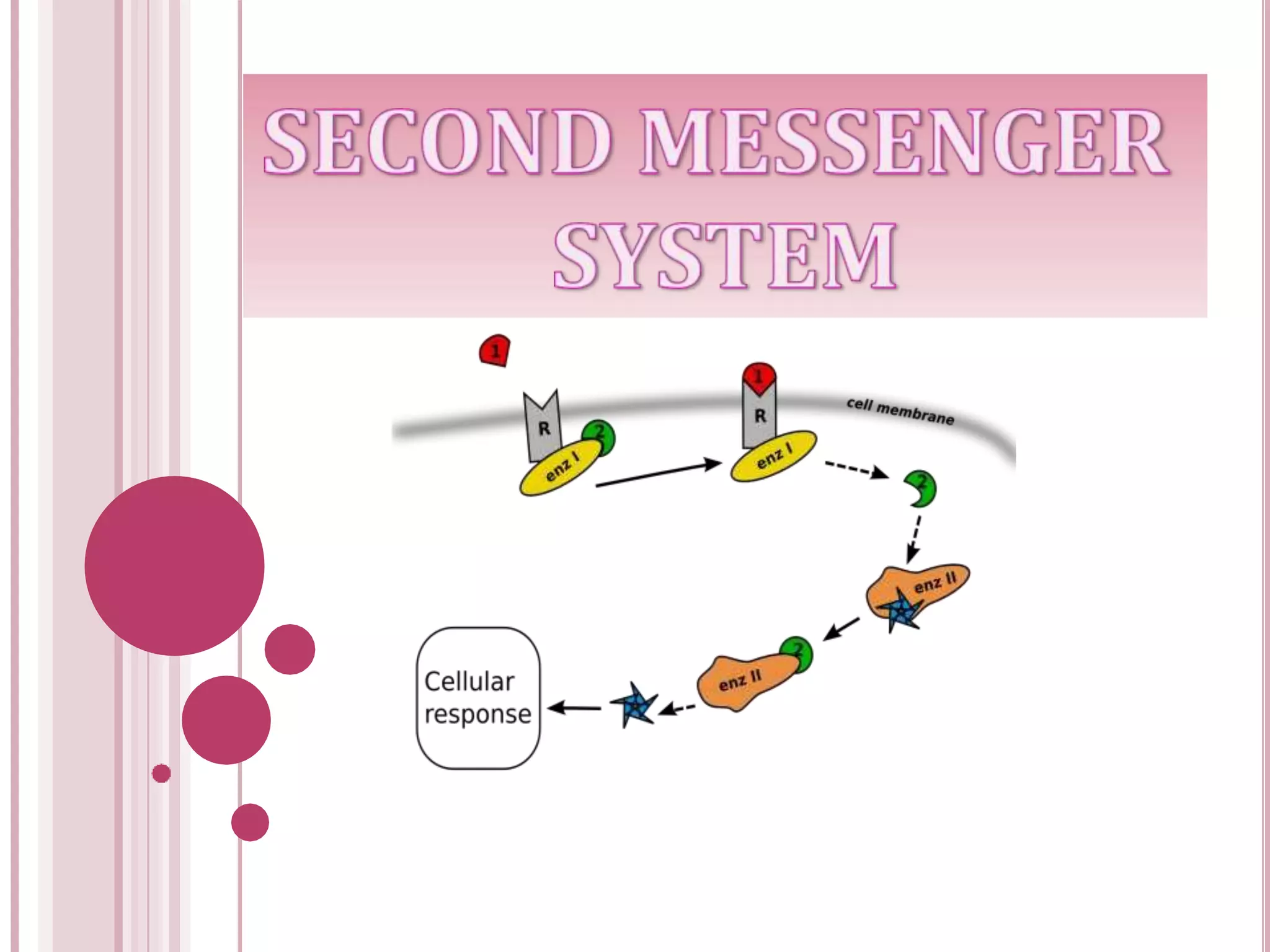
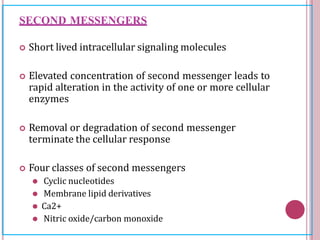
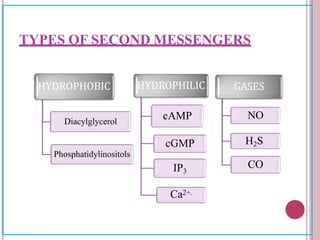
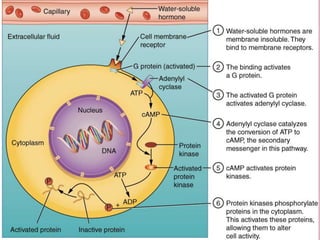
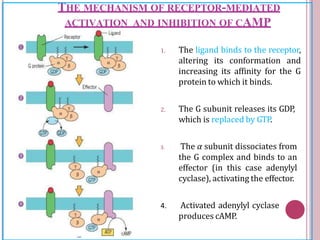
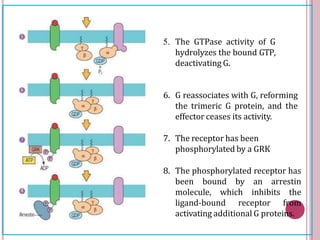
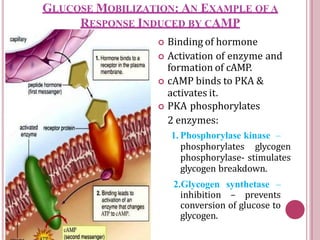
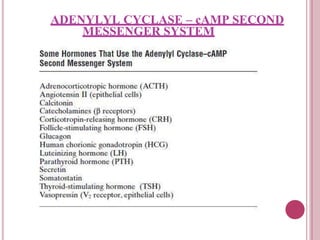
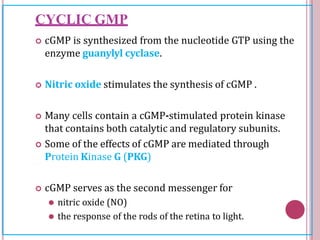
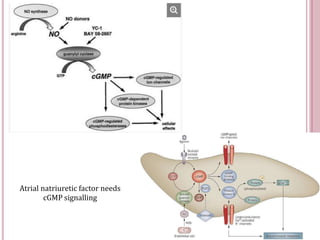
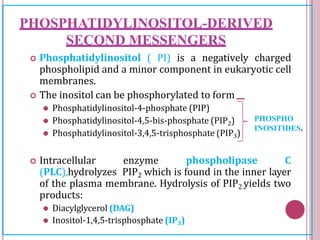
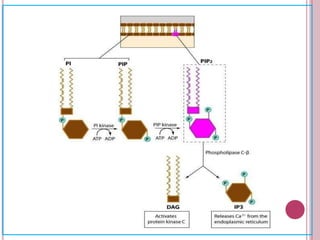
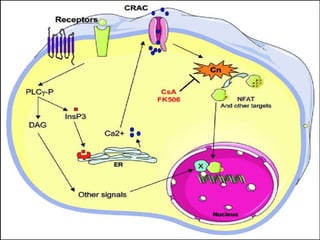
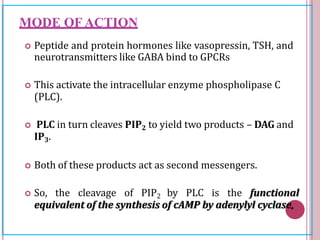
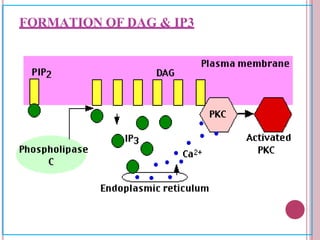
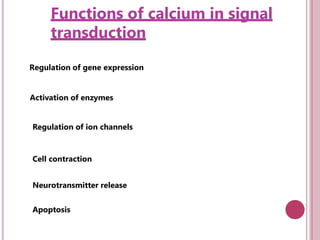
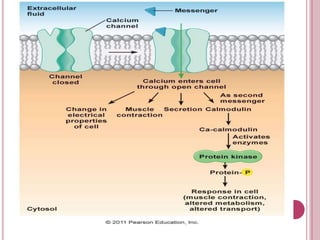
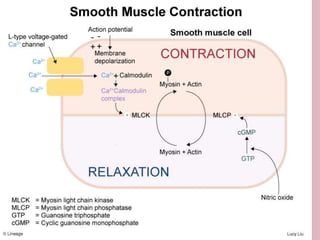
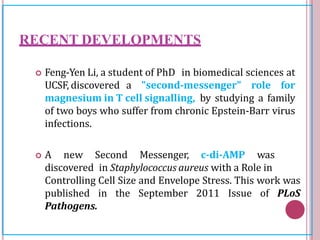
Second messengers are small intracellular molecules that amplify signals received at cell surface receptors and help transmit them to target molecules within the cell. They include cyclic nucleotides like cAMP and cGMP, calcium ions, inositol trisphosphate, diacylglycerol, and nitric oxide. These second messengers activate intracellular enzyme and protein targets that trigger cellular responses like changes in metabolism, gene expression, and cell growth. Earl Sutherland discovered cAMP as the first second messenger and won the 1971 Nobel Prize for this foundational discovery in cell signaling pathways.