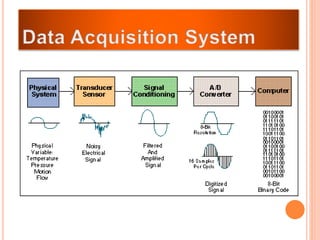
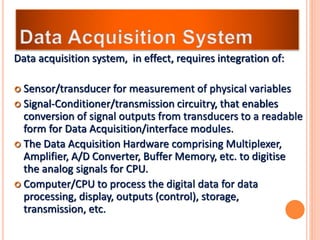
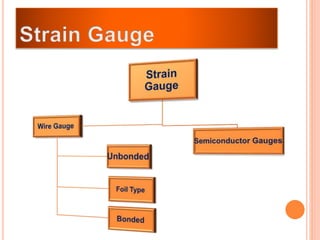
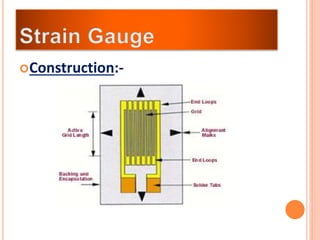
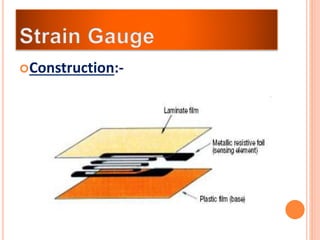
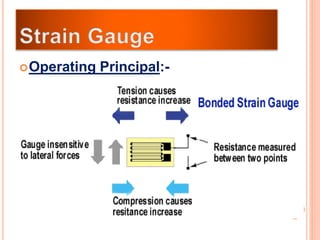
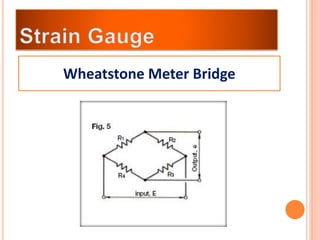
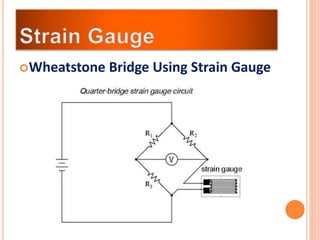
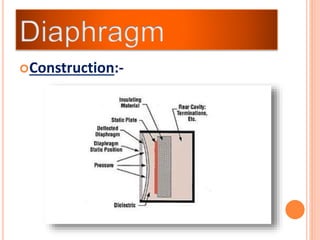
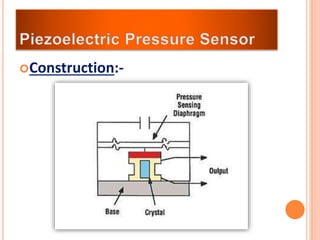
The document discusses the key components required for a data acquisition system: sensors/transducers to measure physical variables and convert them to electrical signals, signal conditioning circuitry to prepare the signals for processing, and data acquisition hardware like multiplexers and ADCs to digitize the analog signals for a computer to process, display, store, and transmit the data. It provides examples of common transducers for measuring variables like displacement, temperature, light, and describes strain gauges, piezoelectric transducers, and different types of pressure transducers in more detail.