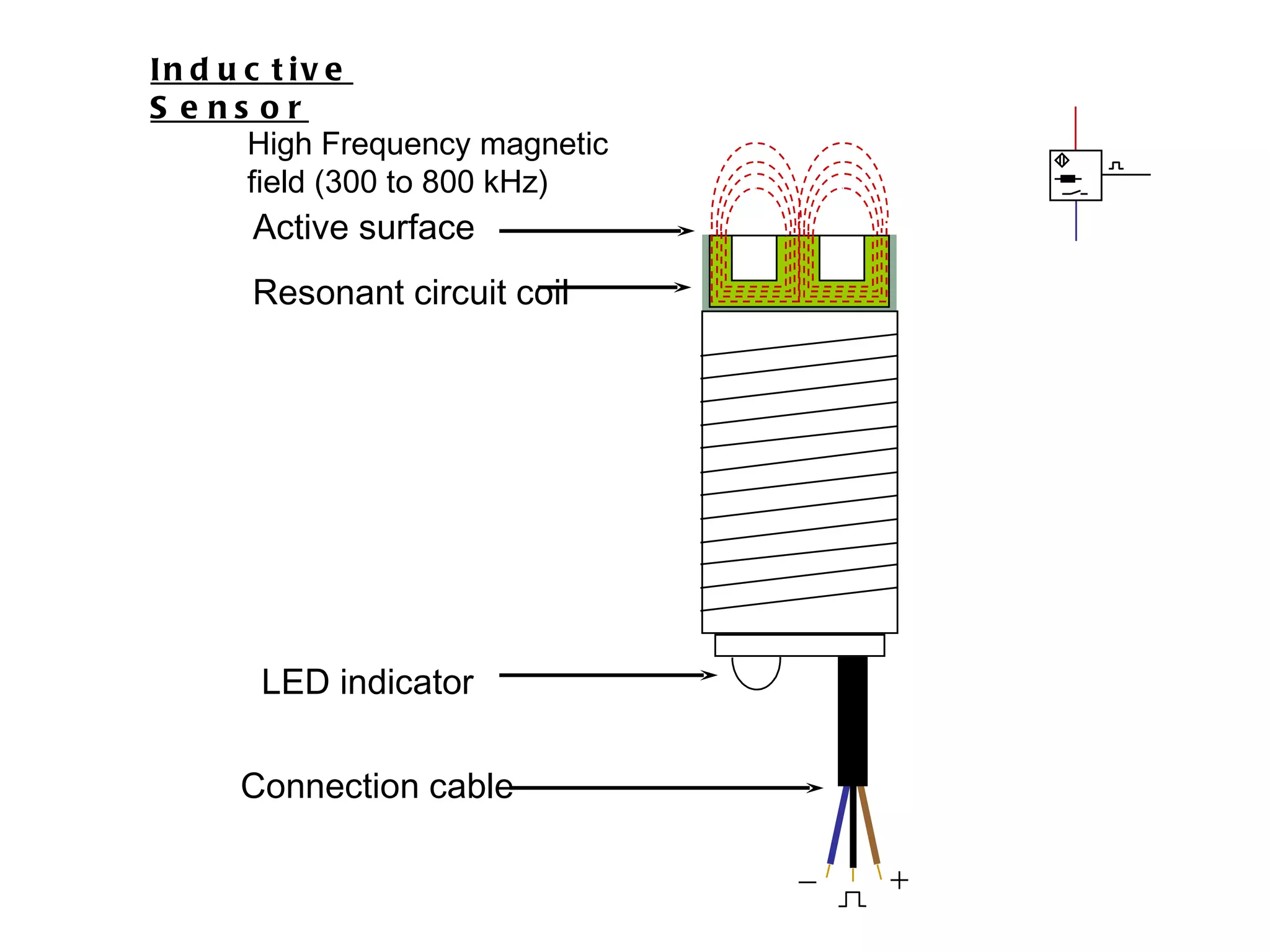
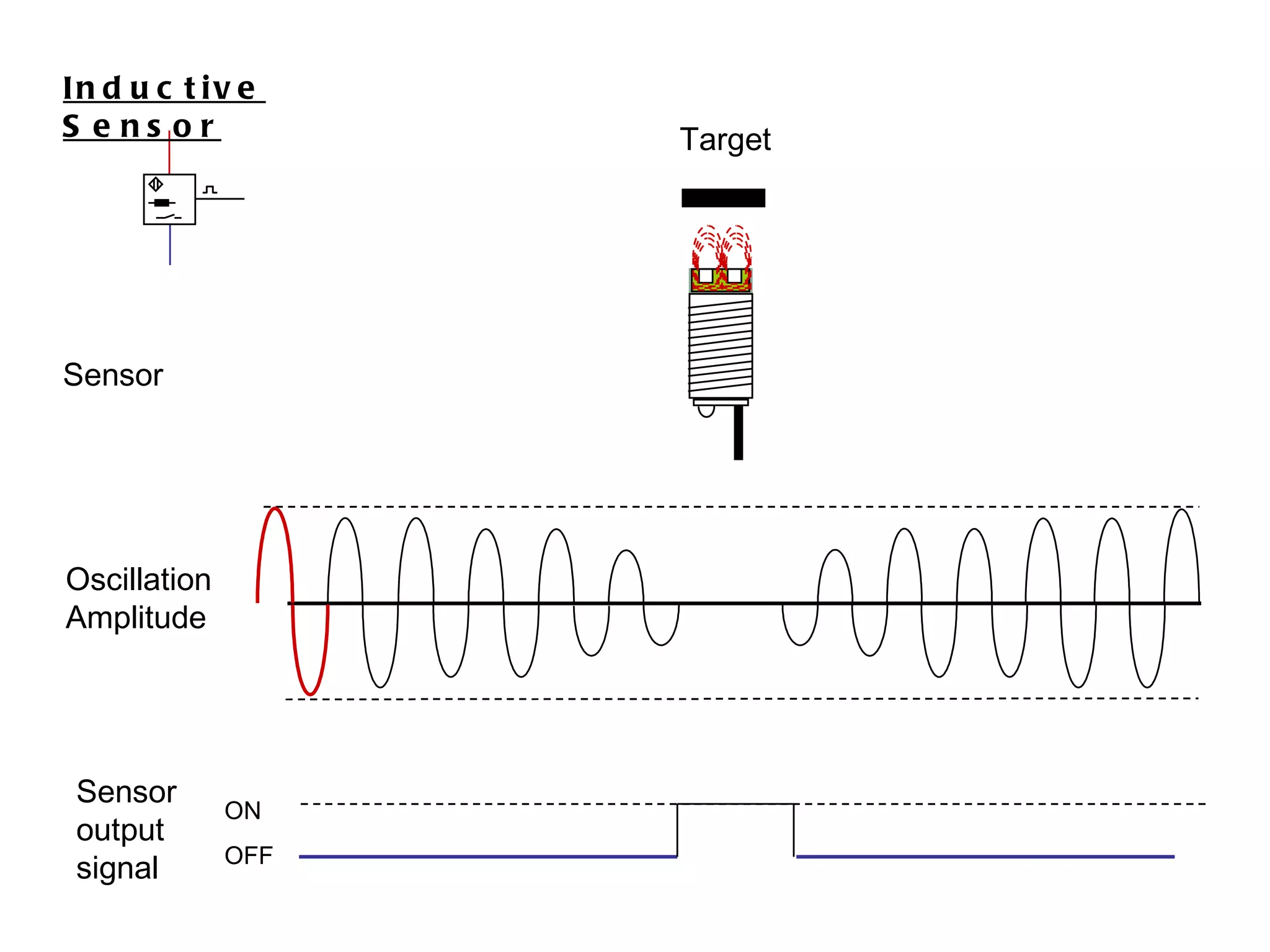
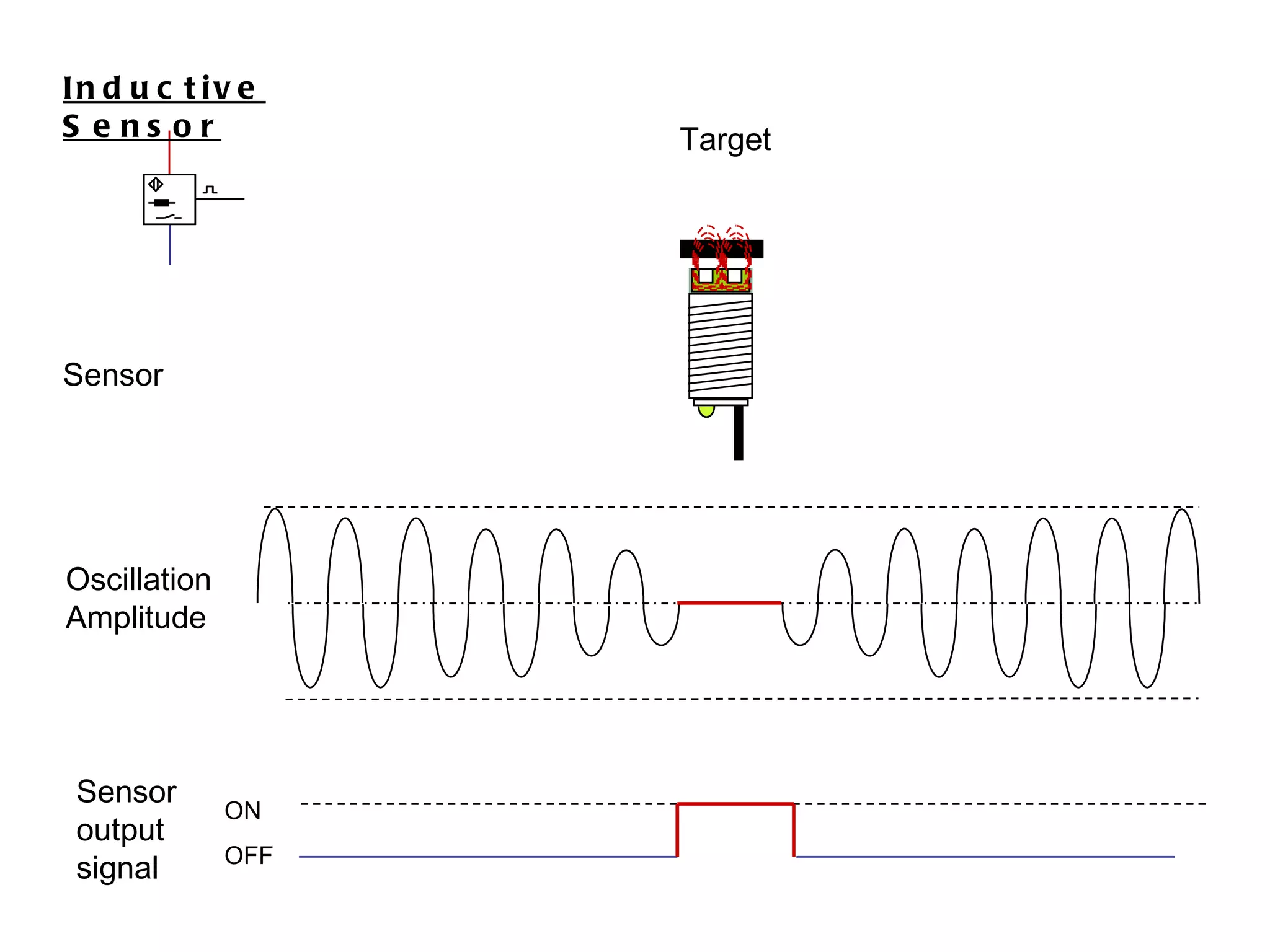
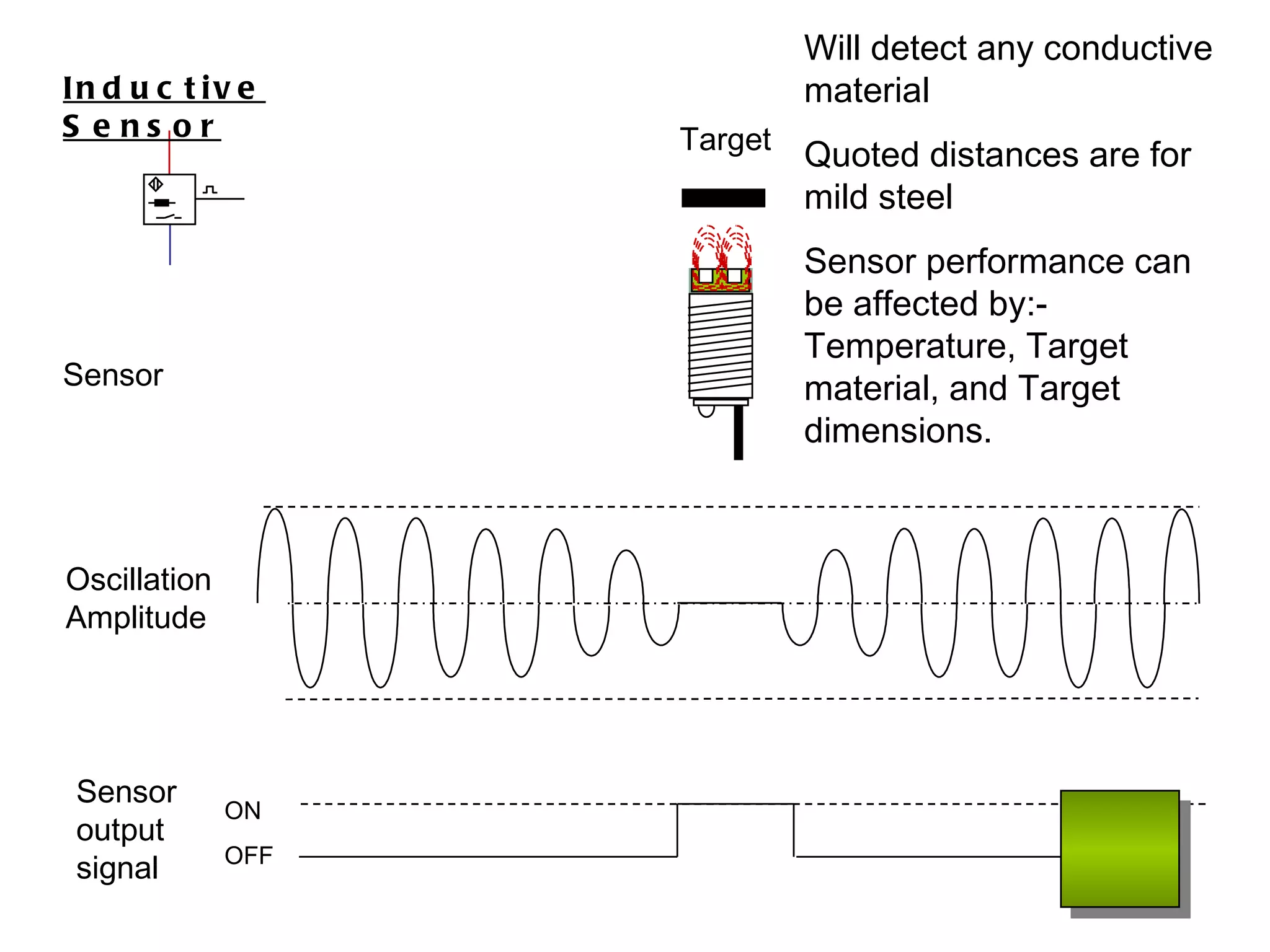
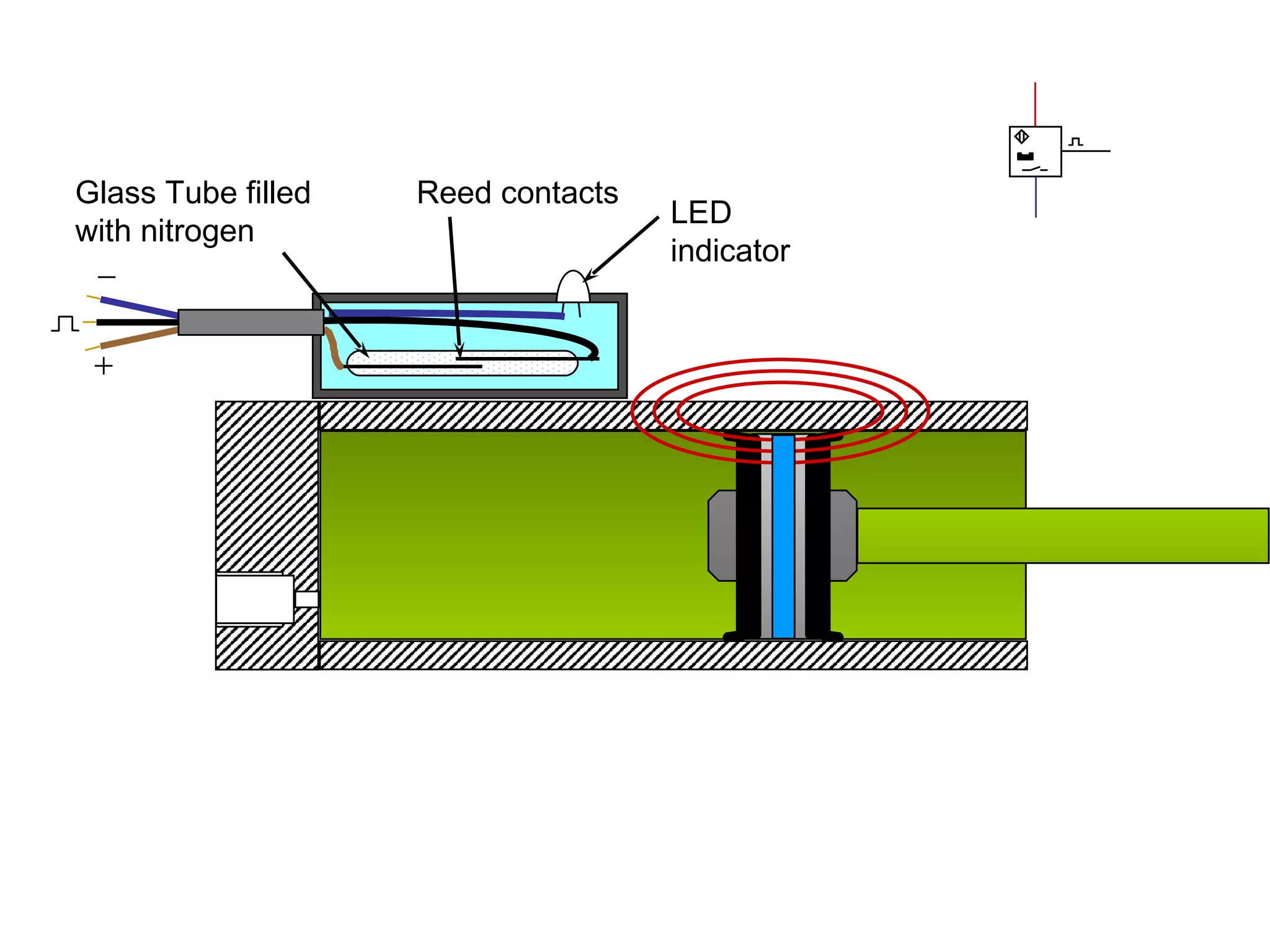
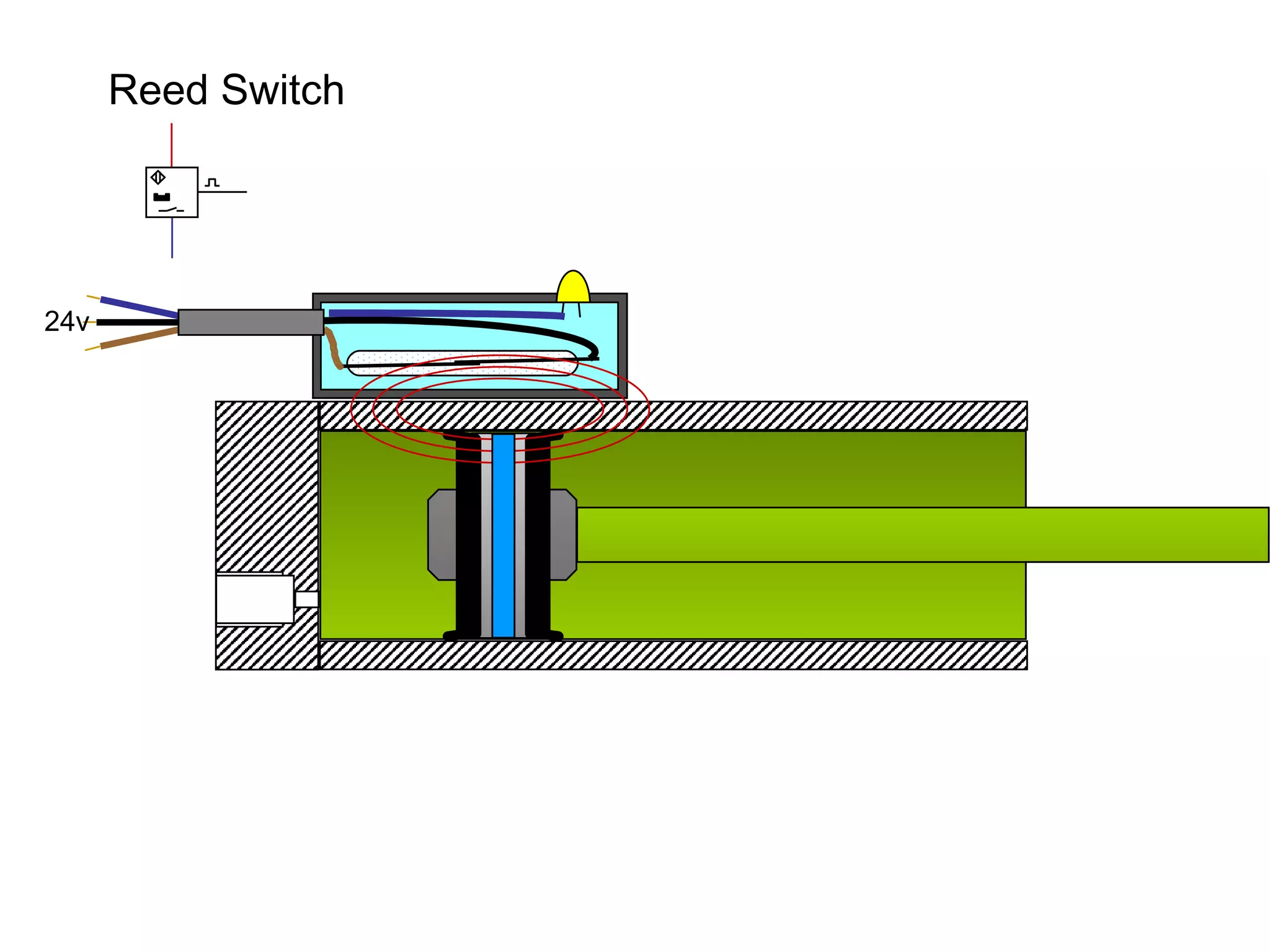
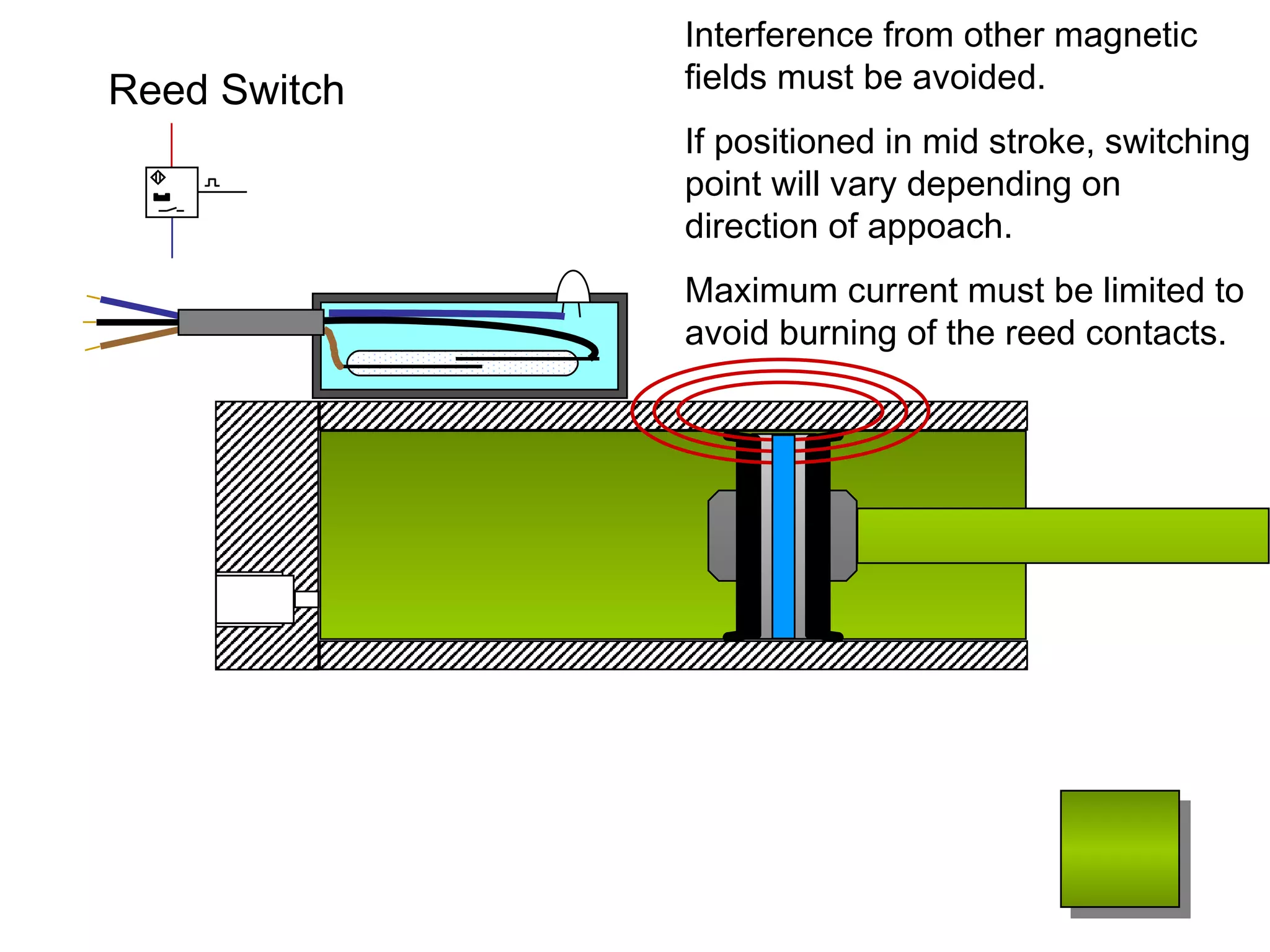
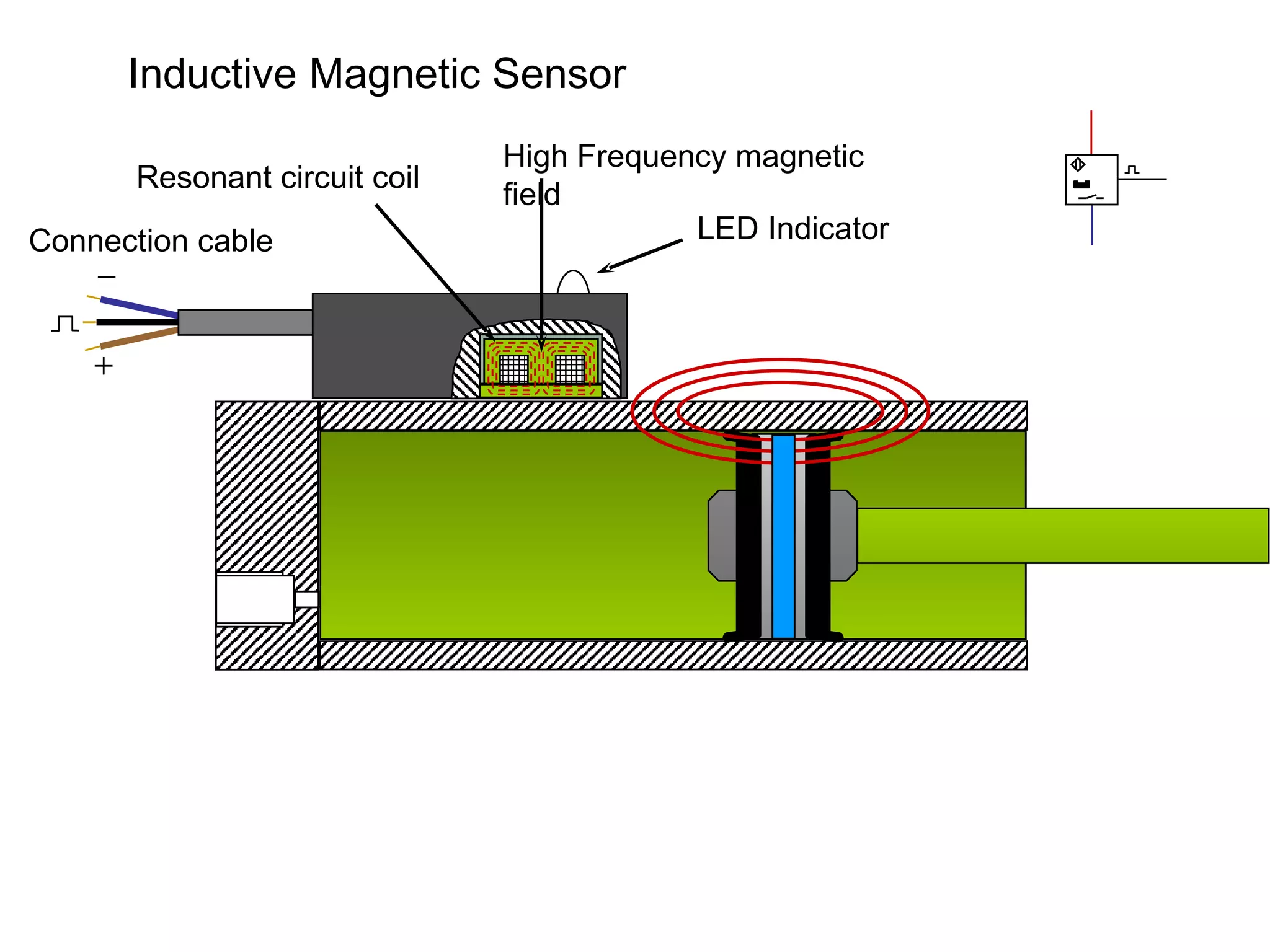
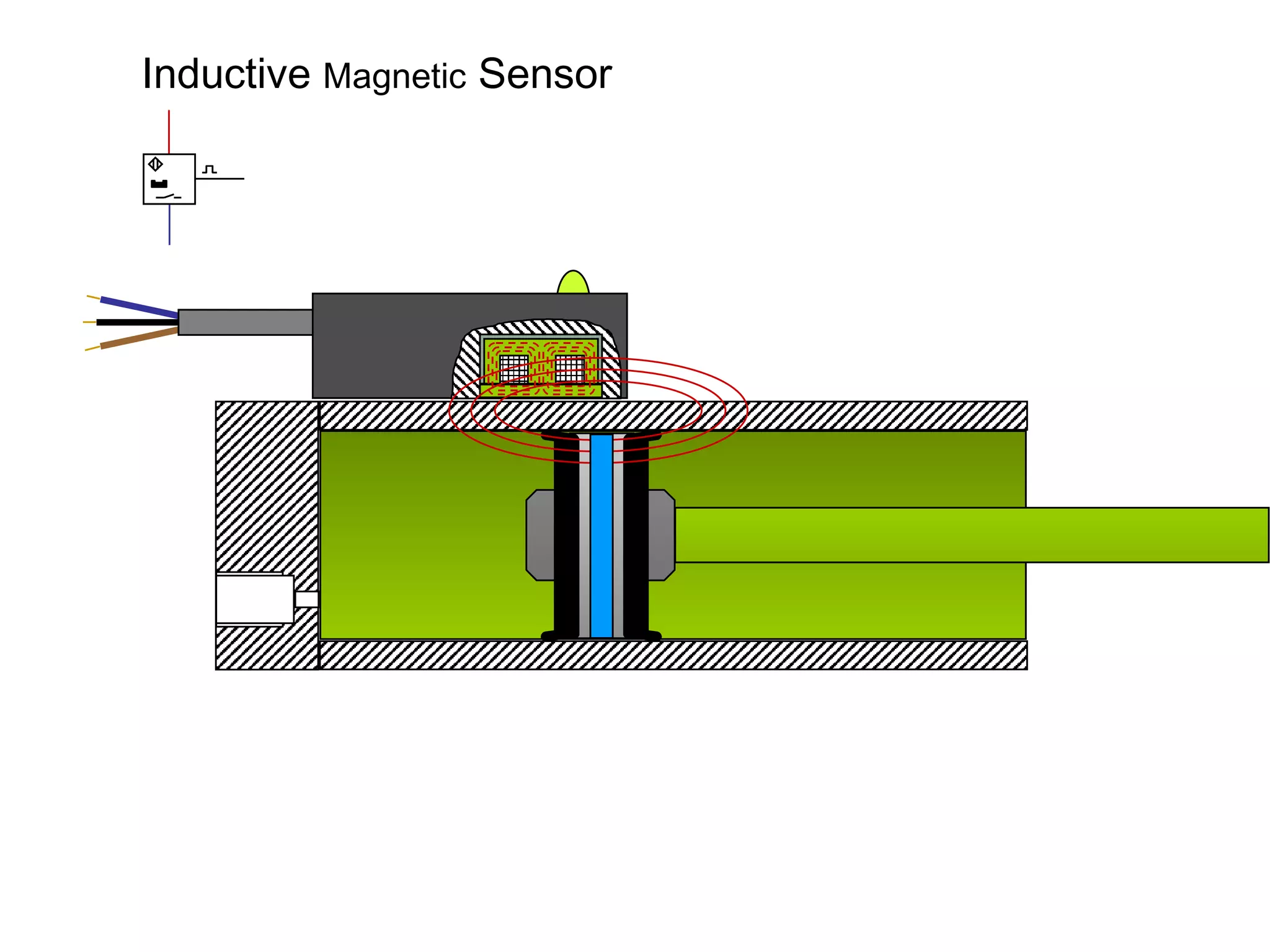
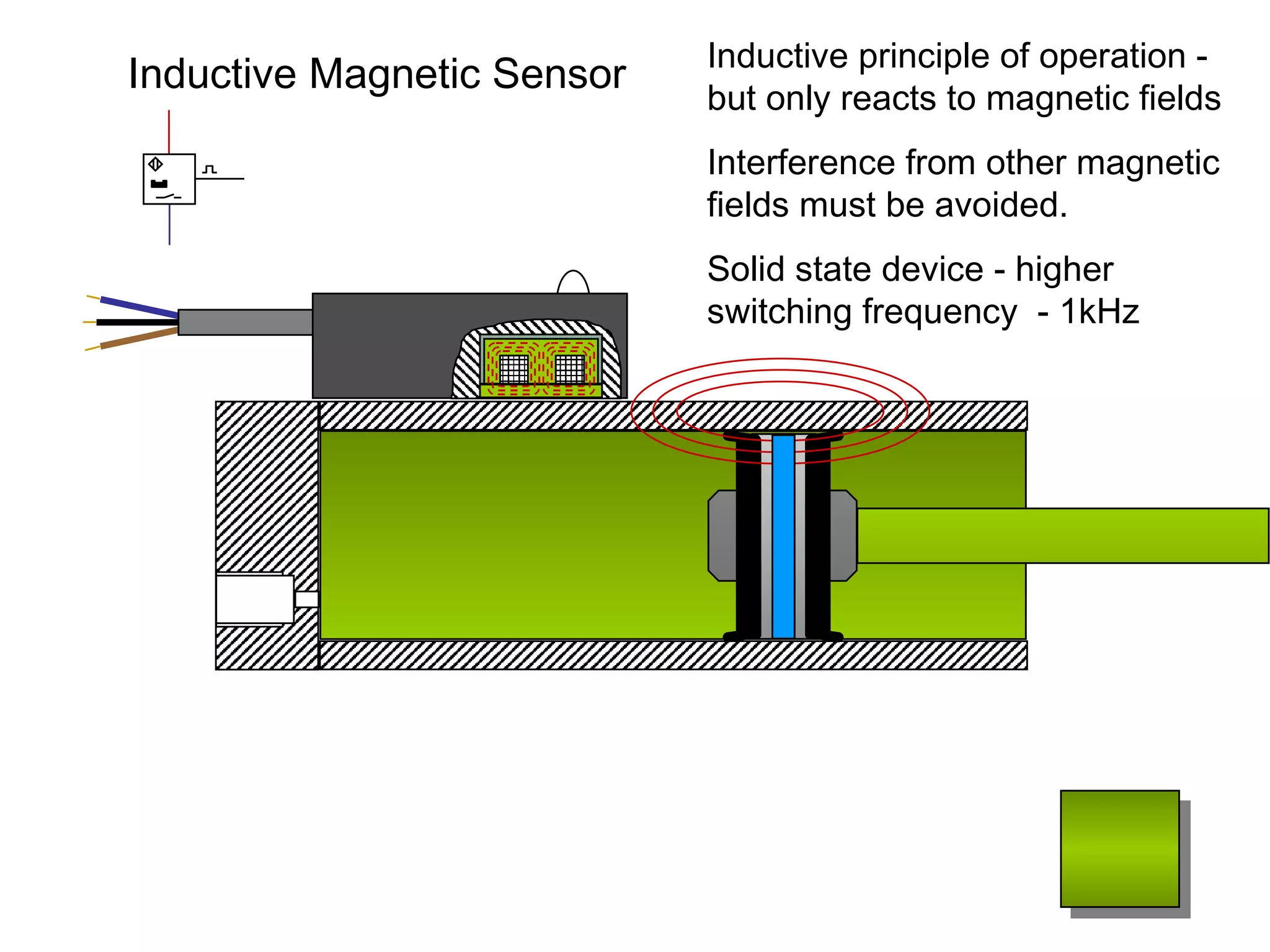
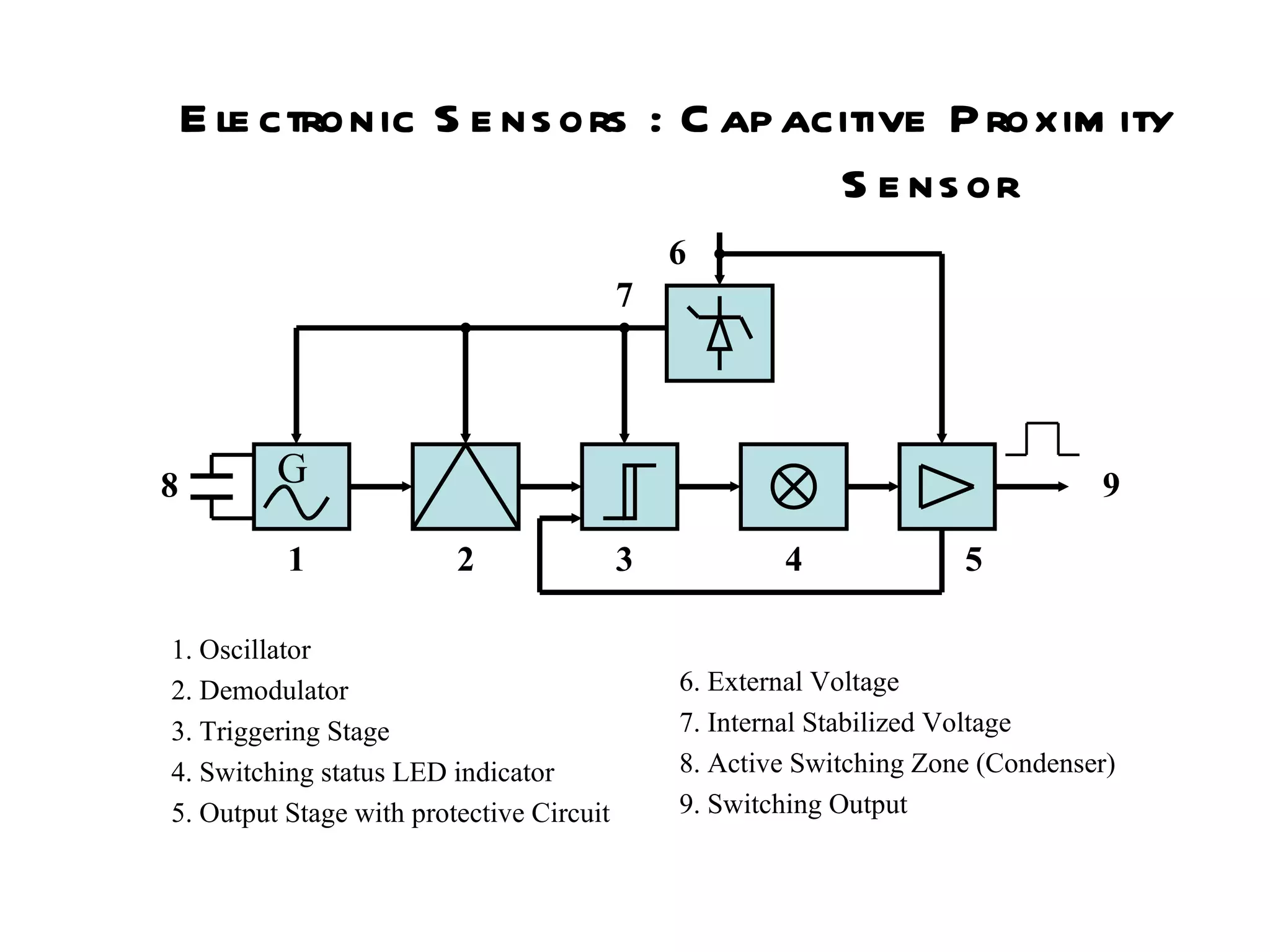
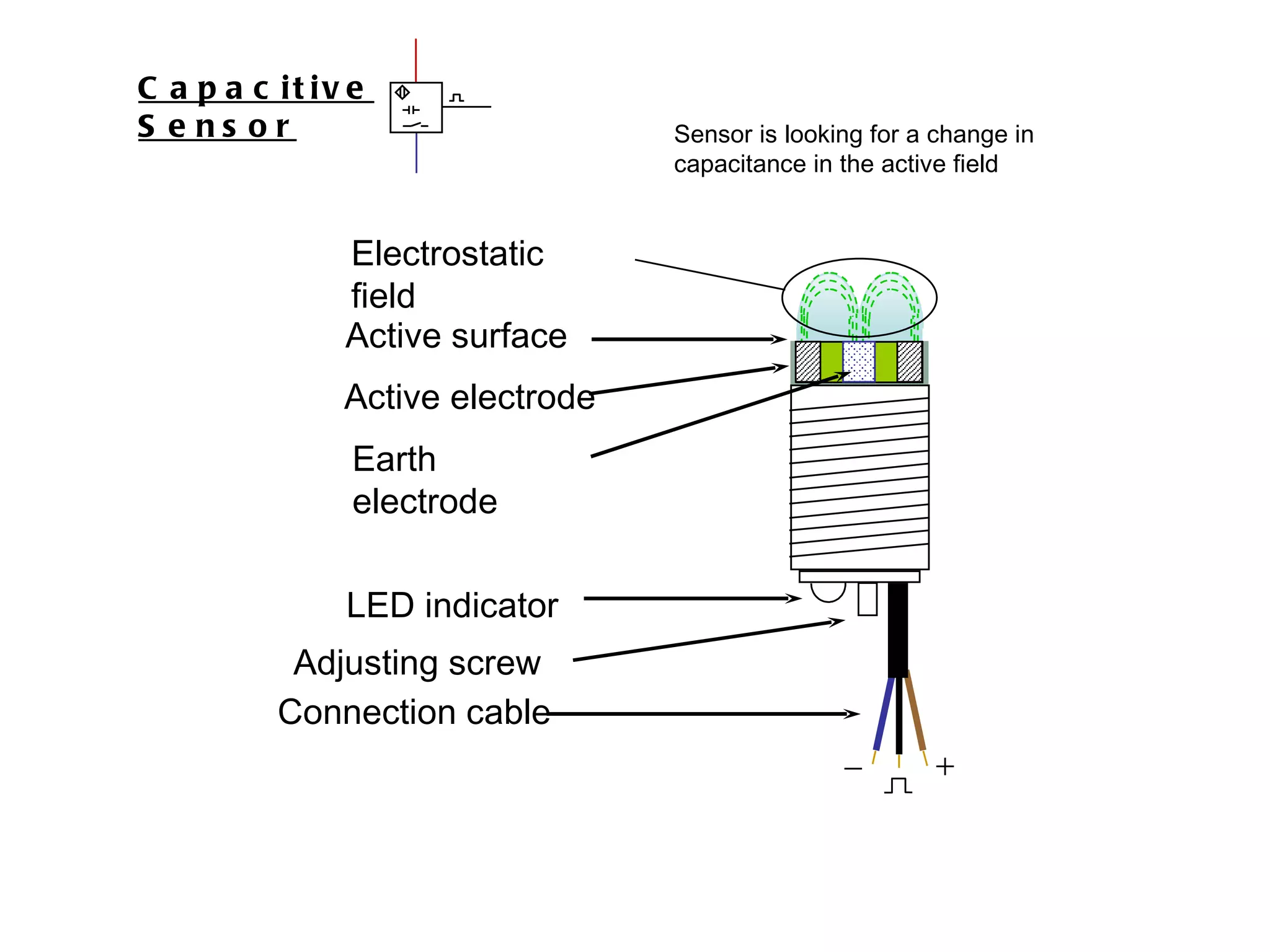
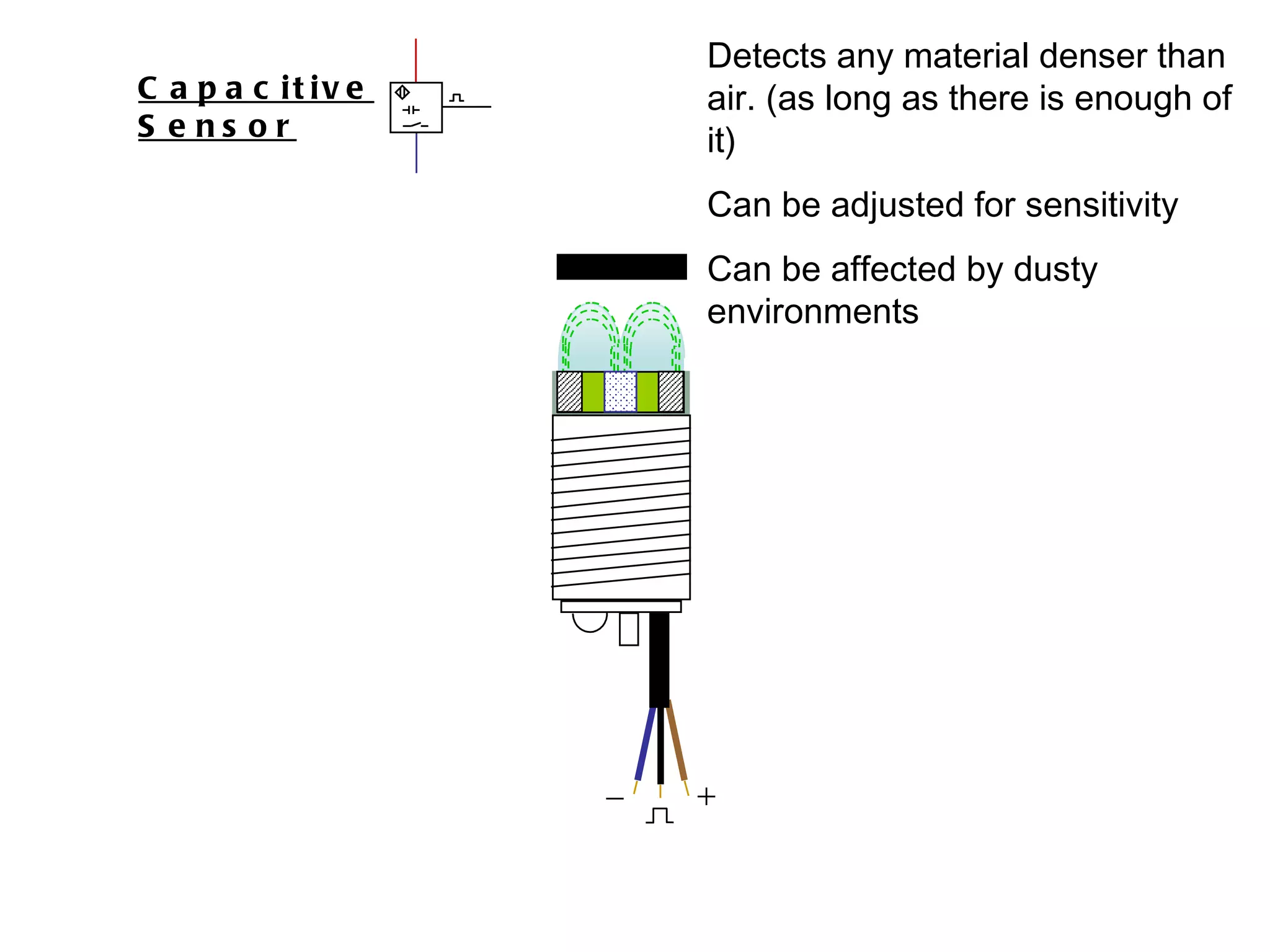
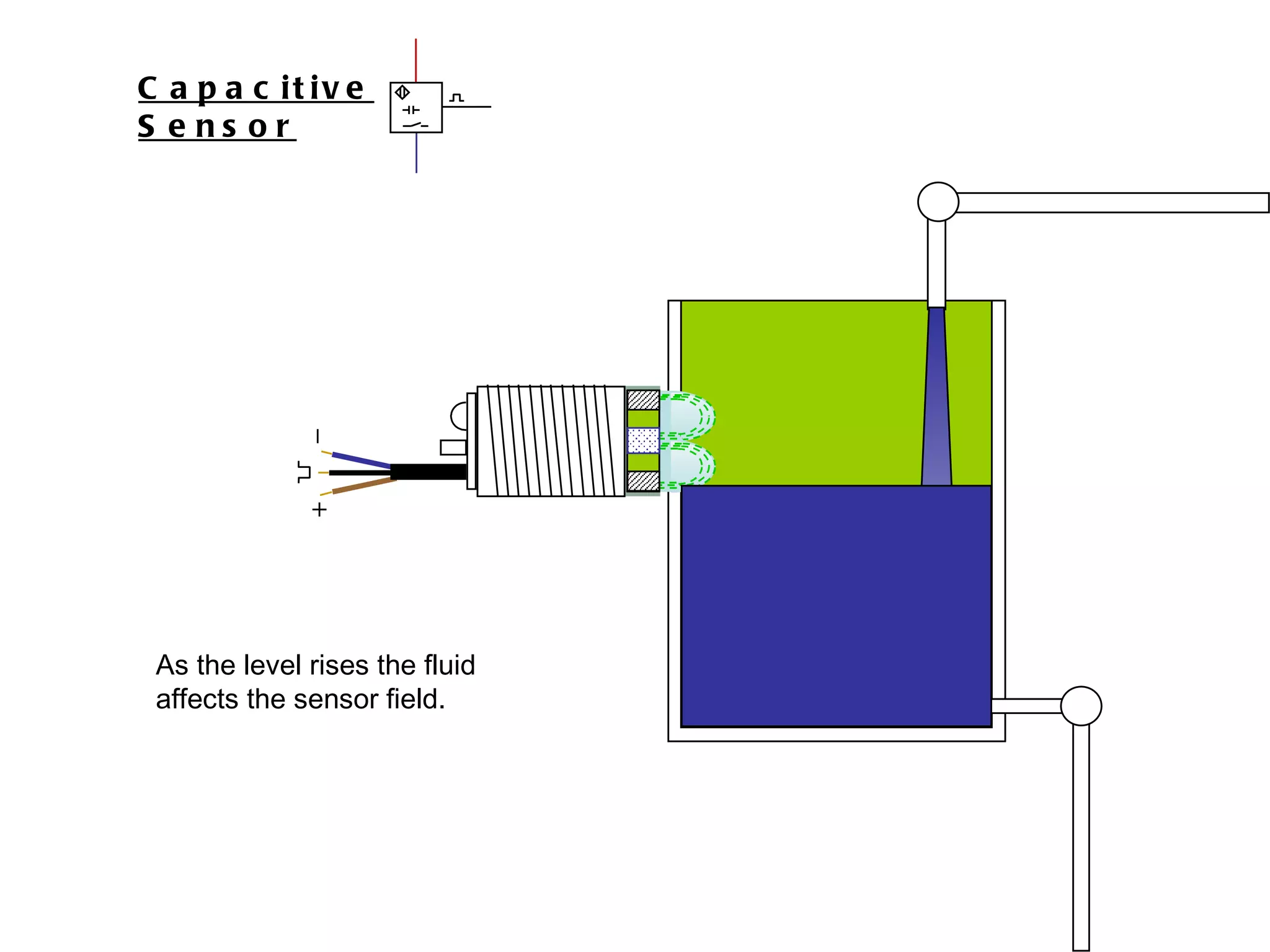
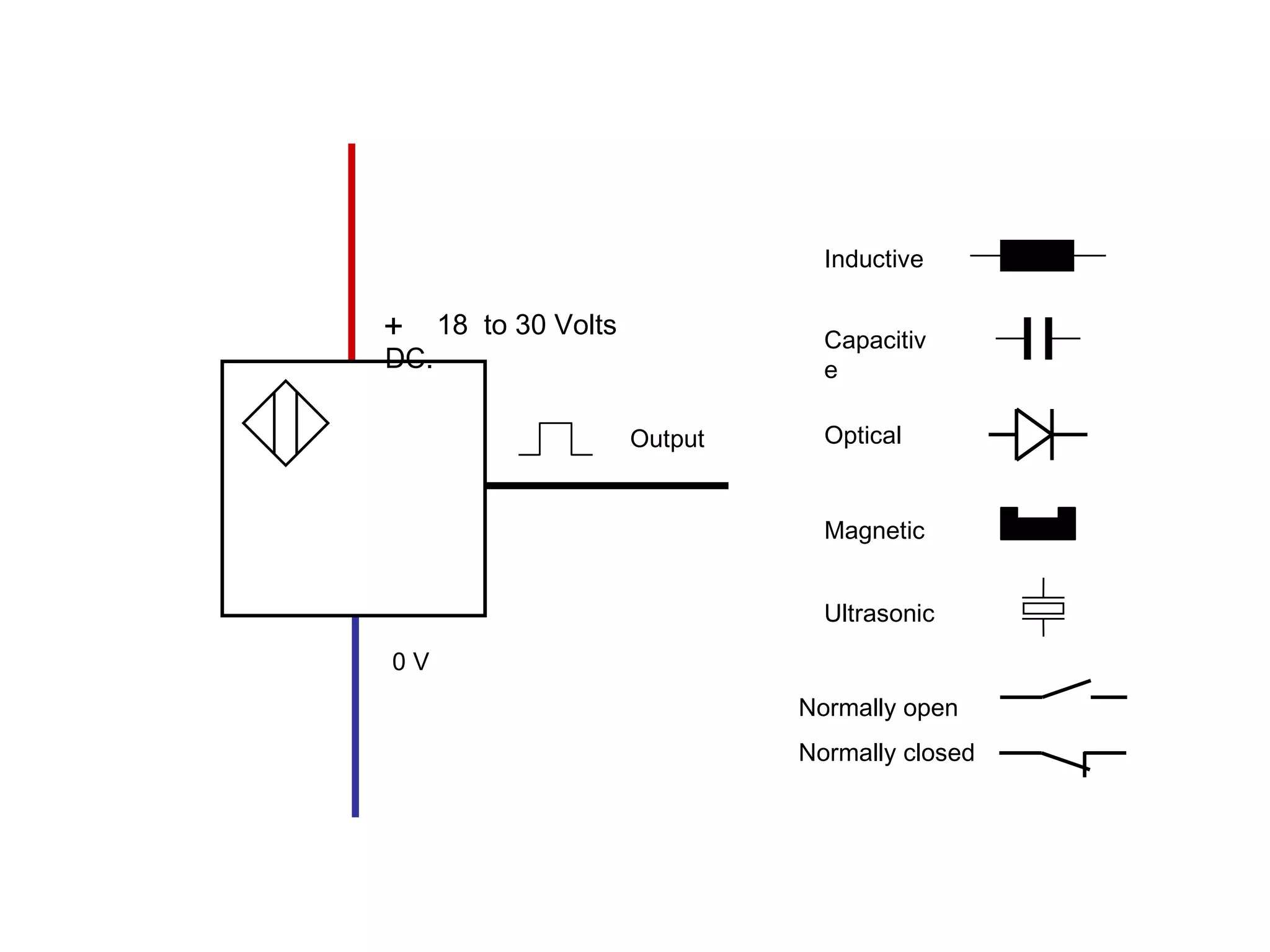
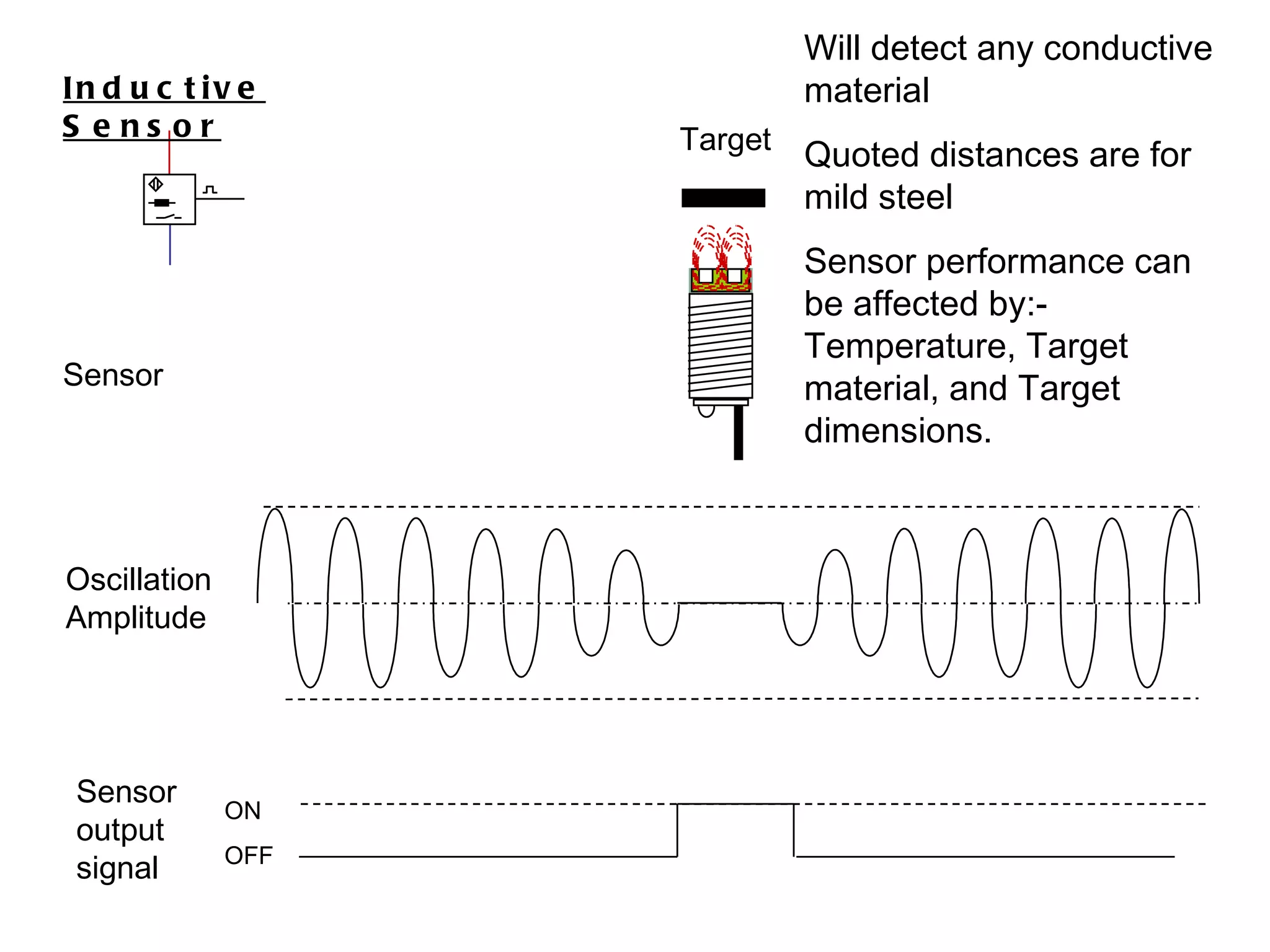
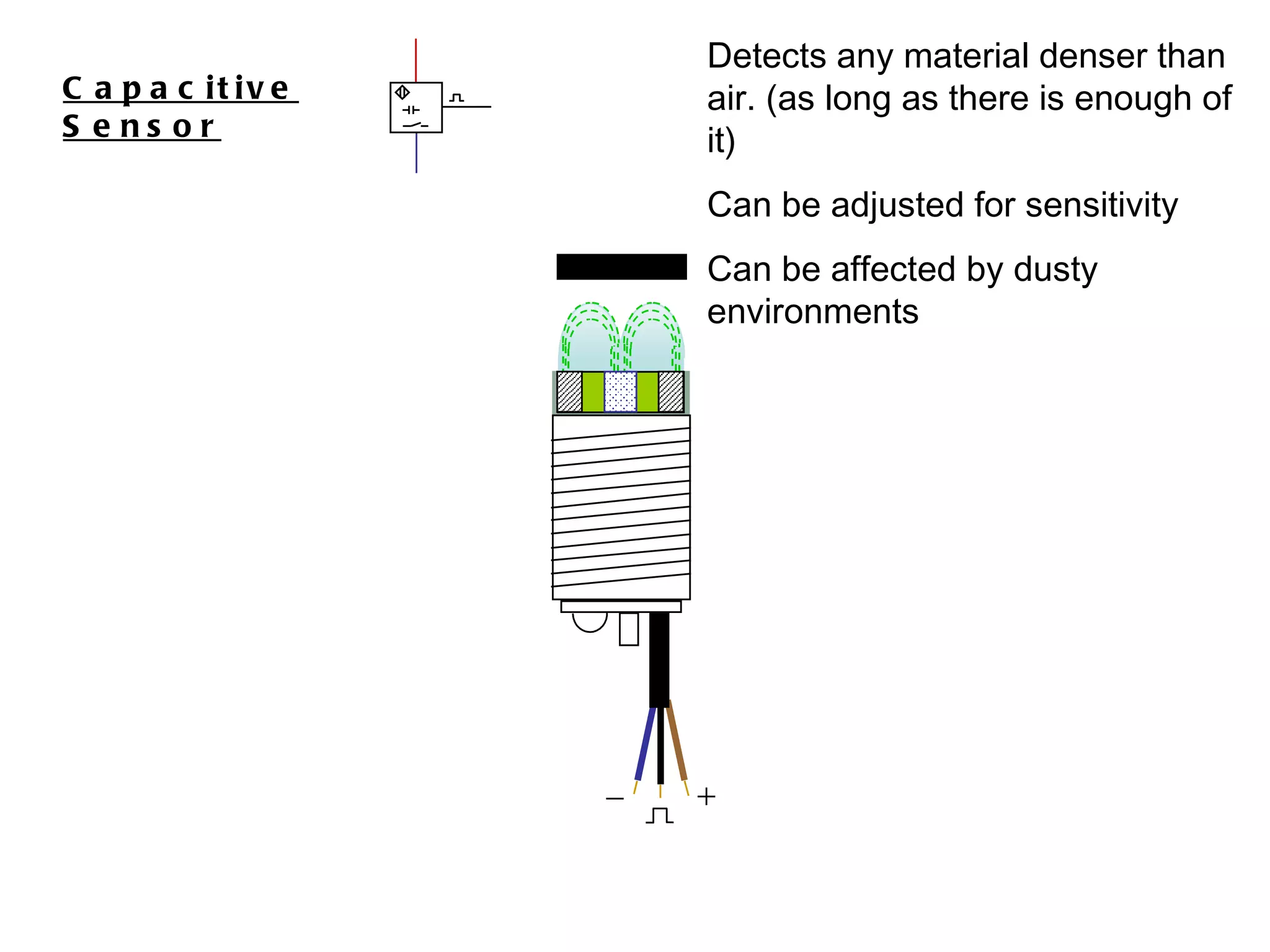
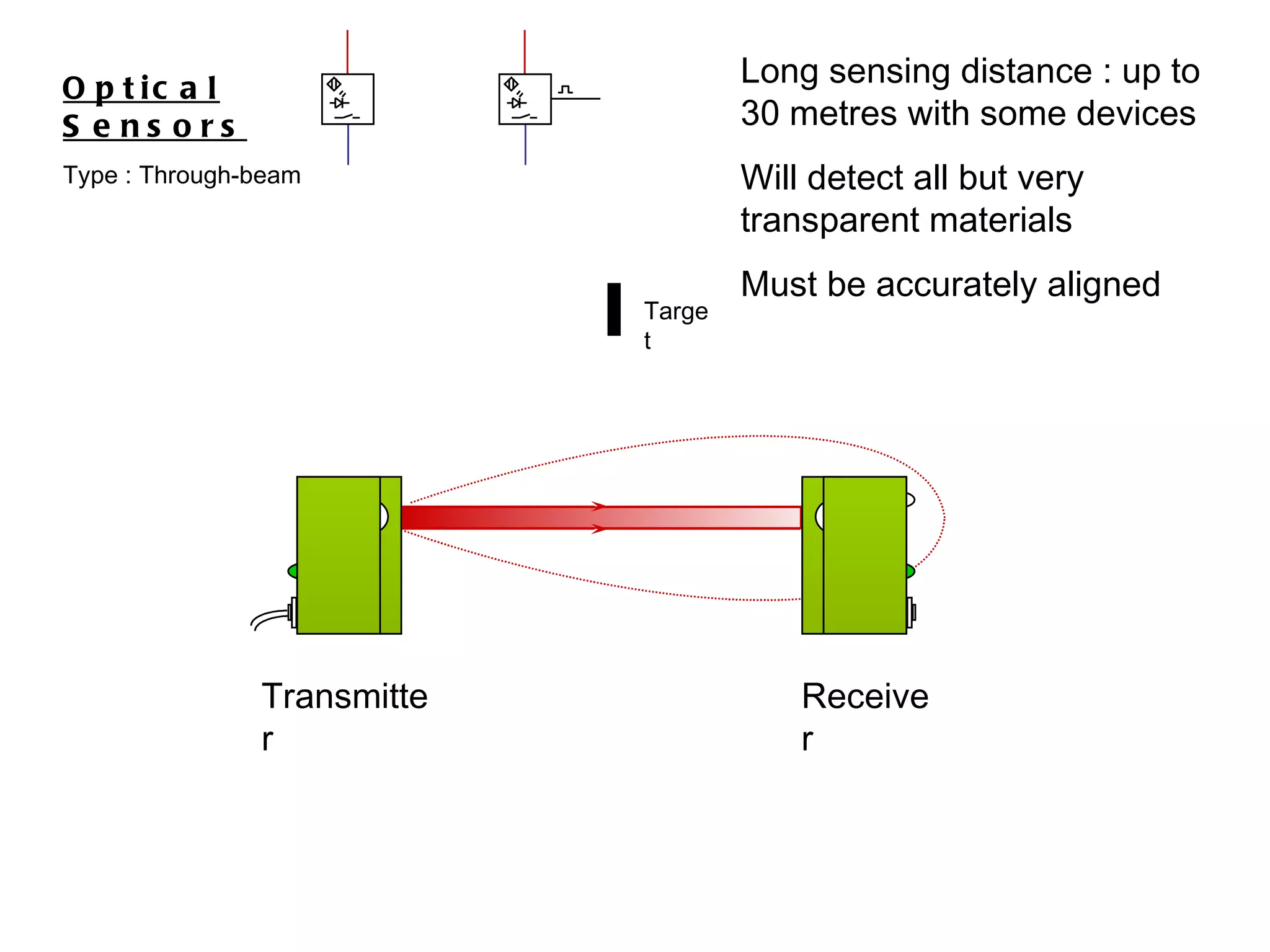
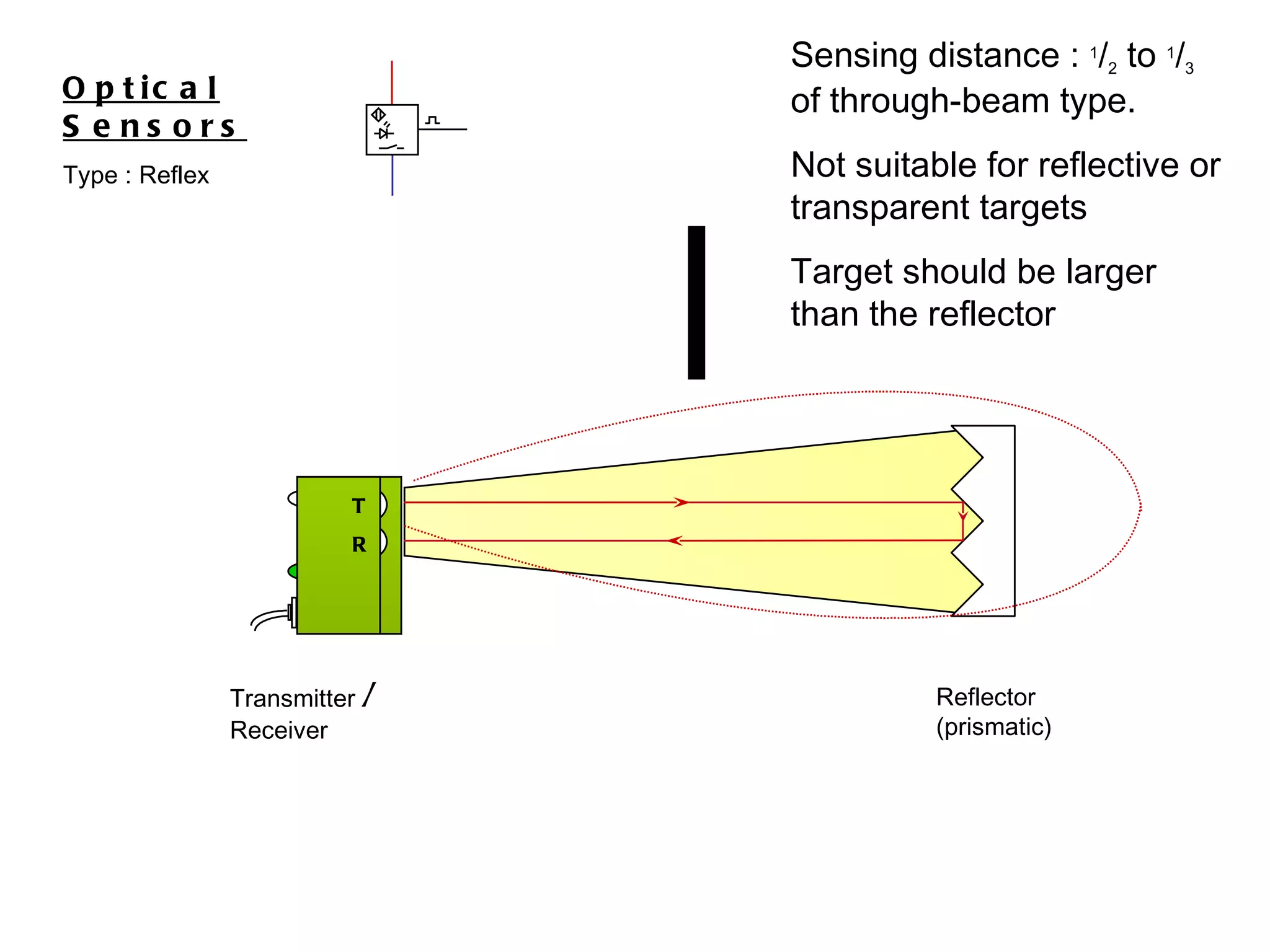
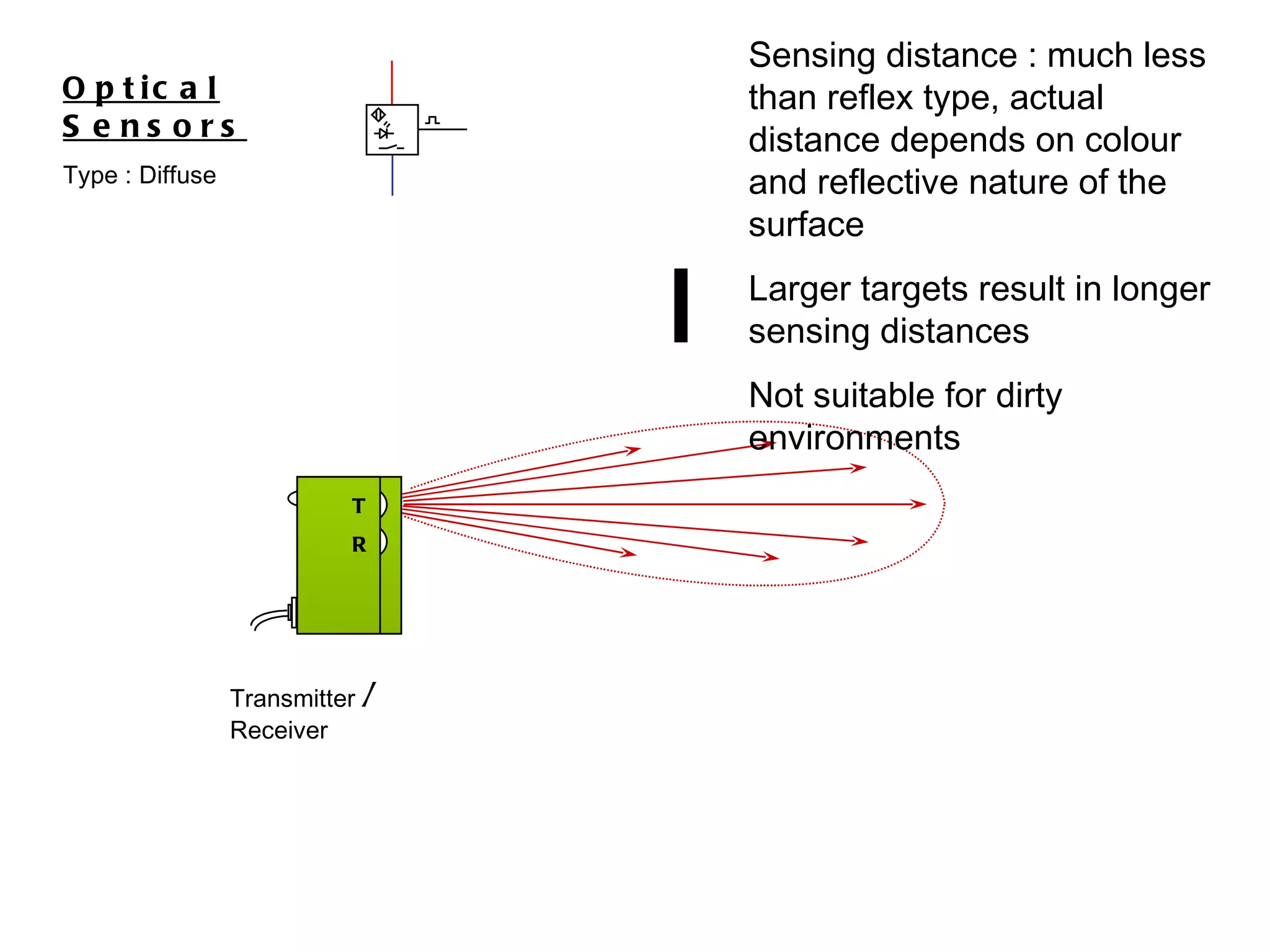
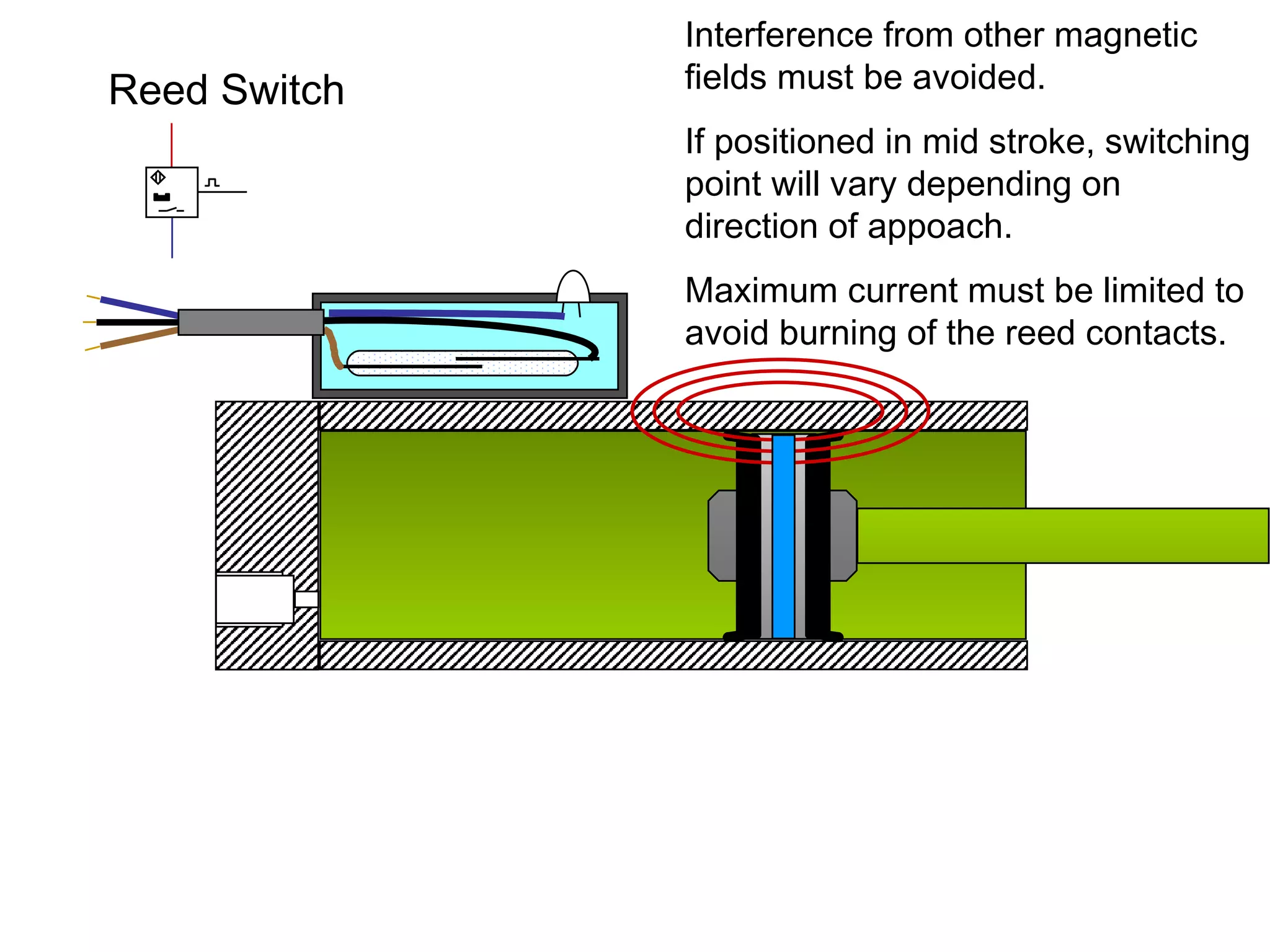
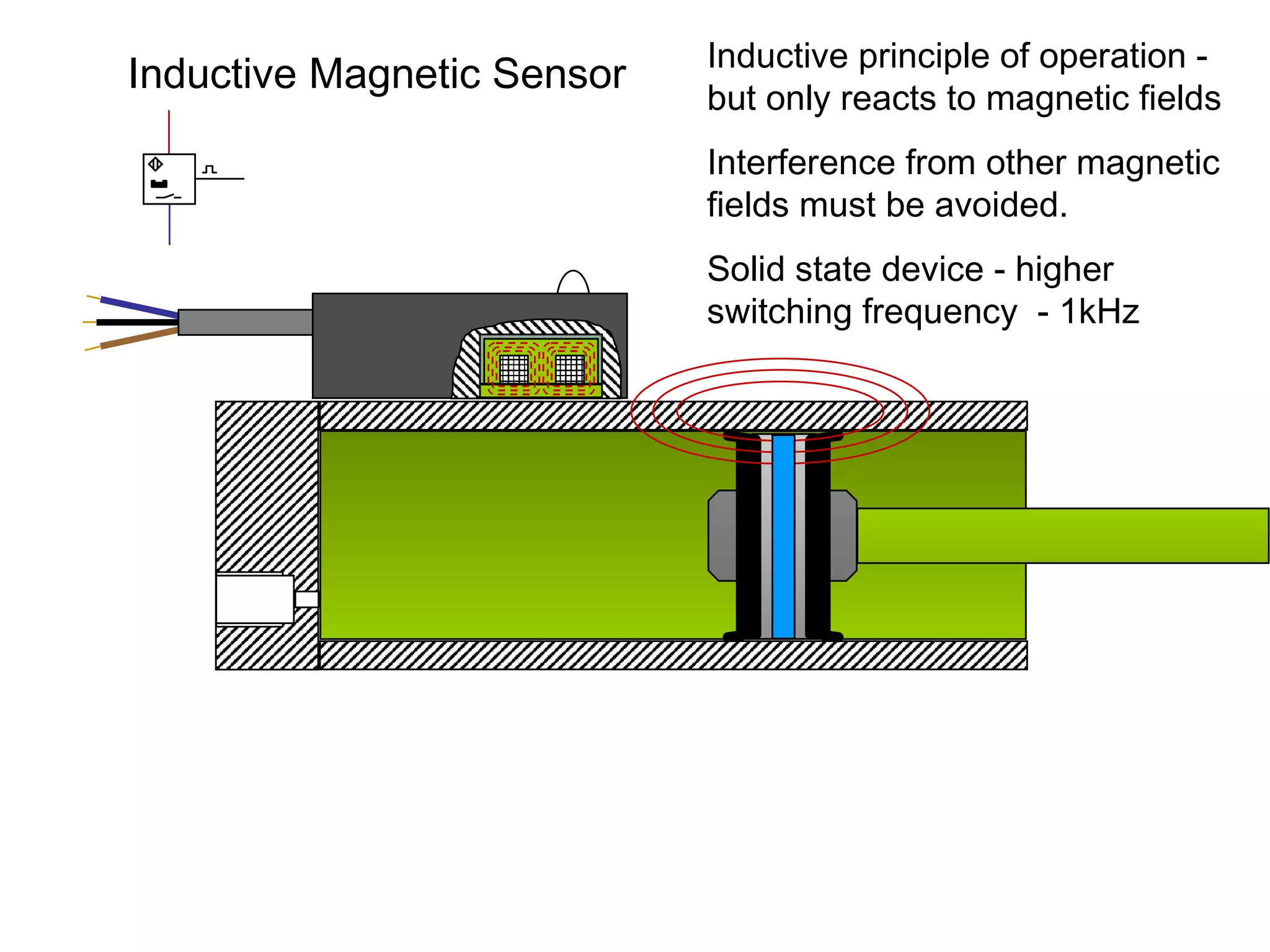
The document discusses different types of sensors based on their output and principles of operation. There are discrete (digital) sensors that provide a single logical output and proportional (analog) sensors that provide an output such as voltage or current. Optical, inductive, reed, magnetic, and capacitive sensors are described in terms of their operating principles, outputs, advantages, and limitations. Symbols are provided for common sensor types.