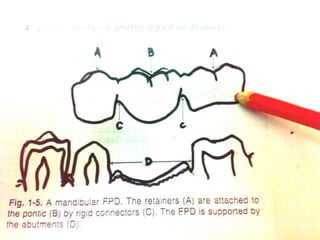
This document discusses different types of retainers used for fixed prosthodontics. It describes full veneer crowns and partial veneer crowns, which differ based on the amount of tooth coverage. Conservative retainers require minimal preparation while considerations for selection include factors like age, oral hygiene and tooth condition. Material options addressed are all metal, metal-ceramic and all-ceramic retainers. The advantages and disadvantages of each type are outlined to aid in appropriate selection based on a patient's needs and dental situation.