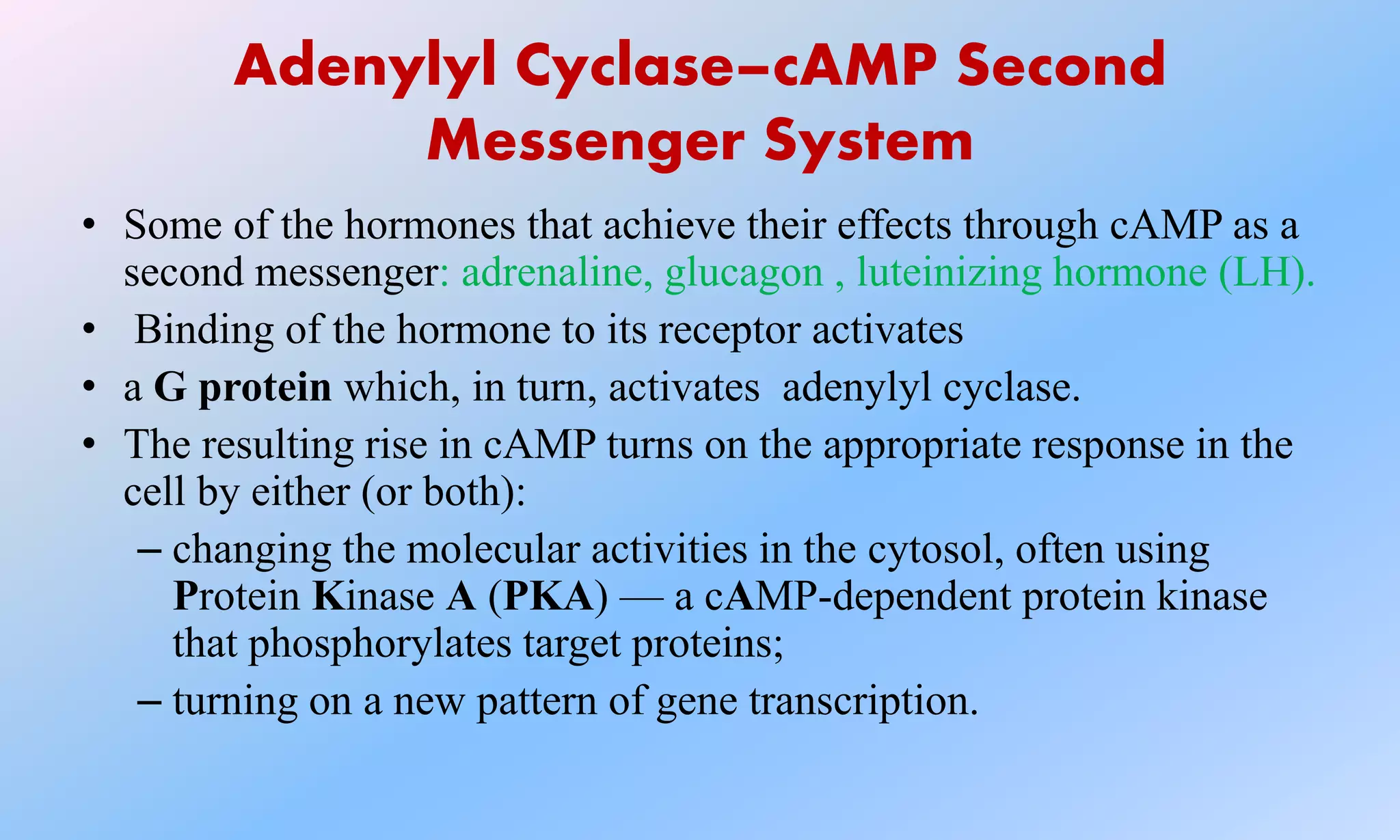
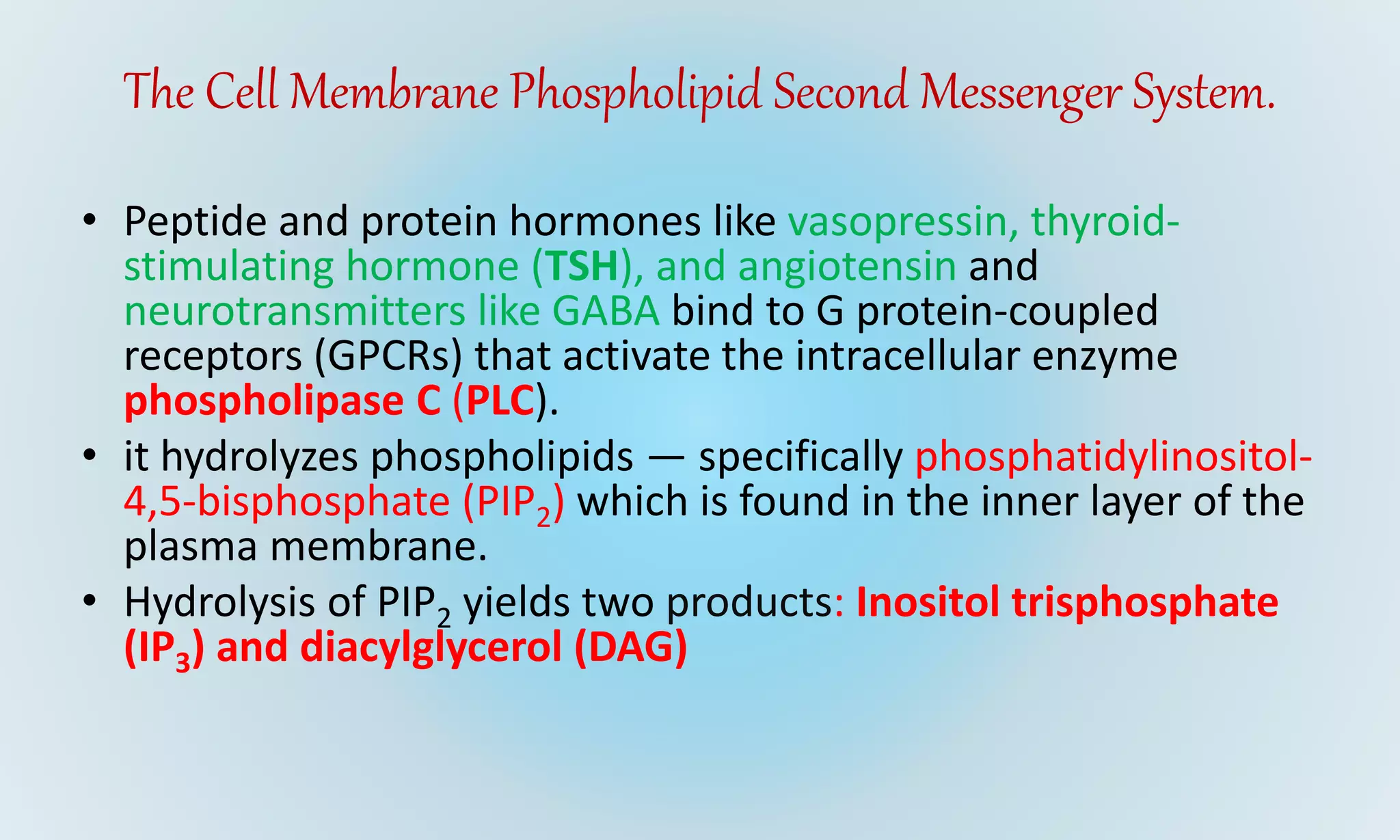
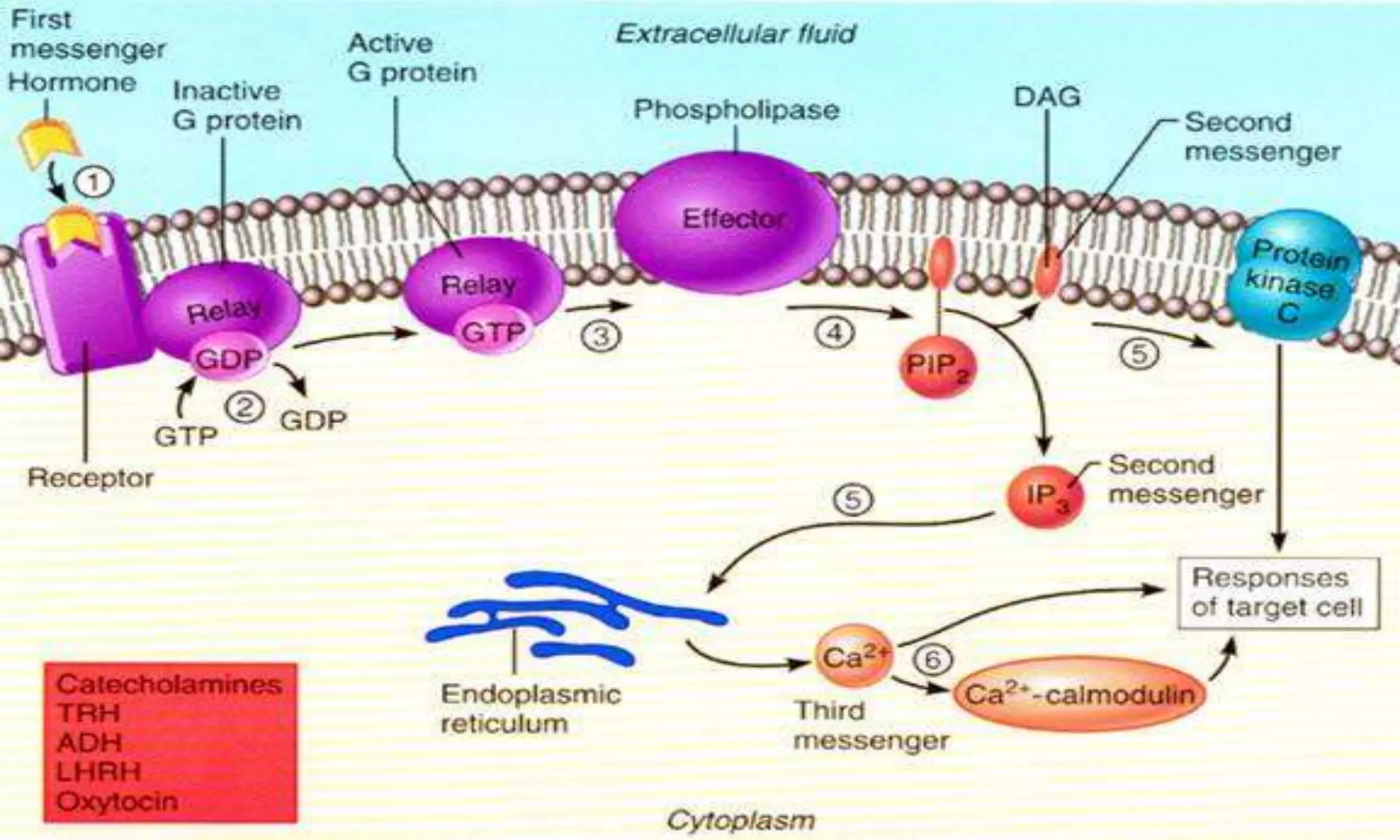
This document discusses second messenger systems, which relay signals from cell surface receptors to target molecules inside cells. There are three major classes of second messenger systems: 1) the adenylyl cyclase-cAMP system, which is activated by hormones like epinephrine and glucagon and uses cAMP as the second messenger; 2) the phospholipid system, which uses IP3 and DAG as second messengers; and 3) the calcium-calmodulin system, where calcium acts as the second messenger and binds to and activates calmodulin. These second messengers amplify signals and allow hormones and neurotransmitters to trigger intracellular responses.












![…..contd
Getting Ca2+ into (and out of) the cytosol:
• Voltage-gated channels open in response to a change in membrane
potential, e.g. the depolarization of an action potential;
are found in excitable cells:
– skeletal muscle
– smooth muscle (These are the channels blocked by drugs, such as
felodipine [Plendil®], used to treat high blood pressure. The influx of Ca2+
contracts the smooth muscle walls of the arterioles, raising blood pressure.
The drugs block this.)
– neurons. When the action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal, the
influx of Ca2+ triggers the release of the neurotransmitter.
– the taste cells that respond to salt.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondmessengersystem-160917042753/75/Second-messenger-system-16-2048.jpg)




