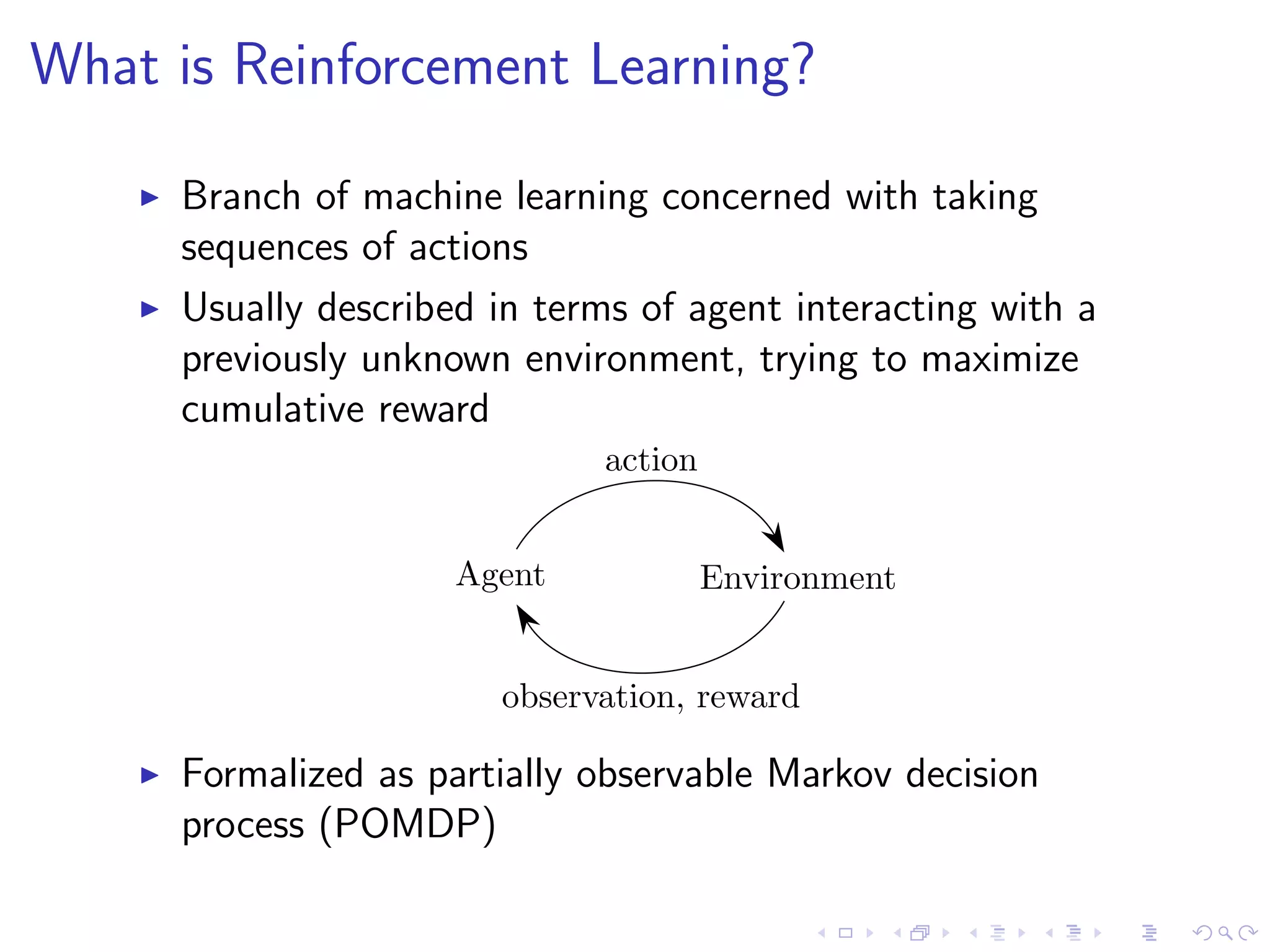
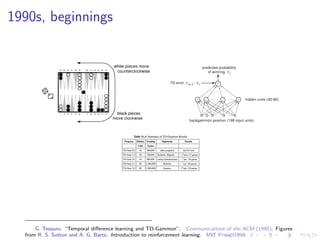
Reinforcement learning is a branch of machine learning concerned with agents taking actions in an environment to maximize rewards. It can be used for problems like robotics, inventory management, and machine translation. Deep reinforcement learning uses neural networks to approximate functions like policies, value functions, and dynamics models. Unlike supervised learning, reinforcement learning agents interact with a stateful environment and do not receive full examples, but must learn through interaction and trial and error. Recent successes include using deep RL for Atari games, robotics tasks, and Go with techniques like Q-learning, policy gradients, and Monte Carlo tree search.