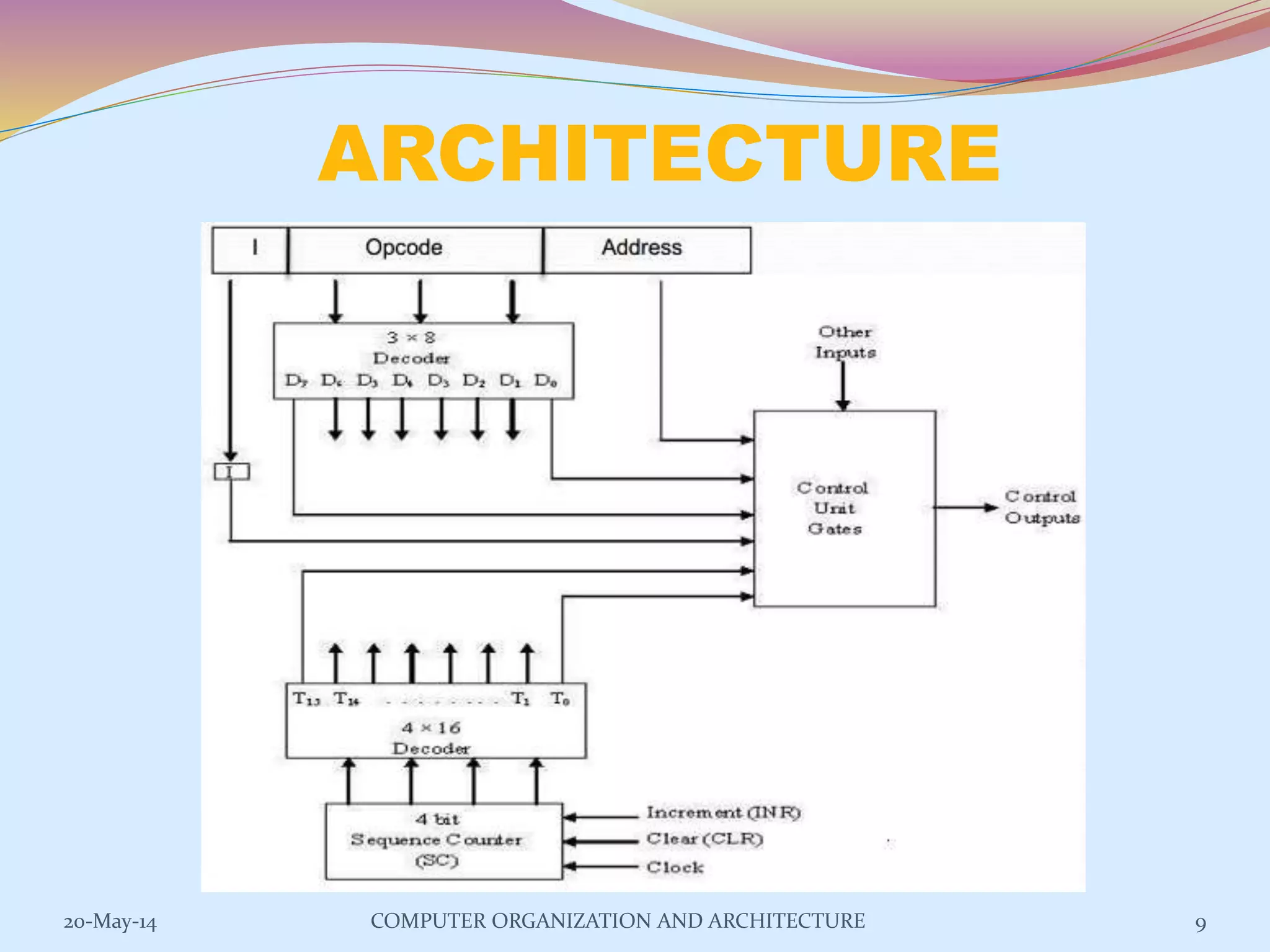
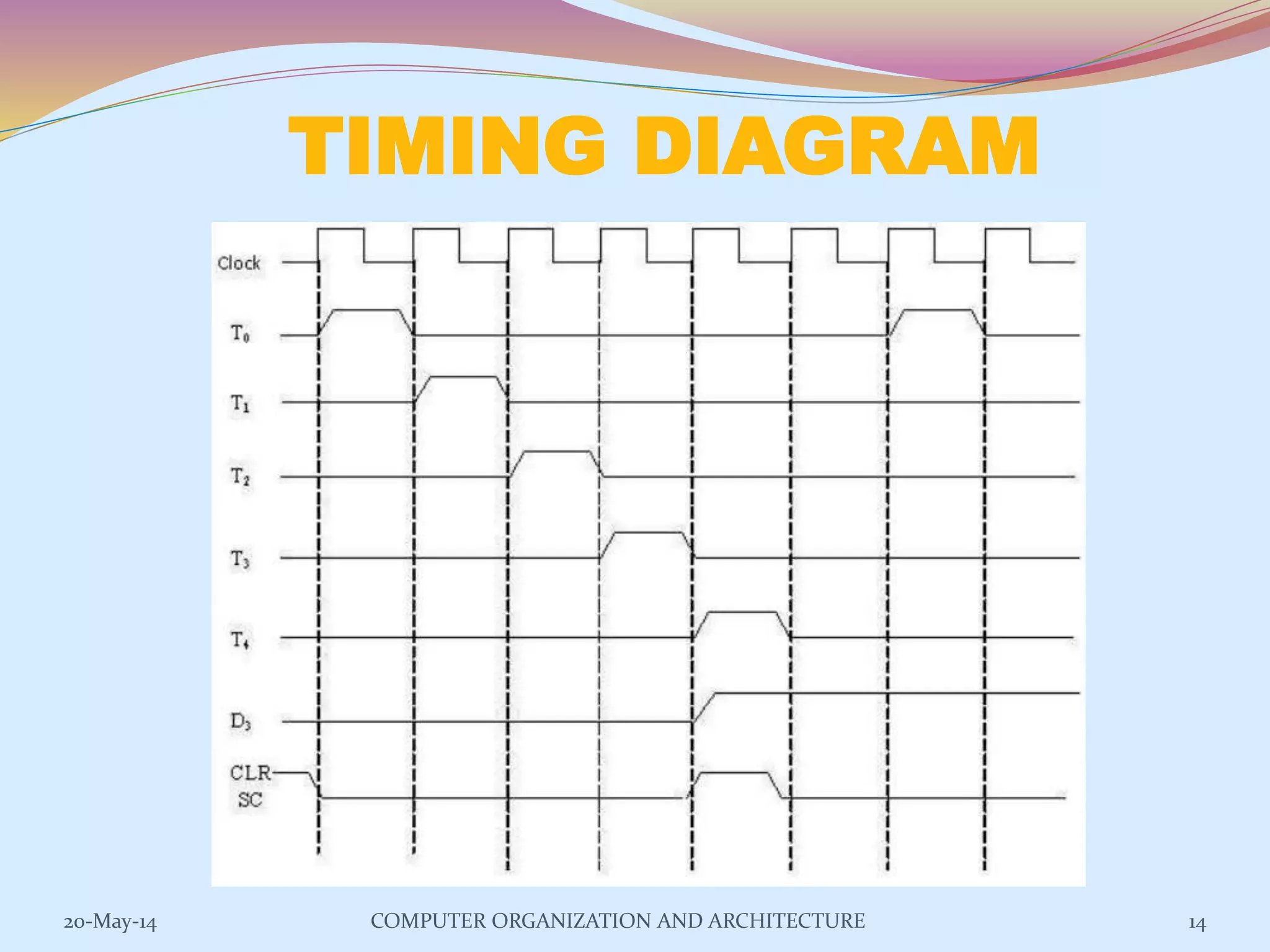
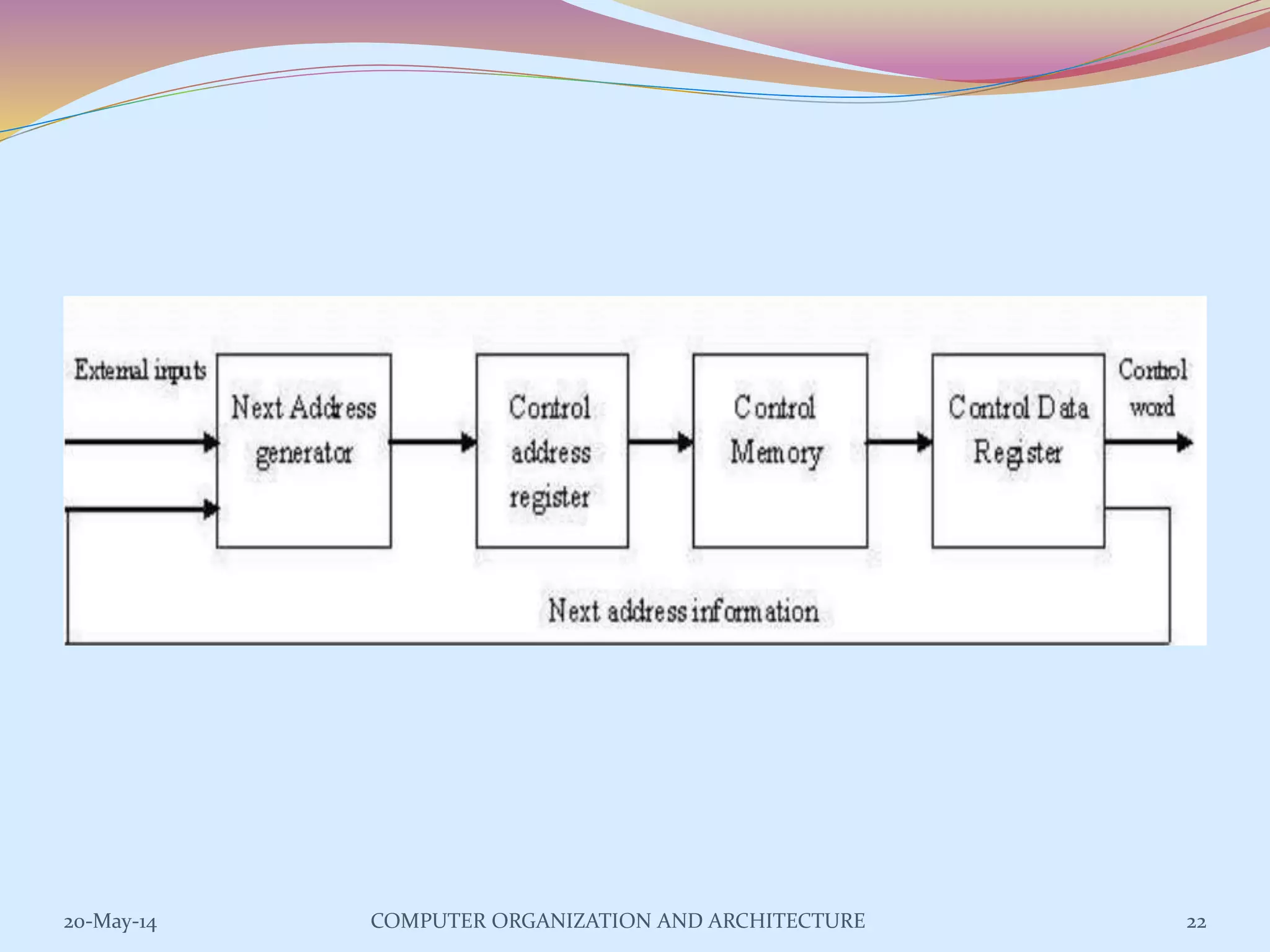
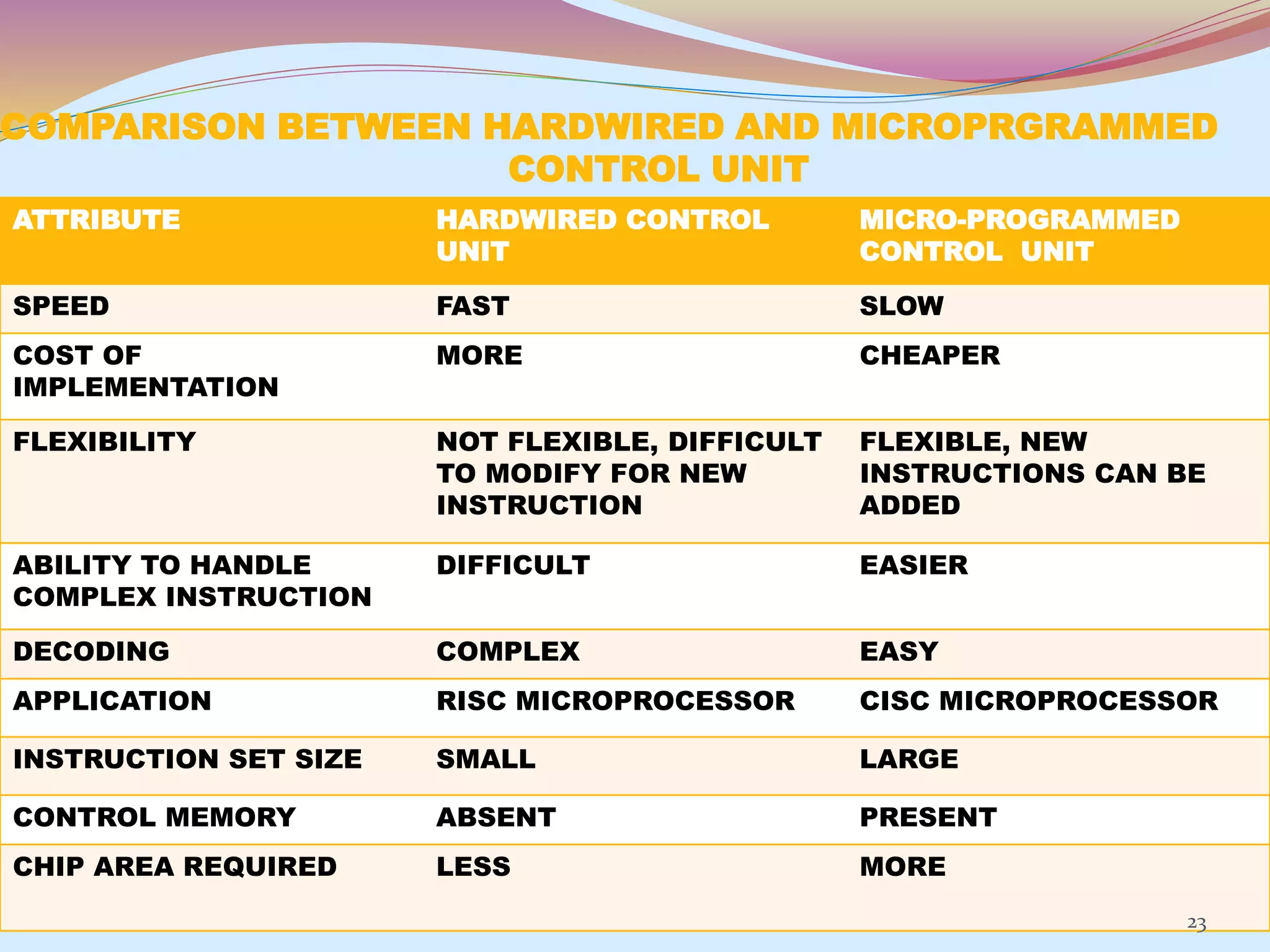
The control unit is responsible for controlling the flow of data and operations in a computer. It generates timing and control signals to coordinate the arithmetic logic unit, memory, and other components. Control units can be implemented using either hardwired or microprogrammed logic. A hardwired control unit uses combinational logic circuits like gates and flip-flops to directly generate control signals, while a microprogrammed control unit stores control sequences as microprograms in a control memory and executes them step-by-step using microinstructions. Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages related to speed, flexibility, cost, and complexity of implementation.