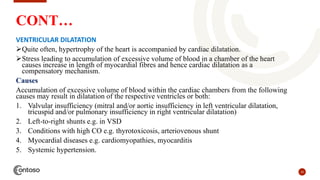
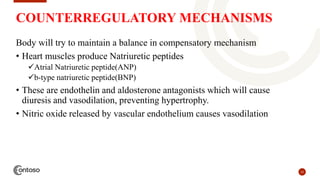
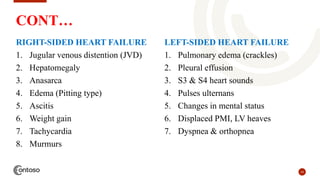
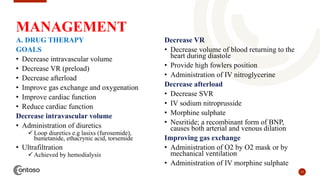
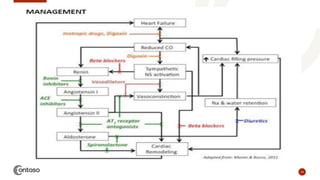
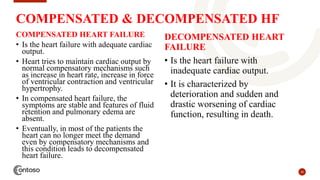
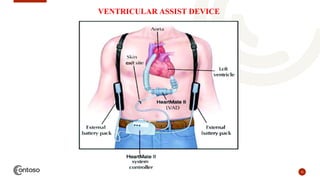
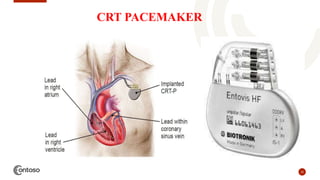
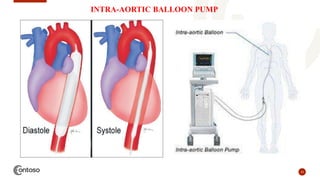
This document provides an outline on heart failure, covering definitions, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, diagnosis, and management. Heart failure is defined as a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. The most common causes are high blood pressure and structural heart issues. The pathophysiology involves compensatory mechanisms like activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Clinical manifestations include dyspnea, edema, fatigue, and liver enlargement. Management involves drug therapy like diuretics and ACE inhibitors, as well as lifestyle changes like sodium and fluid restriction.