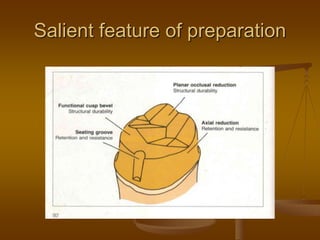
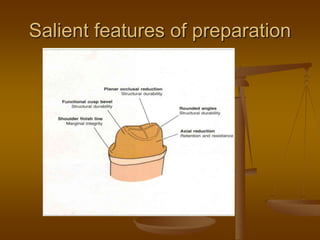
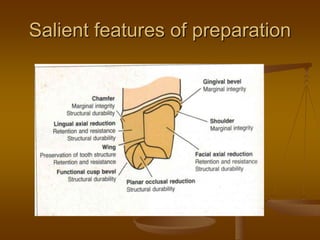
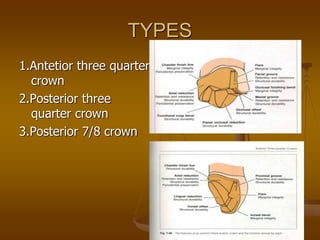
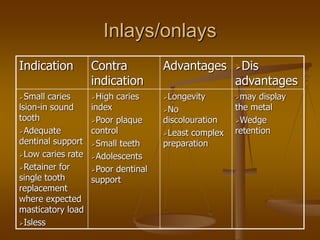
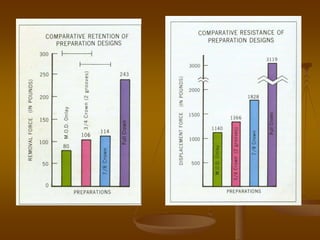
This document discusses different types of dental retainers used in fixed prosthodontics (FPD). It classifies retainers as either extracoronal or intracoronal, and describes various extracoronal retainers including full veneer crowns made of full metal, full ceramic, or metal-ceramic; partial veneer crowns; and resin-bonded retainers. Requirements, indications, contraindications, advantages and disadvantages are provided for each type. Intracoronal retainers discussed include inlays and onlays. Radicular retainers are also summarized, which involve a post and core to retain a crown on an endodontically treated tooth.