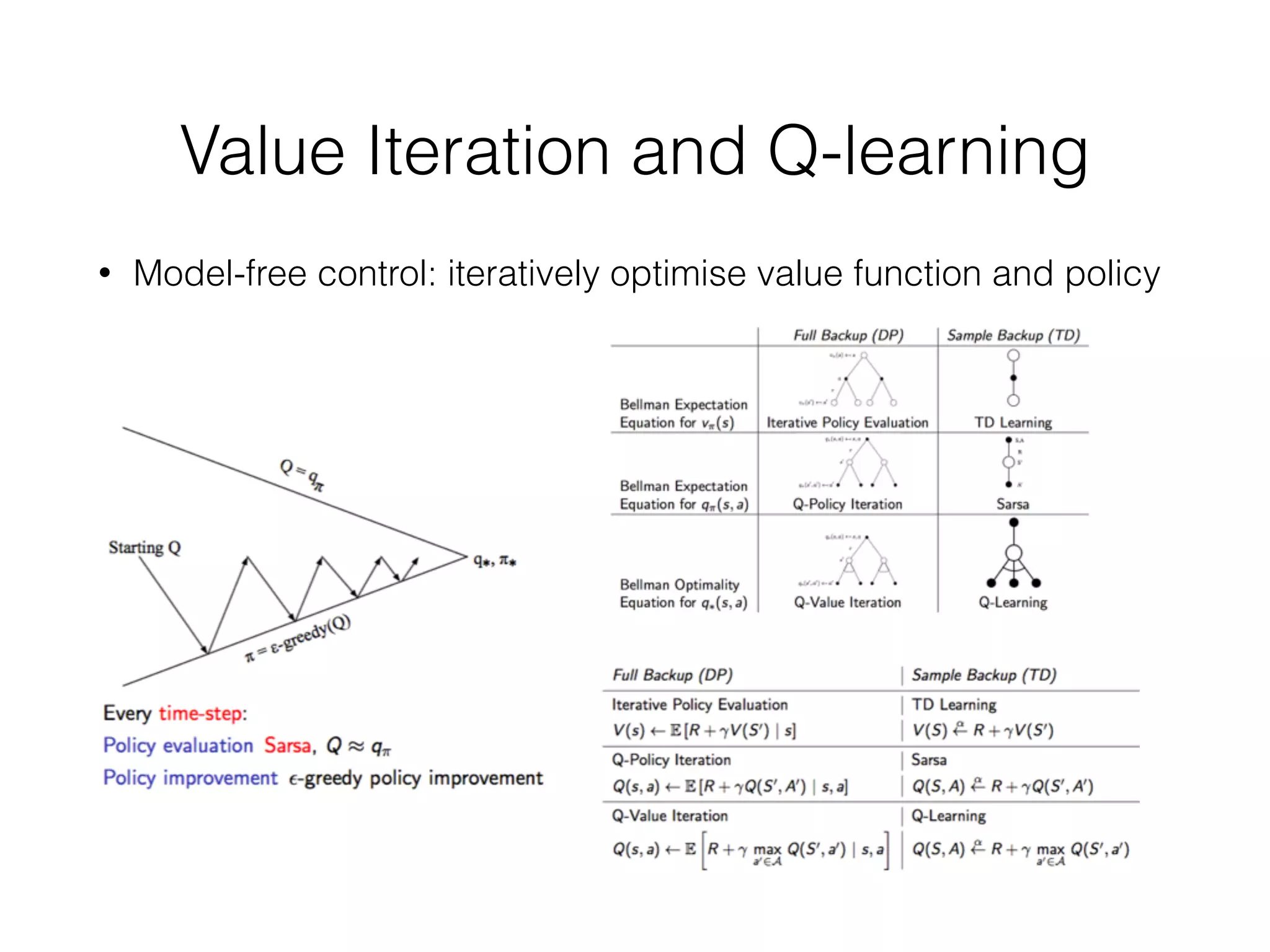
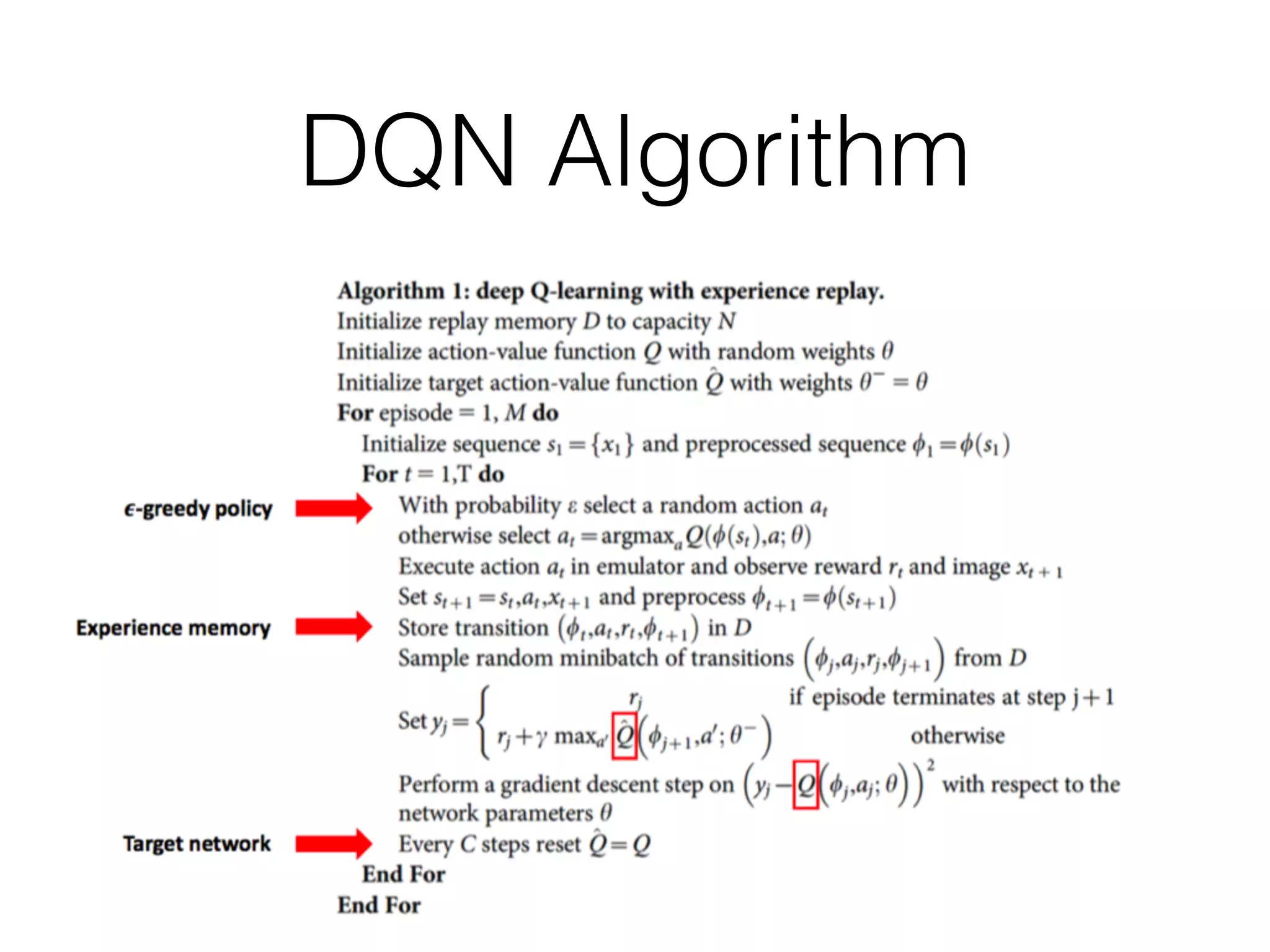
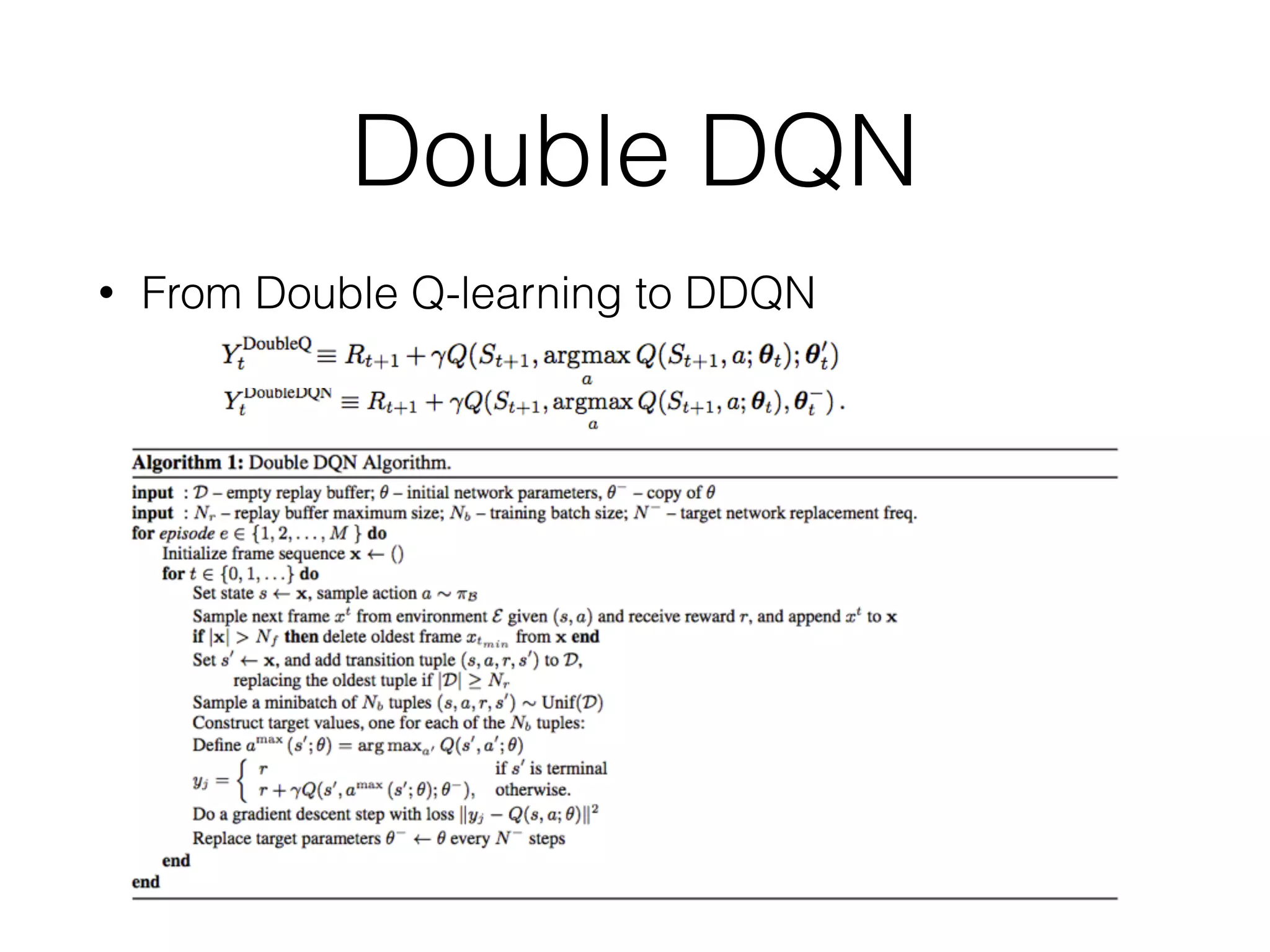
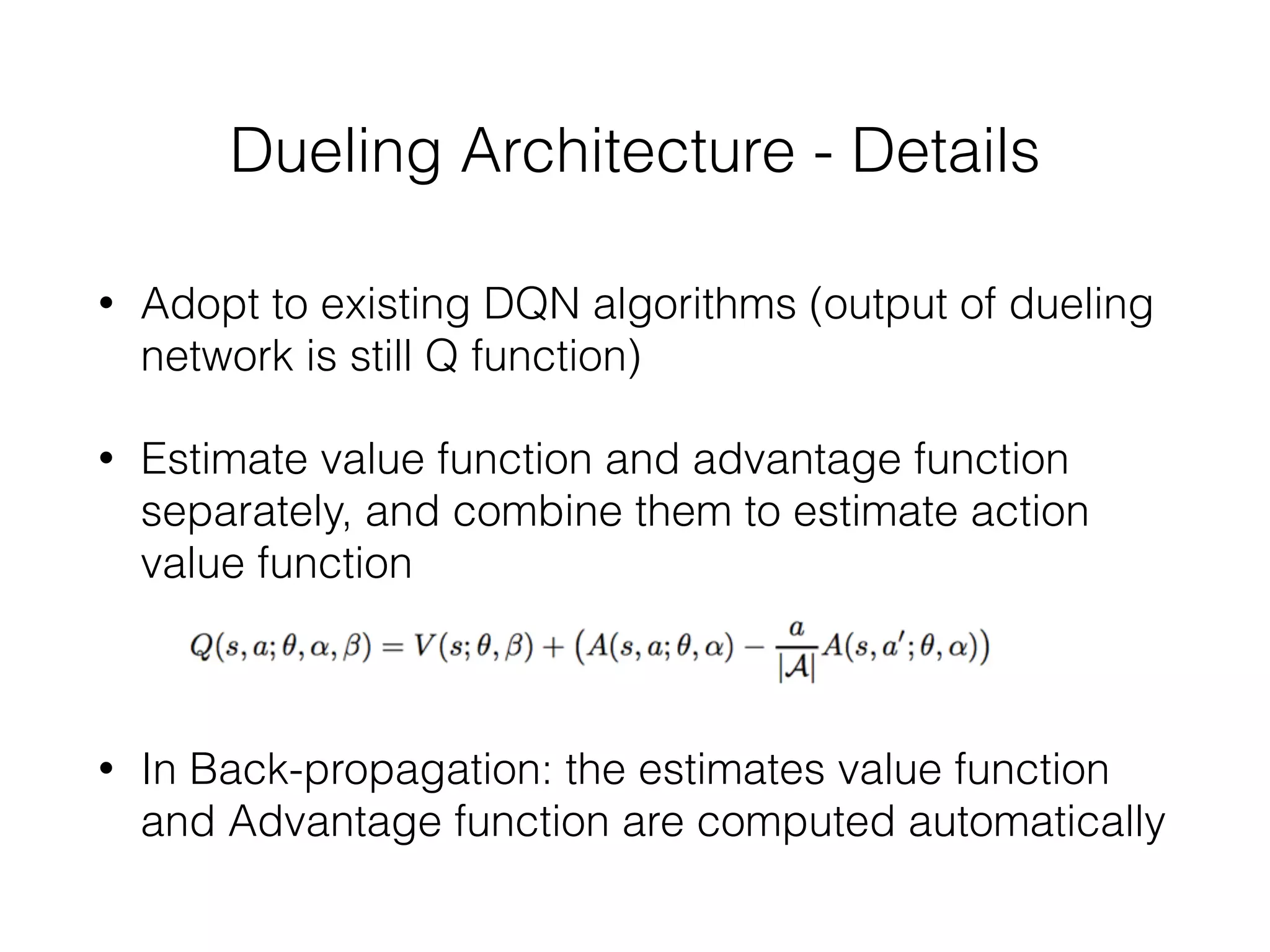
The document discusses Deep Q-Network (DQN), which combines Q-learning with deep neural networks to allow for function approximation and solving problems with large state/action spaces. DQN uses experience replay and a separate target network to stabilize training. It has led to many successful variants, including Double DQN which reduces overestimation, prioritized experience replay which replays important transitions more frequently, and dueling networks which separate value and advantage estimation.