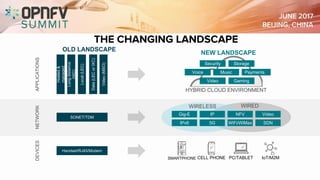
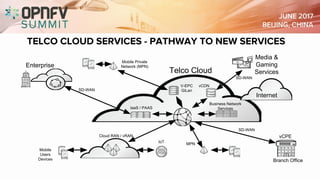
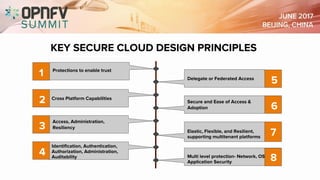
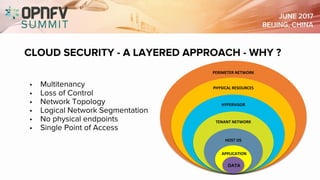
The document discusses the complexities of securing the telco cloud, emphasizing the importance of virtualization and cloudification in modern networking. It highlights various cloud security threats and the need for a layered security approach, including multi-tenancy, access management, and data protection strategies. The document also notes the necessity of automation in managing security vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance within hybrid cloud environments.