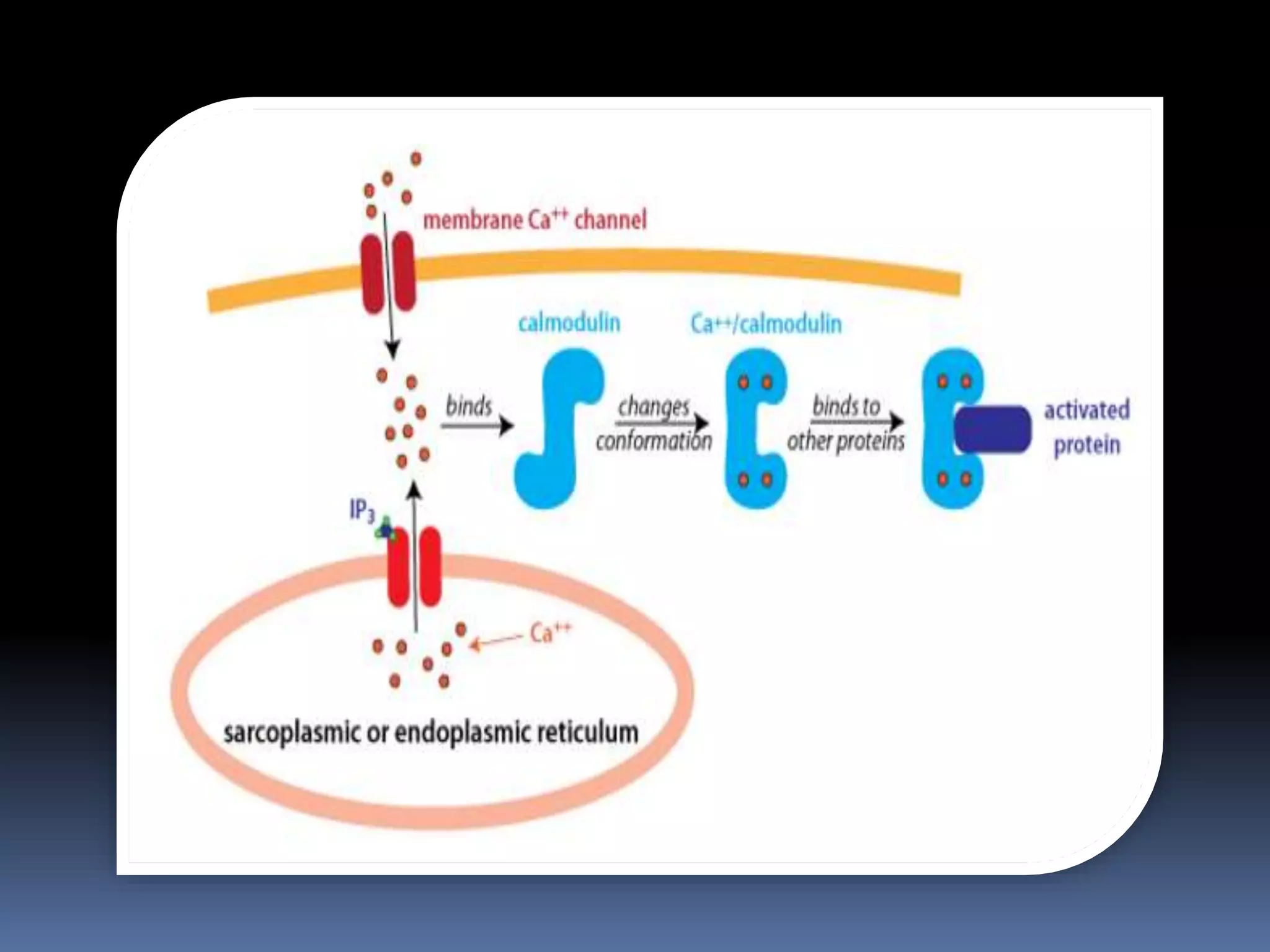
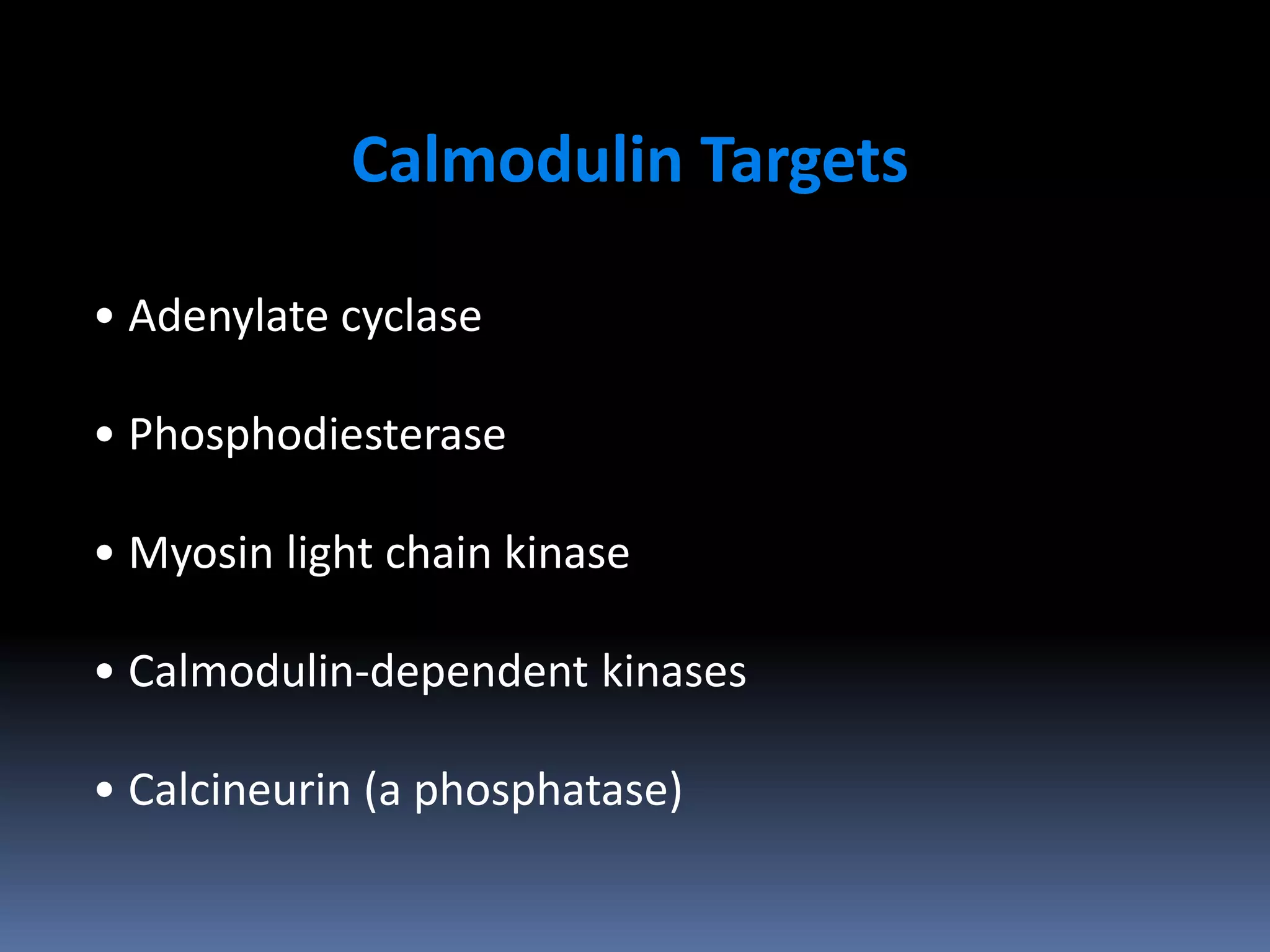
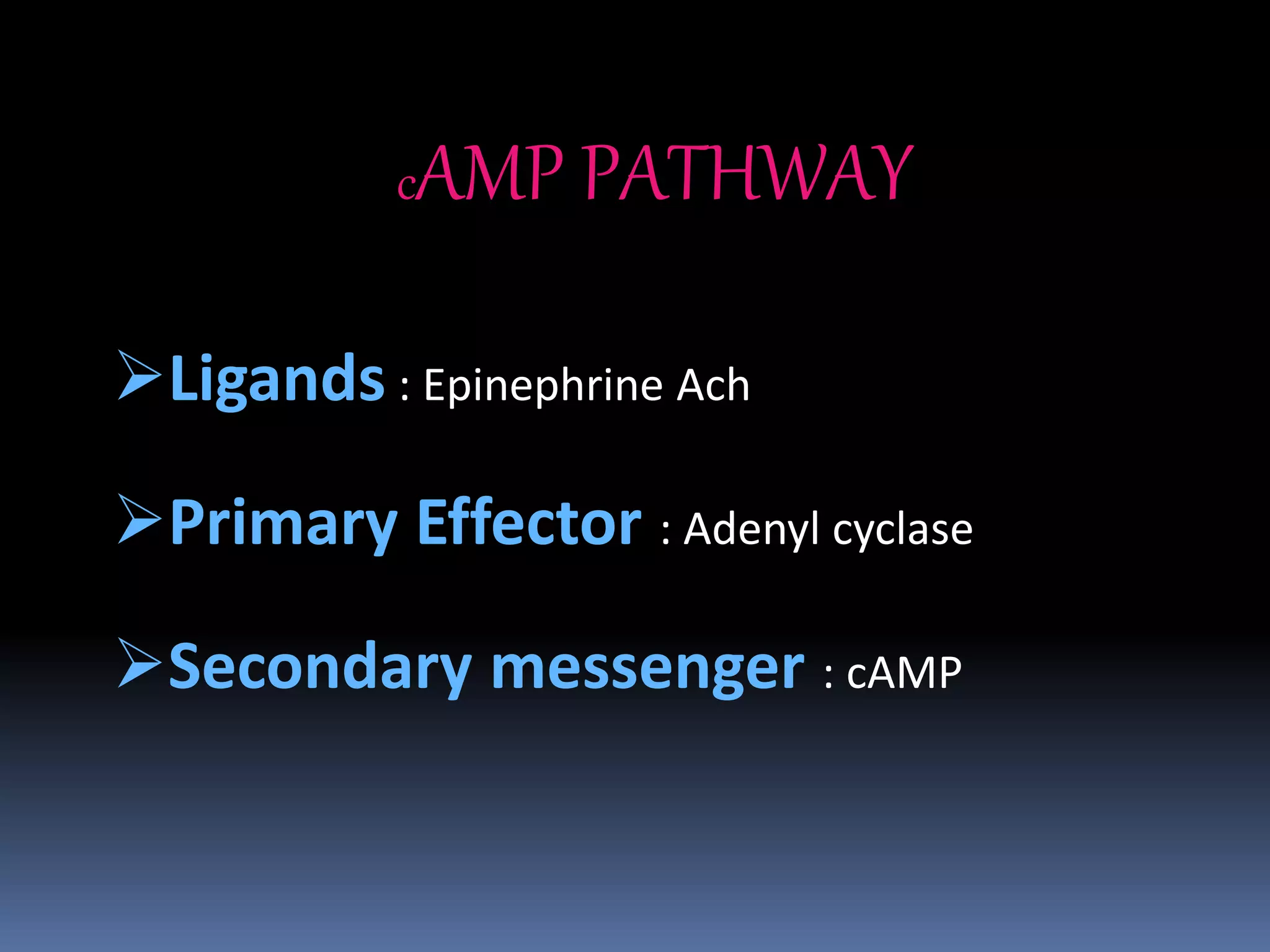
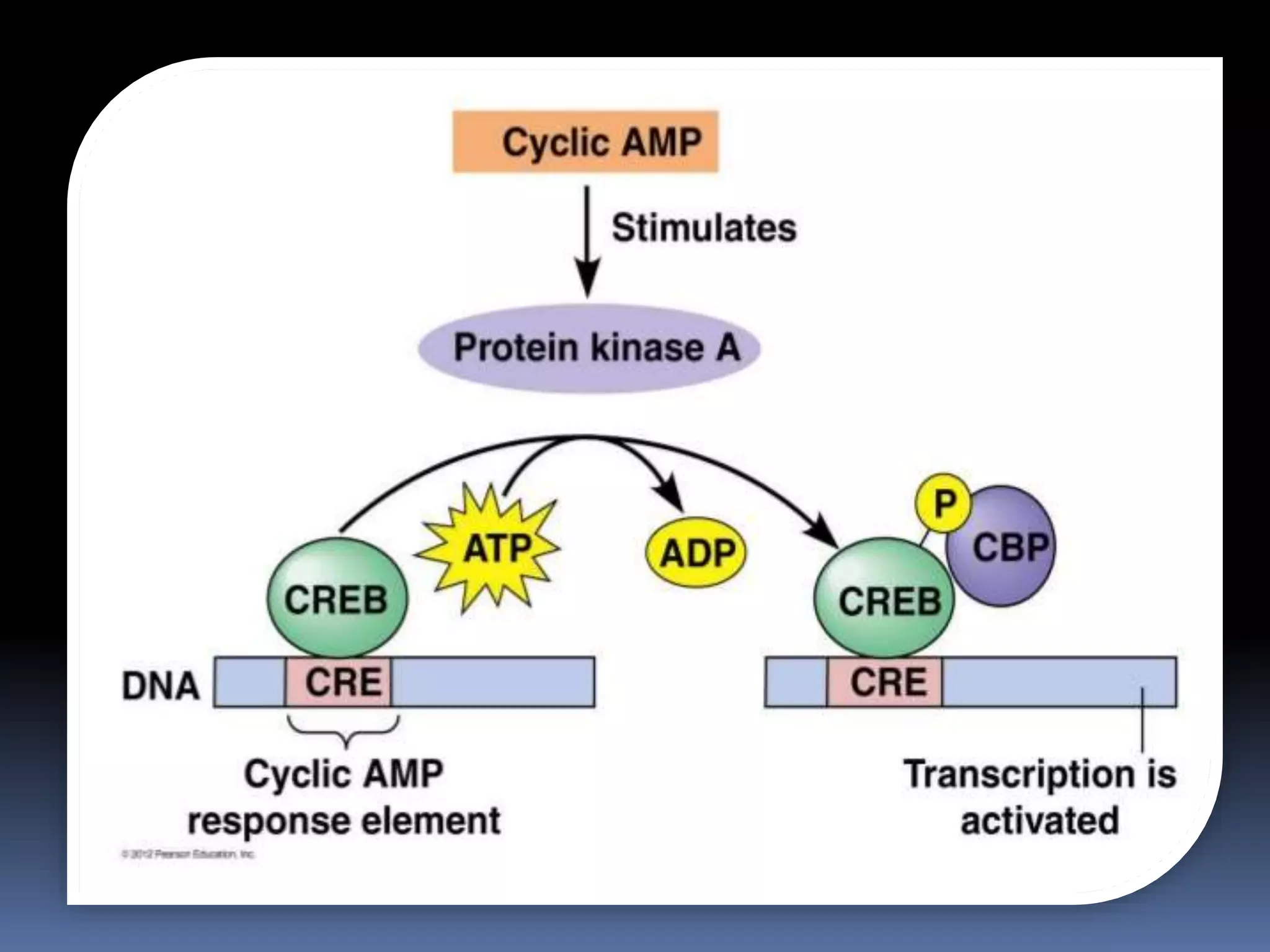
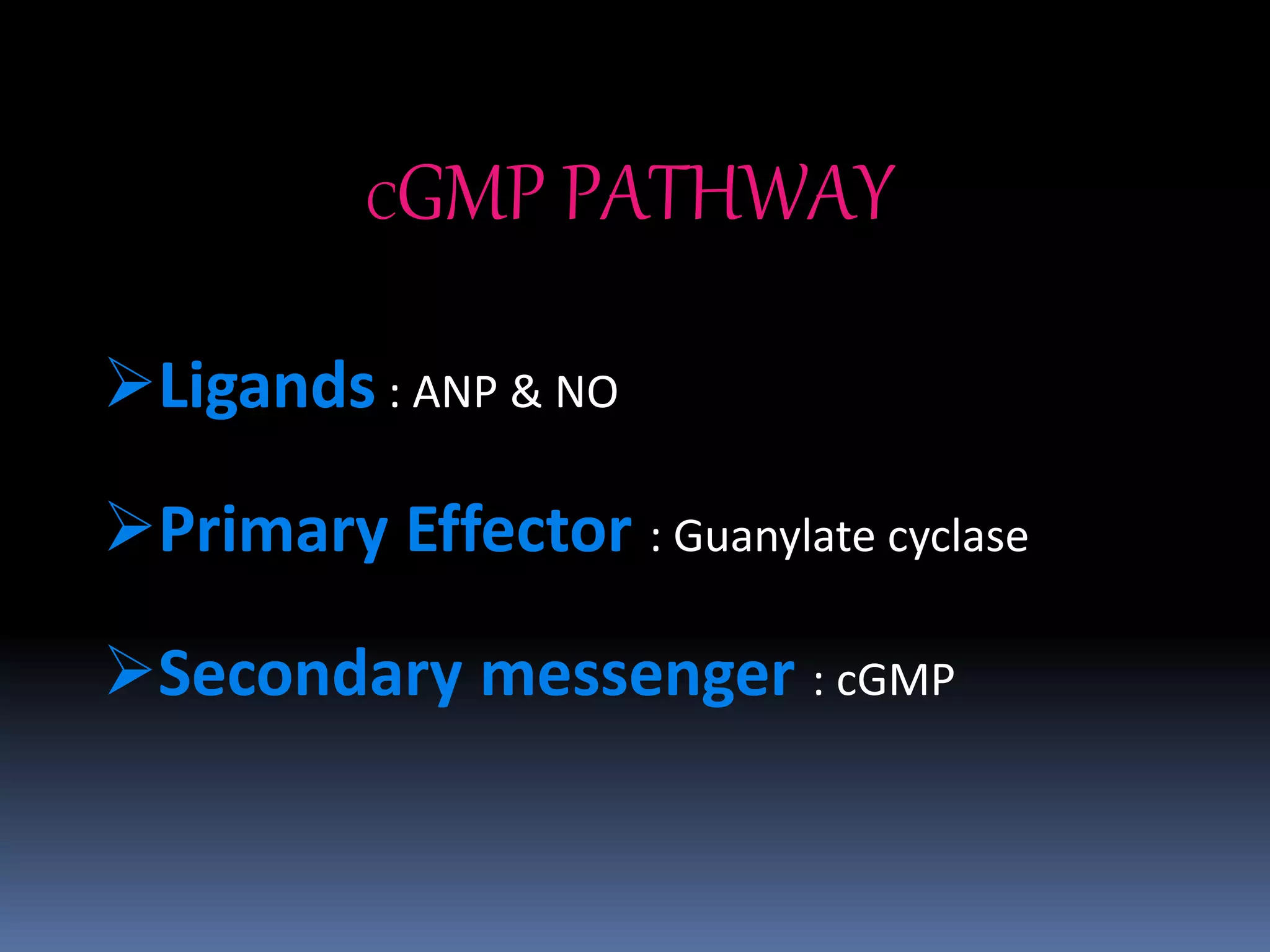
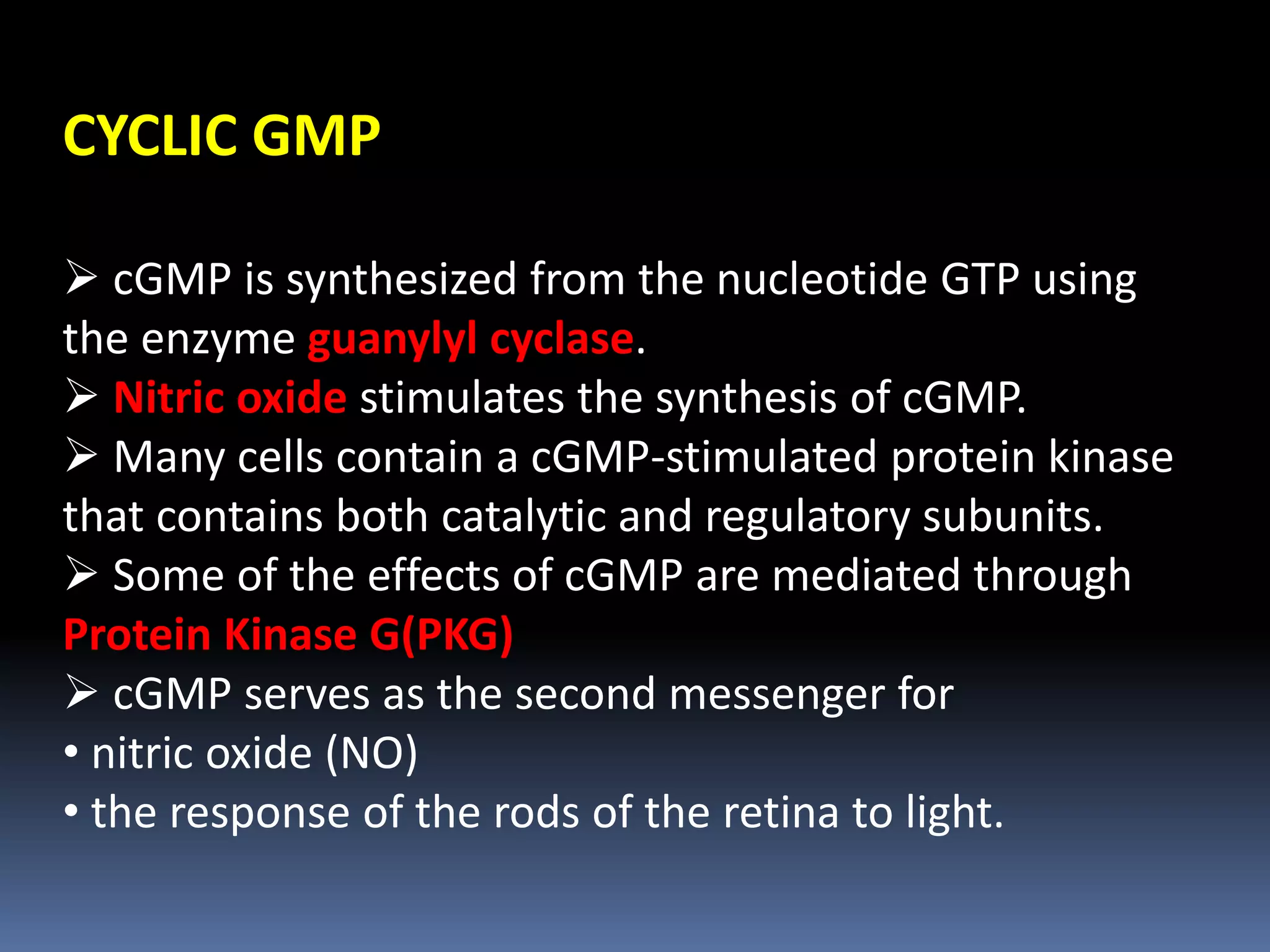
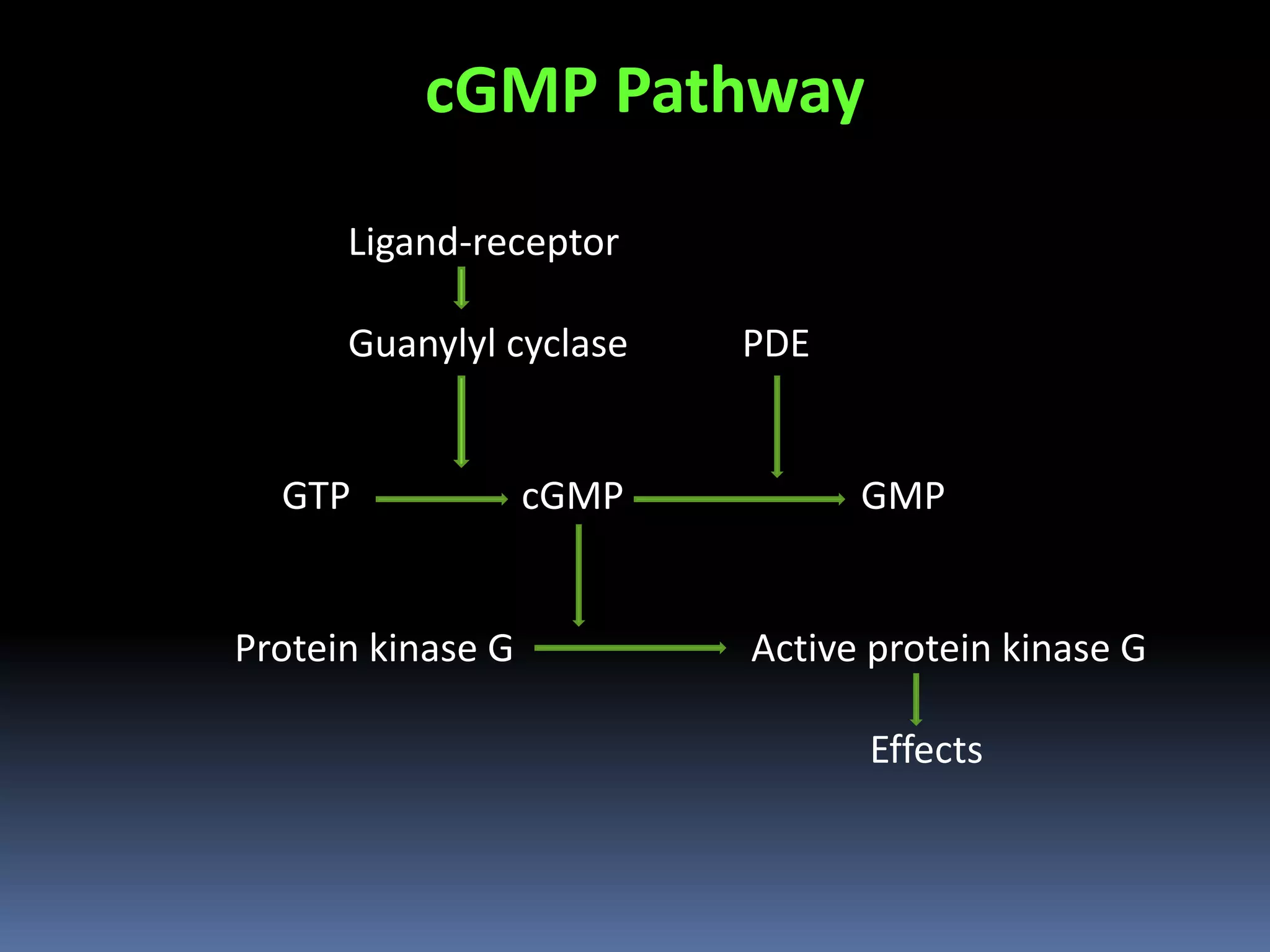
This document discusses second messengers, which are intracellular molecules that amplify and spread signals from receptors on the cell surface. It describes four main classes of second messengers - cyclic nucleotides, membrane lipid derivatives, calcium ions, and gases like nitric oxide. Specifically, it examines the cAMP, cGMP, IP3/DAG, and calcium-mediated signaling pathways, outlining the ligands, effectors, and downstream effects of each messenger. It also provides details on nitric oxide and calcium signaling within cells.














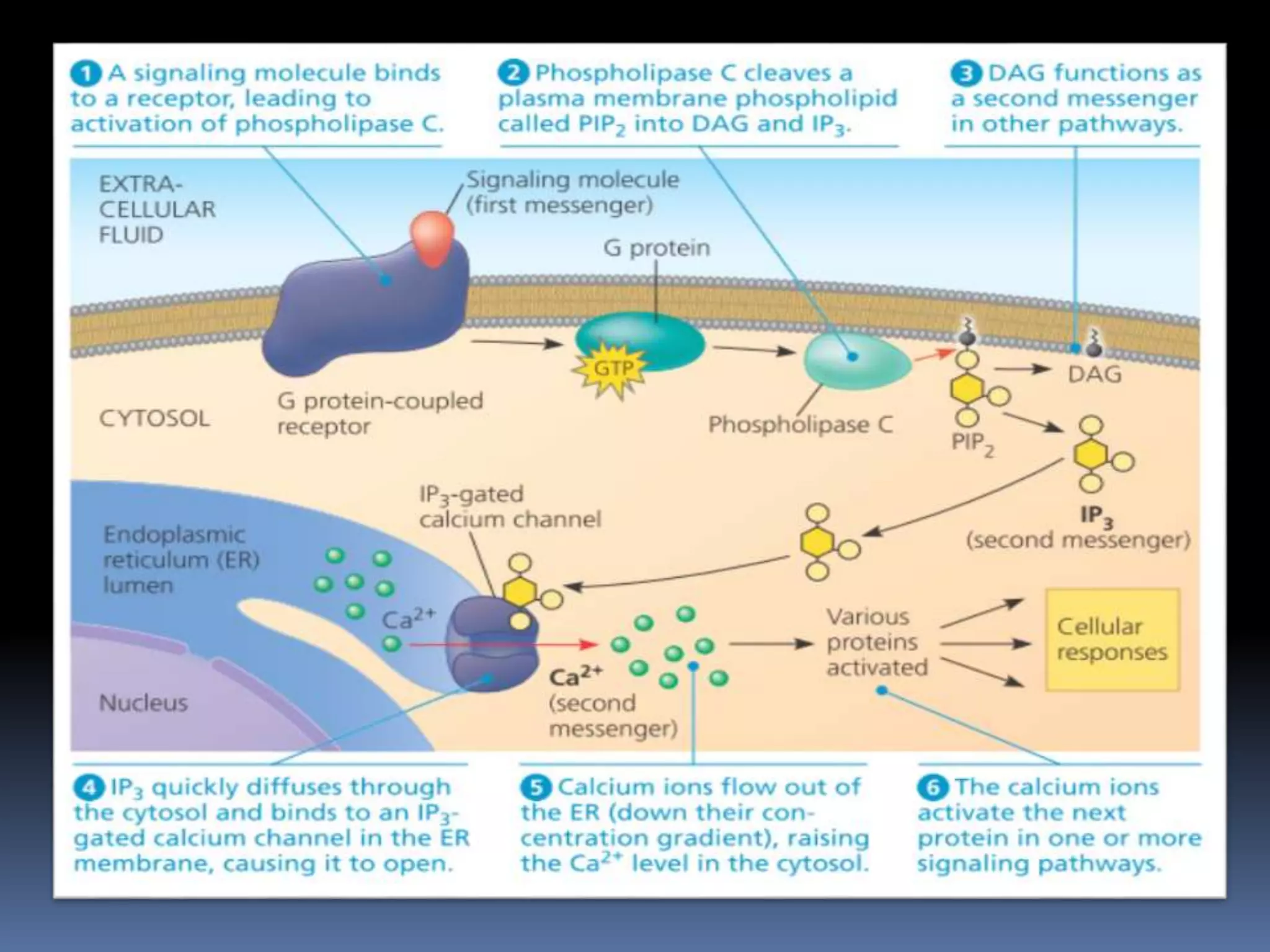
![IP3/DAG
Inositol
triphosphate
• Hydrophilic
• Agonist for internal
calcium channel
• [Ca++]i rises
• Multiple effects
through Ca++ binding
protein
Diacylglycerol
• Hydrophobic
• Target PKC(a kinase)
• PKC requires Ca++
and DAG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondmessengers-190816140013/75/Secondary-messengers-system-22-2048.jpg)