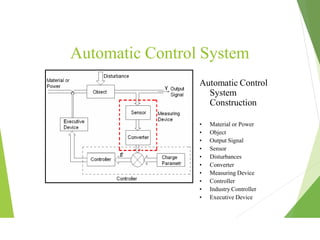
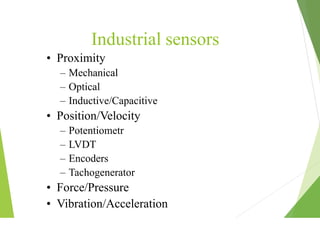
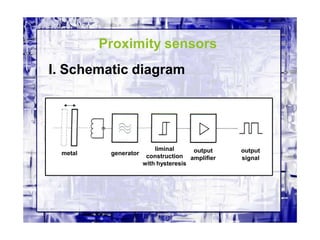
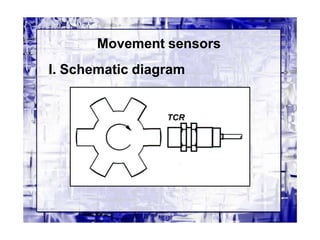
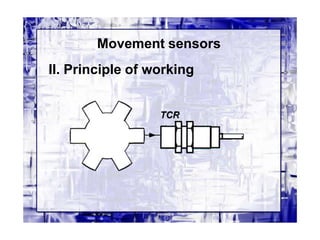
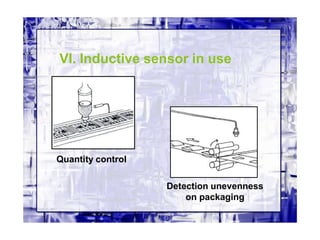
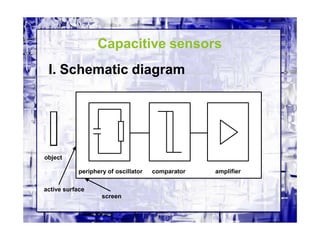
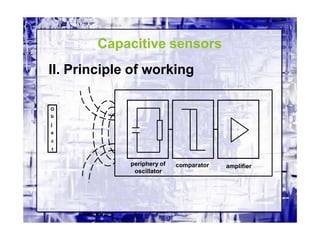
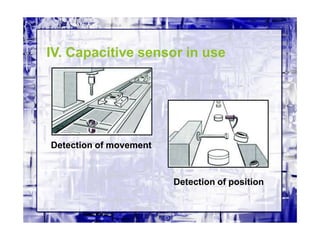
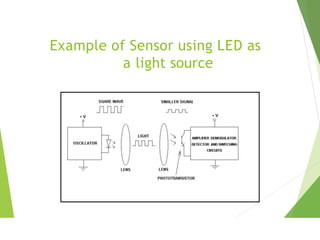
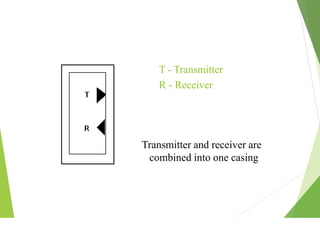
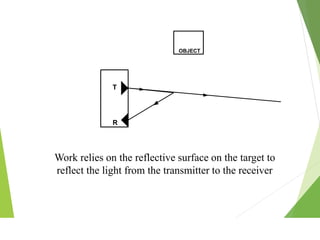
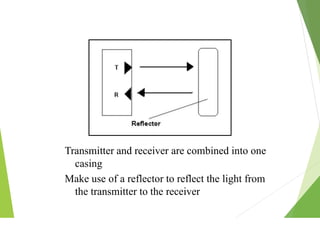
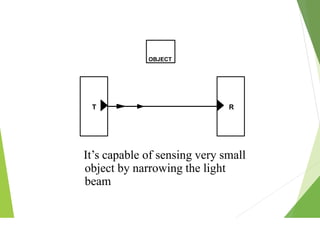
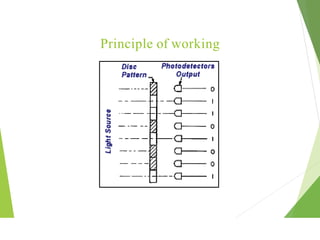
This document discusses different types of industrial sensors used in automatic control systems. It describes contact versus non-contact sensors, with contact sensors having physical contact with the measured parameter and non-contact or proximity sensors not requiring contact. The document then covers various types of industrial sensors including proximity, position, force, vibration, inductive, capacitive, and optical sensors. It provides examples of applications and working principles for each sensor type.