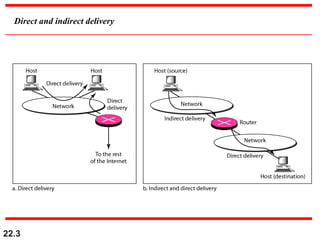
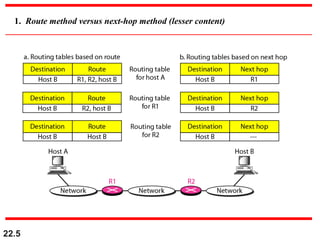
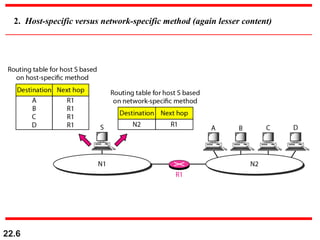
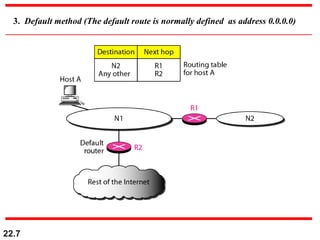
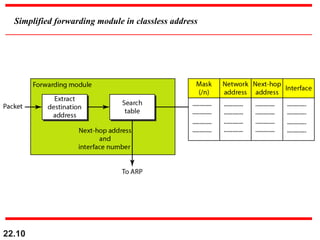
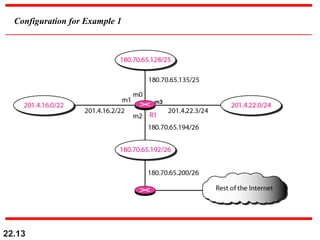
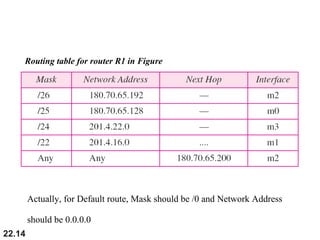
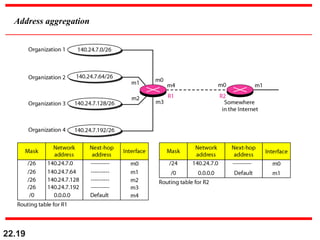
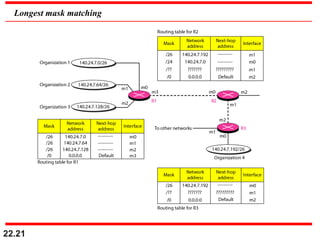
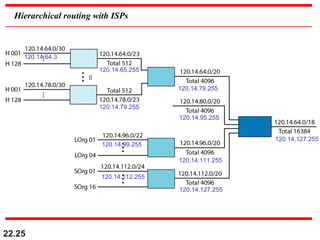
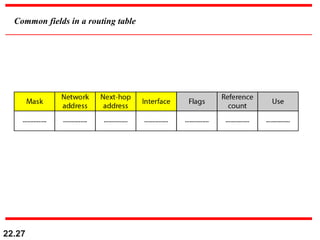
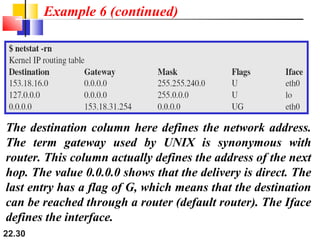
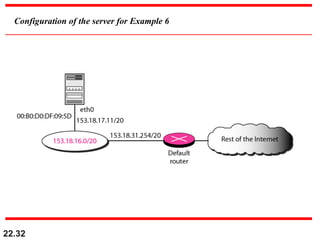
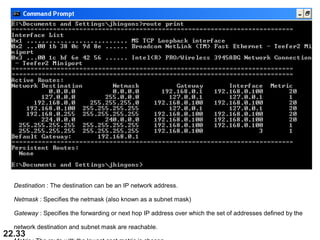
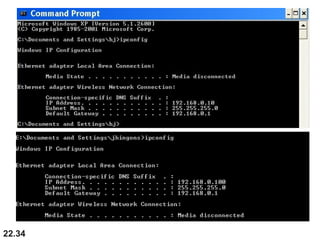
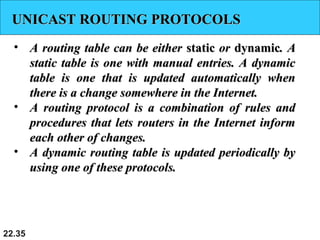
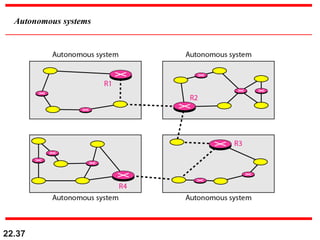
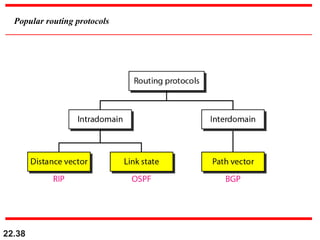
The document discusses delivery, forwarding, and routing in computer networks. It defines delivery as handling packets by underlying physical networks based on supervision from the network and data link layers. Forwarding is placing a packet in its route to the destination by using a routing table. Routing refers to how routing tables are created to help with forwarding. Common routing protocols discussed include distance-vector protocols like RIP and IGRP, link-state protocols like OSPF and IS-IS, and BGP for routing between autonomous systems.