Embed presentation


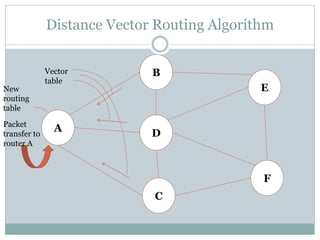
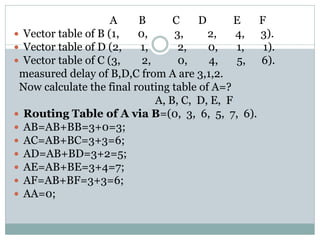
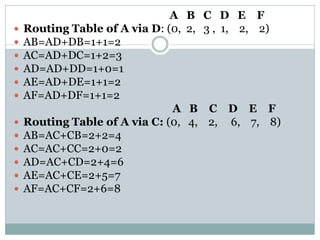


This document provides an example to illustrate how the distance vector routing algorithm works. It shows the vector tables of routers B, D, and C that store the distances to all other routers. It then calculates the routing table for router A based on the distances through neighboring routers B, D, and C, taking the minimum distances. The final routing table for A is (0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2) with routes going through routers D, C, D, D, D respectively.





