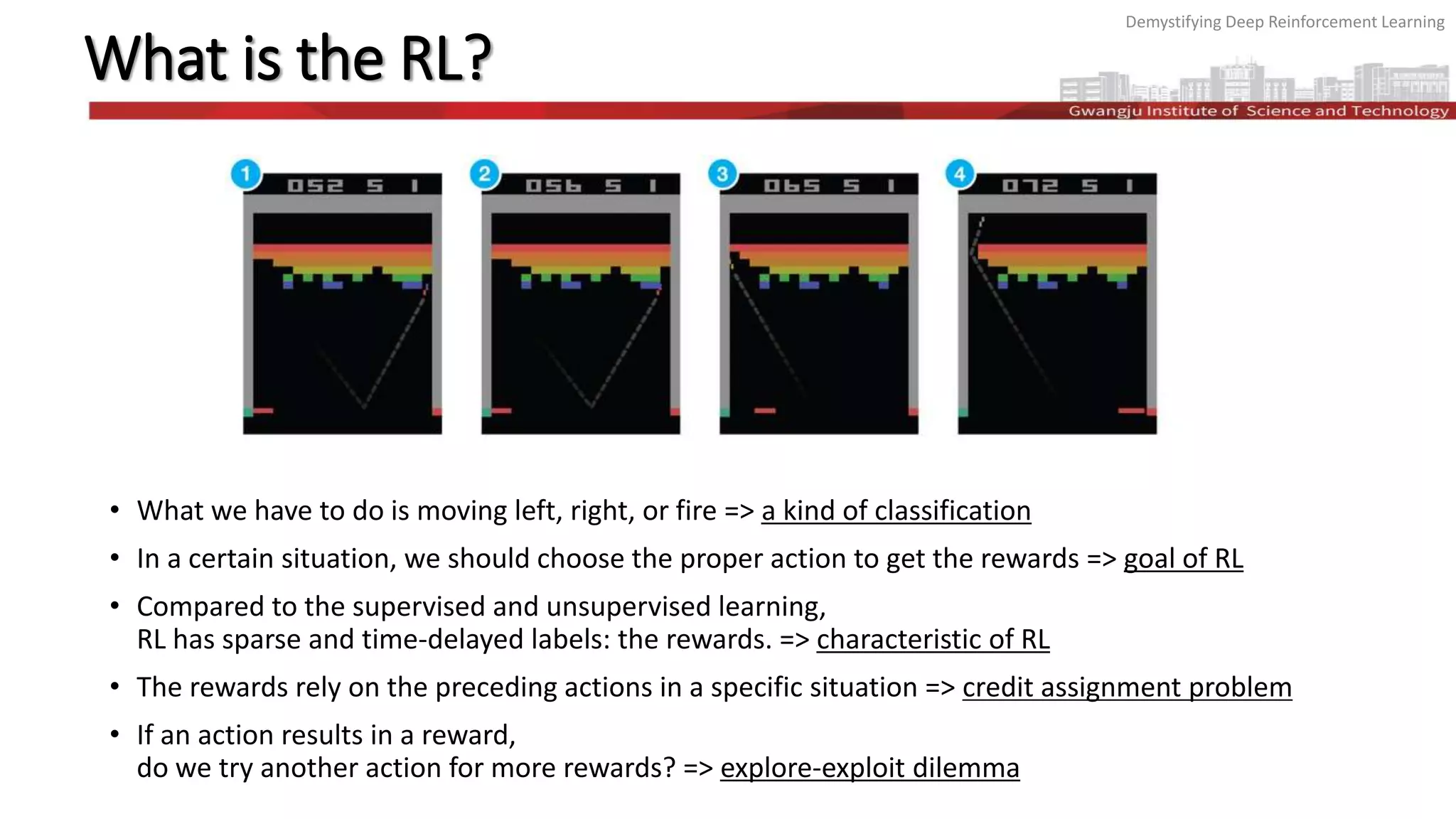
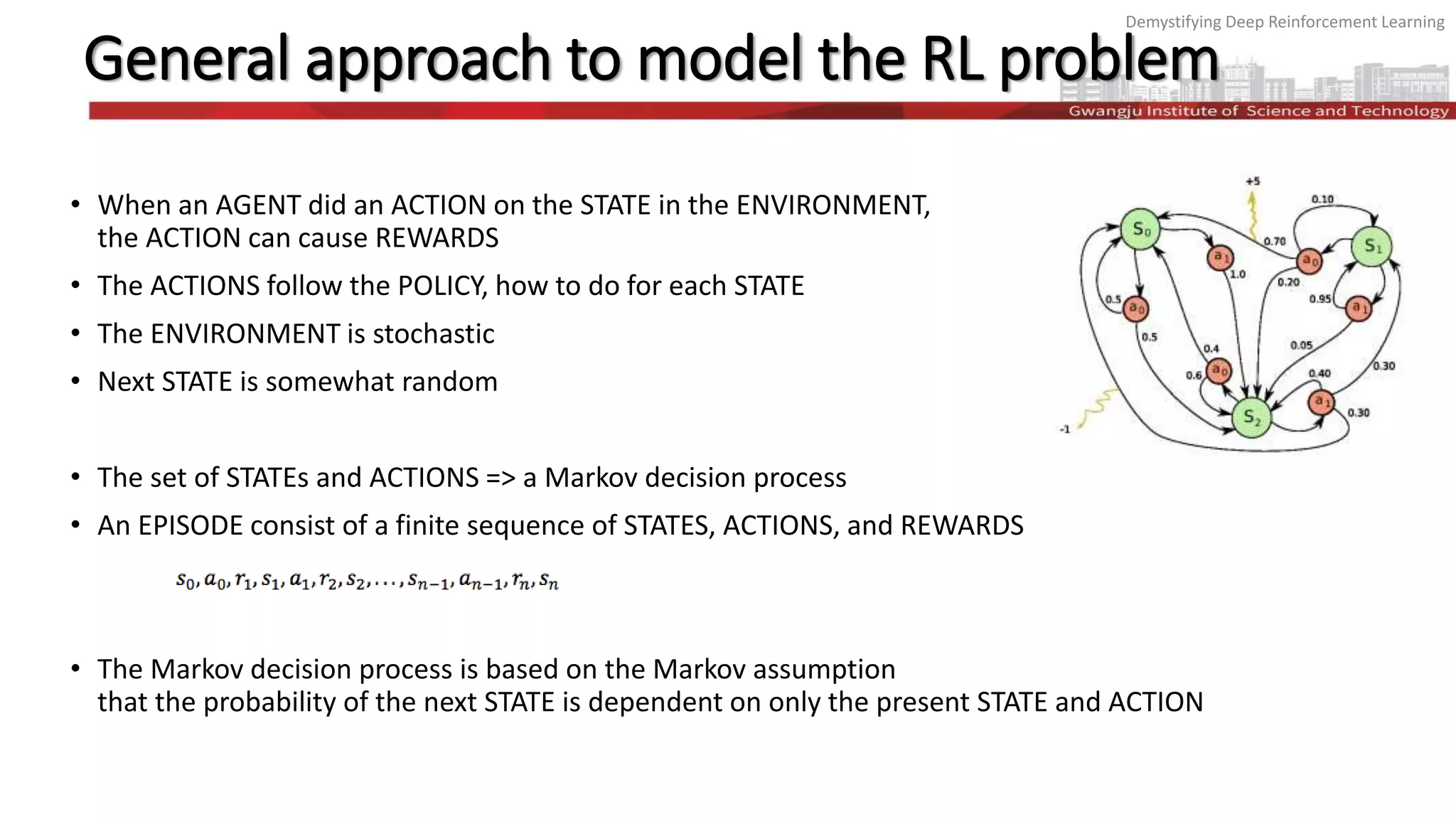
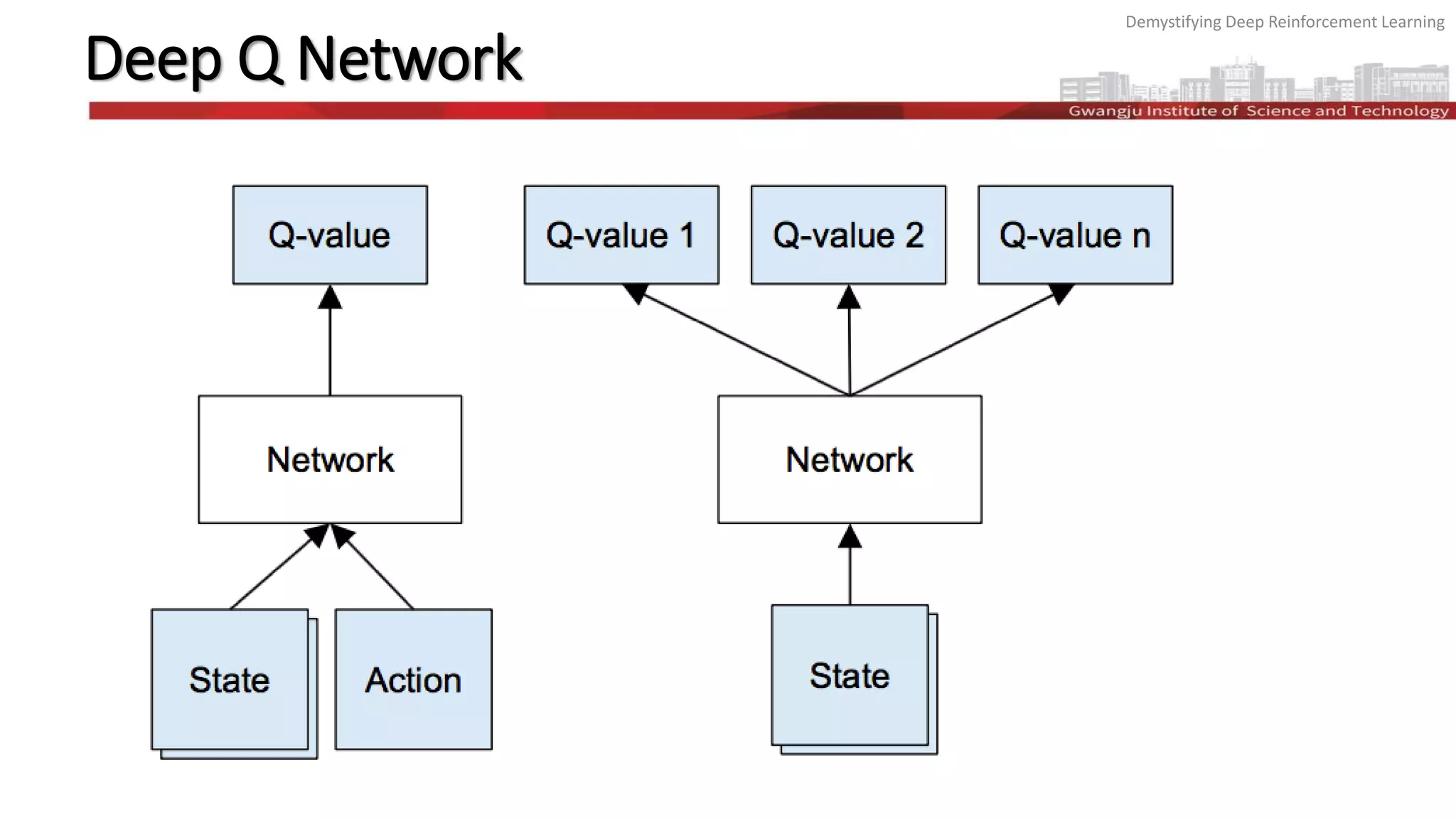
The document discusses the principles and methodologies of deep reinforcement learning (RL), emphasizing its goal to maximize future rewards through exploration-exploitation strategies. It covers key topics such as the Markov decision process, Q-functions, the Bellman equation, and techniques like deep Q networks and experience replay, illustrating their application through examples like Atari games and AlphaGo. The exploration-exploitation dilemma is highlighted, detailing the ε-greedy strategy for balancing exploration of new actions and exploitation of known rewarding actions.