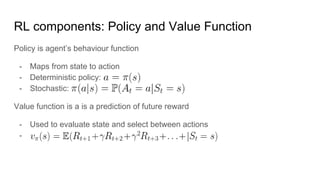
The document discusses deep Q-learning as a reinforcement learning approach, highlighting key concepts such as the reward hypothesis, the exploration-exploitation dilemma, and Markov decision processes (MDPs). It covers the transitions from model-free Q-learning to deep Q-learning (DQN) and the challenges faced in applying neural networks to reinforcement learning, along with proposed solutions like experience replay and policy stabilization techniques. Additionally, it references historical milestones in reinforcement learning, including achievements in games like chess and Go.




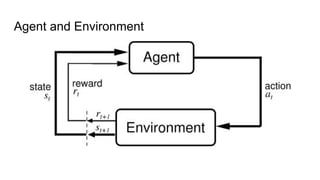


![Maze example: r = -1 per time-step and policy
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-9-320.jpg)
![Maze example: Value function and Model
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-10-320.jpg)




![Bellman Opt Equation for state-value function
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-15-320.jpg)
![Bellman Opt Equation for action-value function
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-16-320.jpg)
![Bellman Opt Equation for state-value function
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-17-320.jpg)
![Bellman Opt Equation for action-value function
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-18-320.jpg)


![Q-Learning
[David Silver. Advanced Topics: RL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-21-320.jpg)
![DQN - Q-Learning with function approximation
[Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-22-320.jpg)
![[Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rl-presentation-160522151115/85/Deep-Q-Learning-23-320.jpg)



