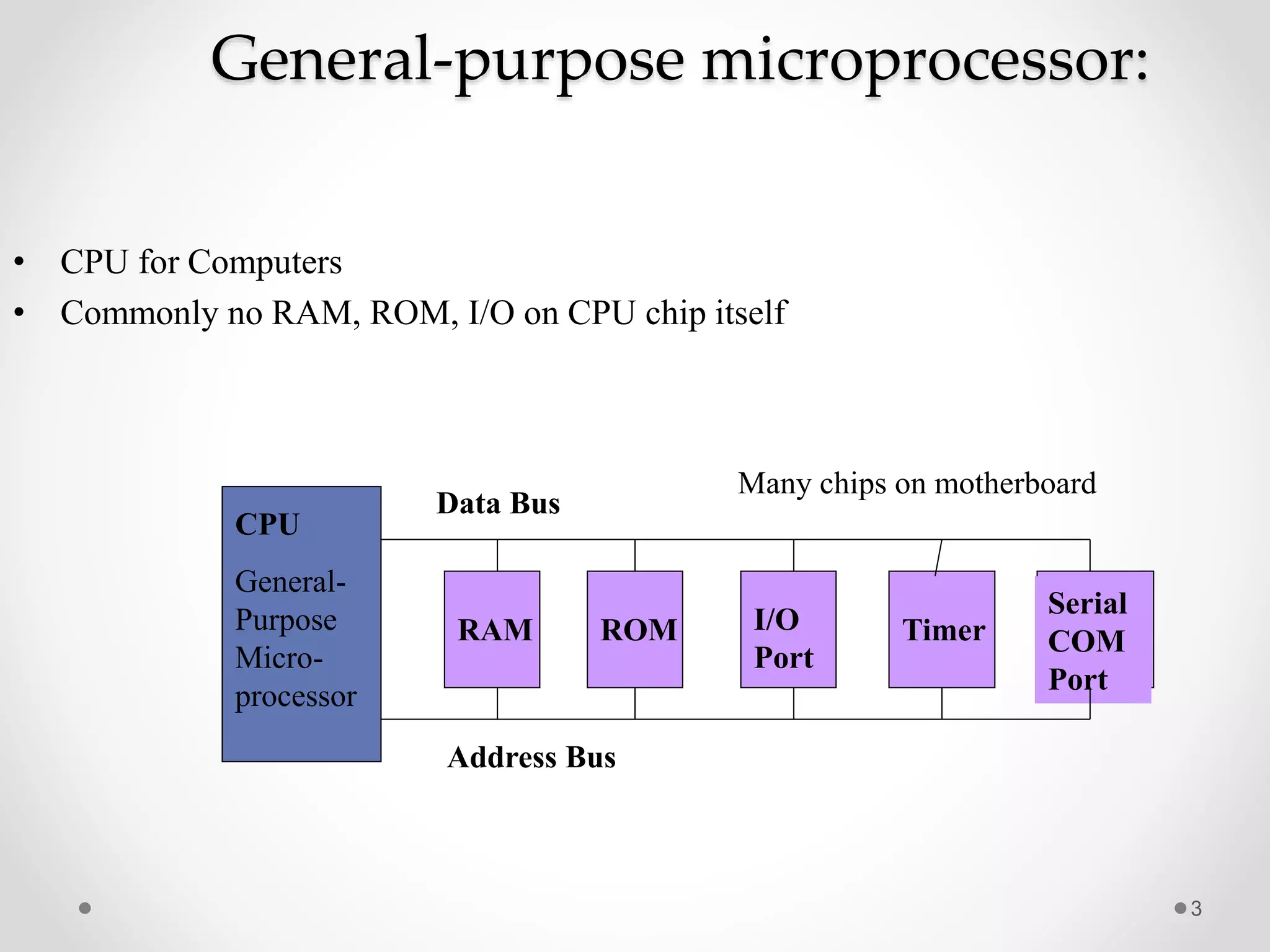
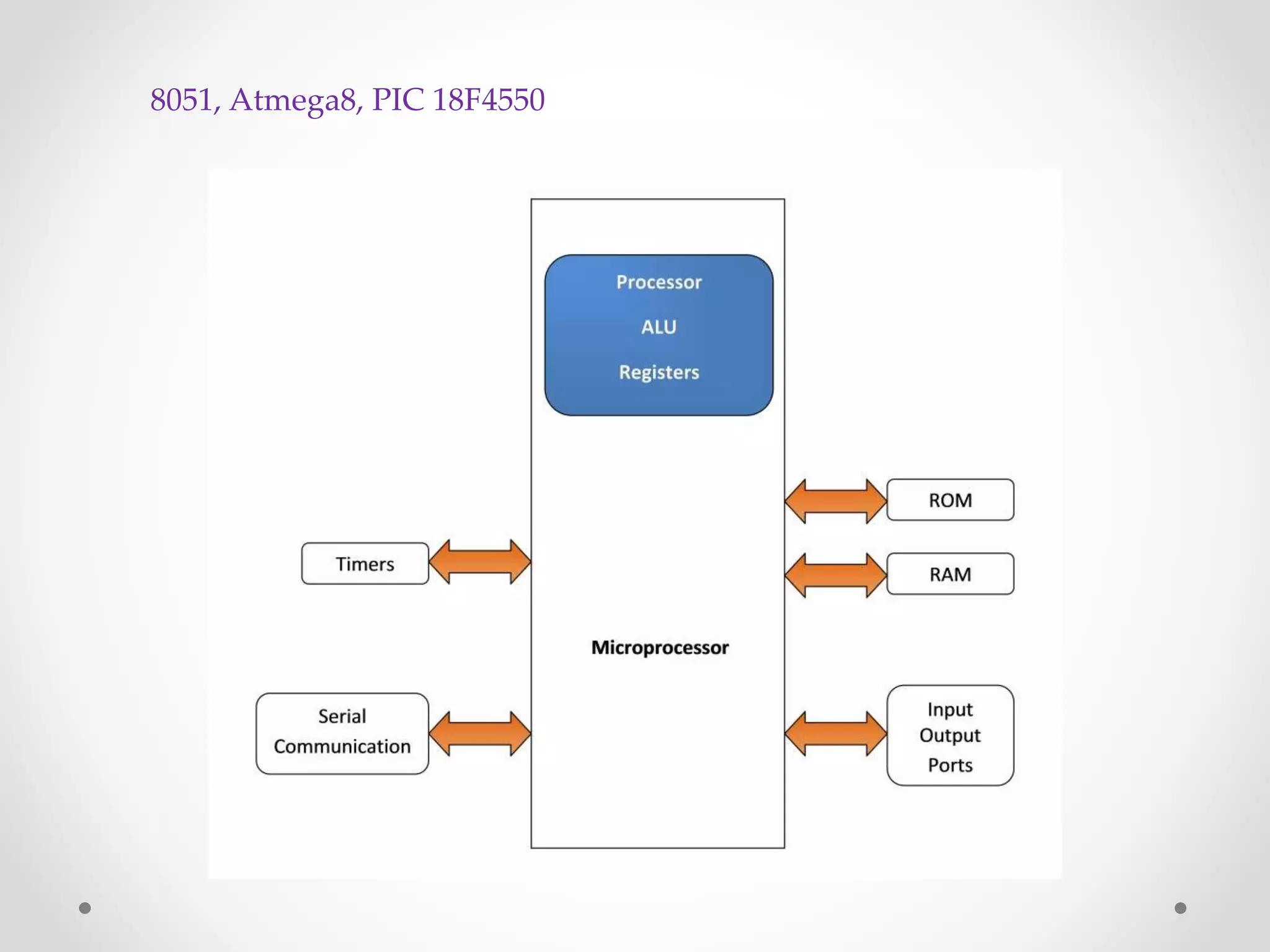
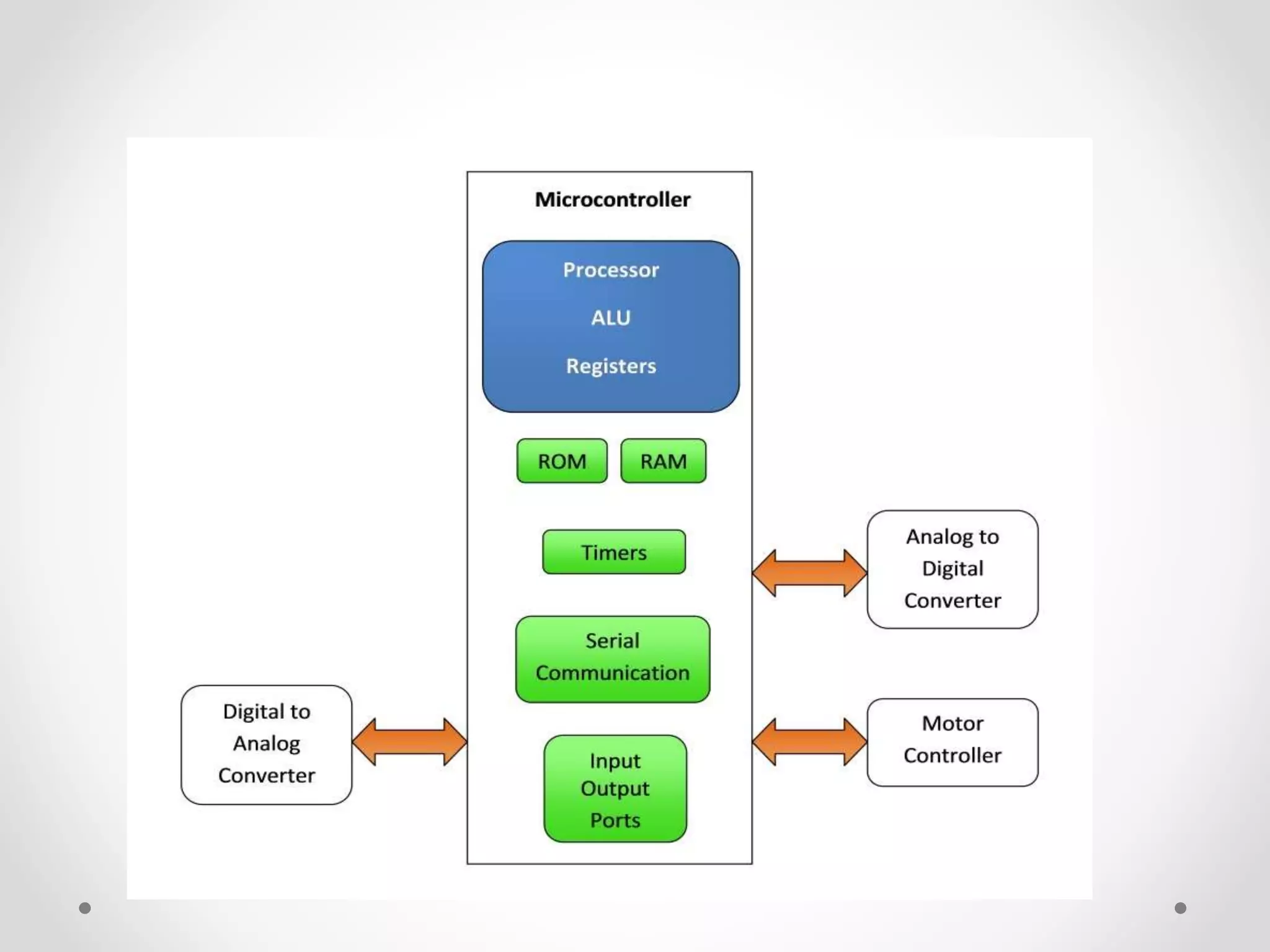
A microprocessor consists of a central processing unit and minimal additional components like registers, while a microcontroller includes more integrated components like memory, input/output pins and communication modules. Specifically, a microcontroller combines a microprocessor with RAM, ROM, timers and other peripherals onto a single chip, making it self-contained and suitable for embedded applications where cost, power and space are priorities. In contrast, a microprocessor's components are separate, providing more flexibility but also greater expense.