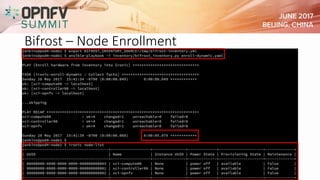
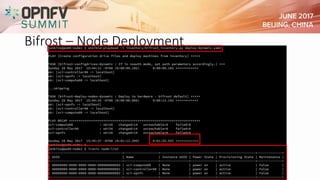
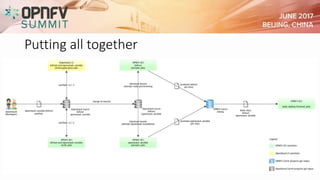
The document outlines the progress and challenges faced by the OPFNV project in deploying OpenStack, highlighting achievements such as multiple releases and numerous deployments. It identifies issues like slow integration cycles and limited developer resources, while proposing improvements through enhanced automation and development practices. The status of tools like Bifrost and OpenStack Ansible is discussed, emphasizing their role in streamlining the integration process for future releases.