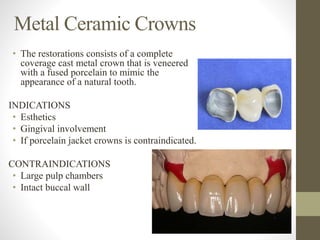
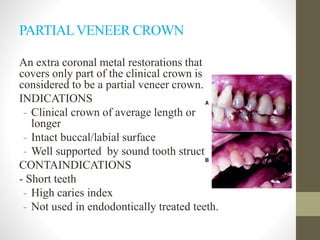
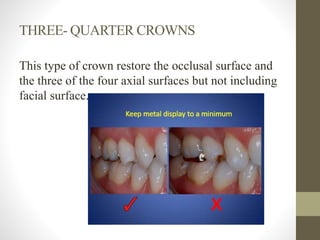
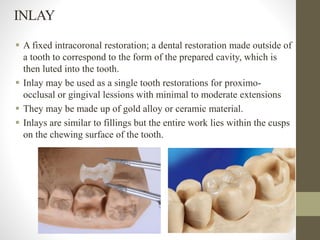
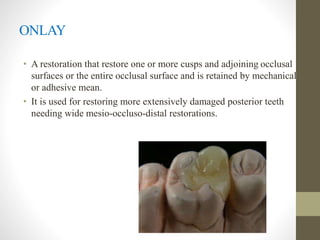
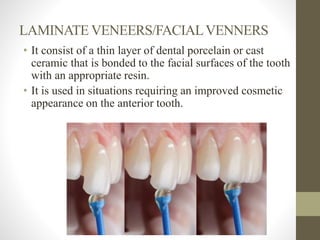
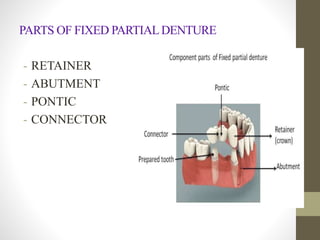
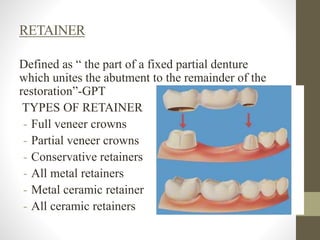
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fixed partial dentures (FPD), including definitions, indications, contraindications, and various components such as crowns, retainers, and pontics. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different types of crowns, including full veneer and partial veneer crowns, as well as restorations like inlays and onlays. Additionally, it outlines the key functions of FPD and offers references for further reading.