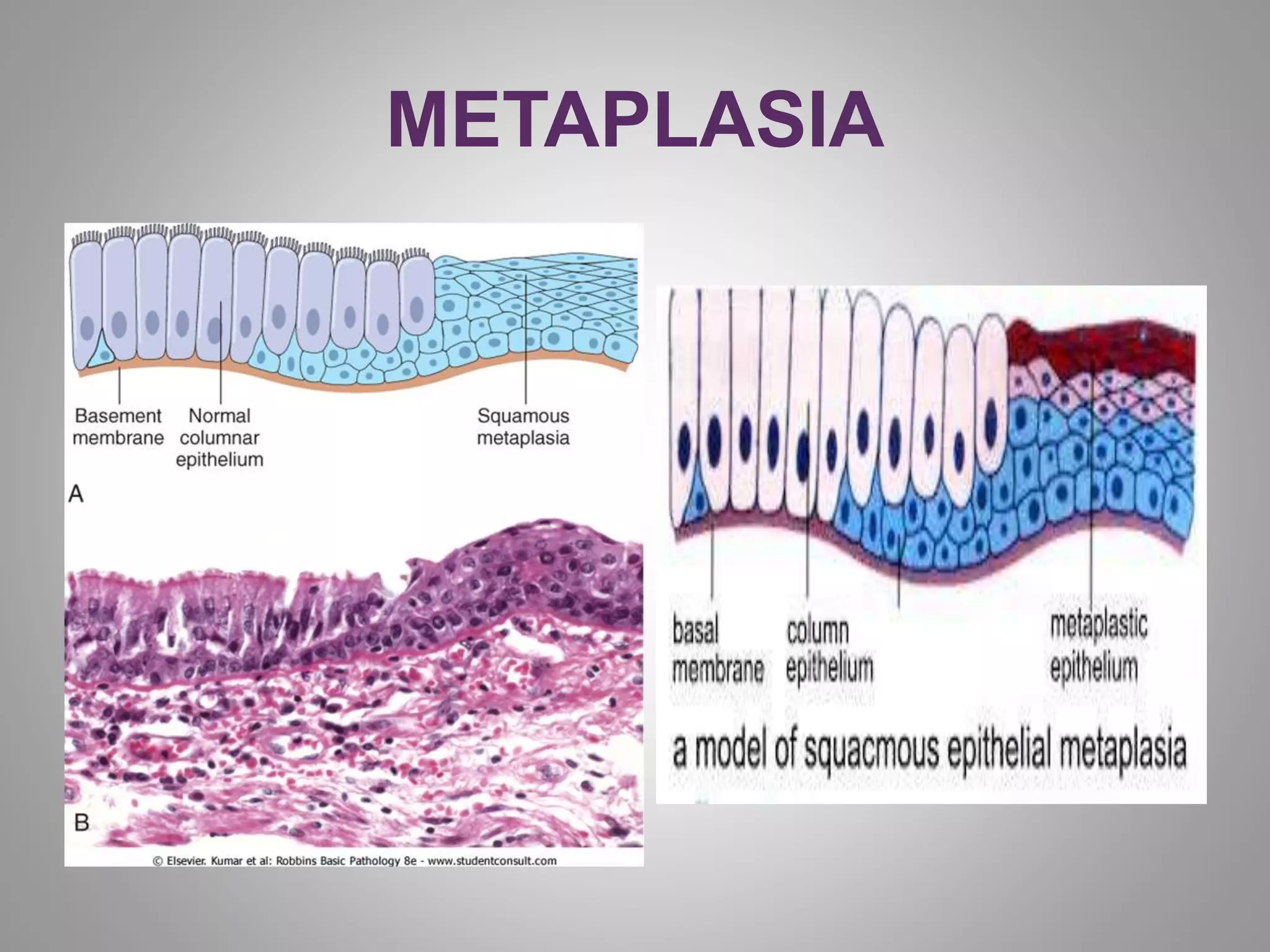
Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue. It can be physiologic, such as during pregnancy, or pathologic, such as with excessive hormone stimulation. Hypertrophy is an increase in cell size within an organ or tissue, often due to increased functional demands. Atrophy is a decrease in cell and organ size due to loss of cell substance from factors like disuse or inadequate nutrition. Metaplasia is a reversible change where one adult cell type replaces another, such as squamous replacing columnar epithelium from chronic irritation. These changes can sometimes progress to cancer if the predisposing stimuli persist long-term.








![HYPERTROPHY
• HYPERTROPHY:
• Definition: an increase in the number of organelles
(e.g. myofilaments) and size of cells and with such
changes an increase in the size of the organs.
• Hypertrophy can be physiologic or pathologic and is
caused by:
• 1 increased functional demand (e.g. hypertrophy of
striated muscle in muscle builders [physiologic] or
cardiac muscle cell in cardiac disease that induce
volume overload [pathologic]
• 2 specific hormonal stimulation (e.g. uterine
hypertrophy or breast enlargement during pregnancy)
• E.g. skeletal muscles of athletes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaplasia-141221070315-conversion-gate01/75/Metaplasia-9-2048.jpg)