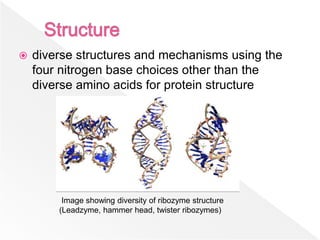
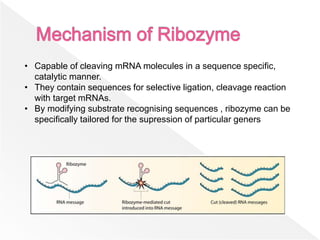
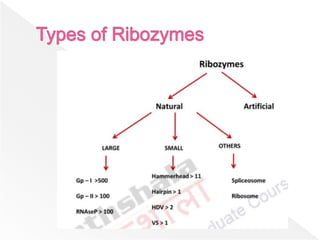
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that can catalyze biochemical reactions similar to protein enzymes. They were first discovered in the 1960s and 1970s through the work of Cech, Altman, and others. Ribozymes exist in all living organisms and play important roles in processing transfer and ribosomal RNA. They exhibit a diverse range of structures and catalytic mechanisms despite being composed only of the four nitrogen bases. Common types of ribozymes include hammerhead, hairpin, hepatitis delta virus, and RNase P ribozymes. Ribozymes have potential applications as tools to target specific mRNAs for research and therapeutic purposes.