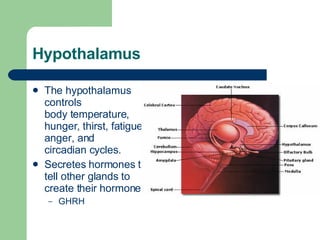
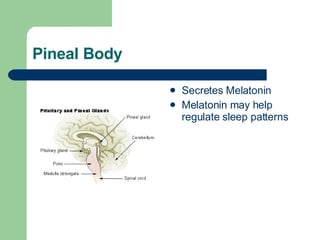
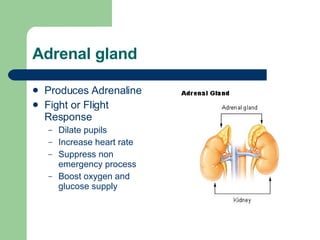
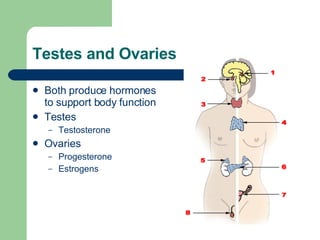
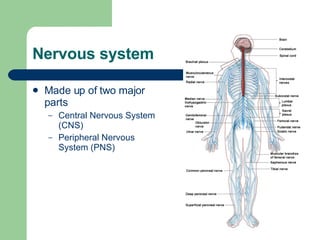
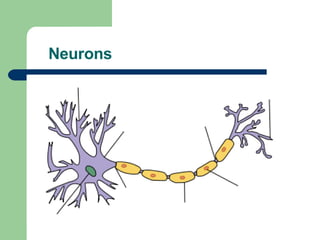
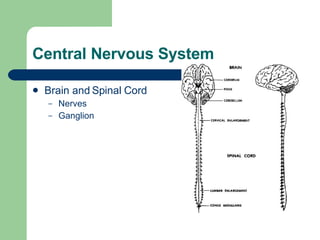
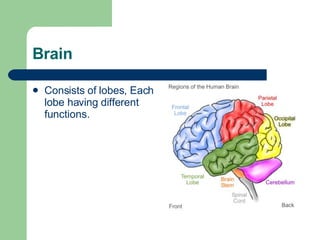
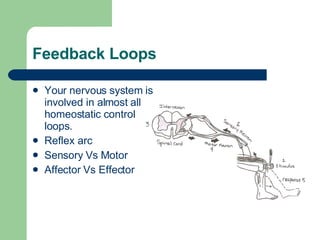
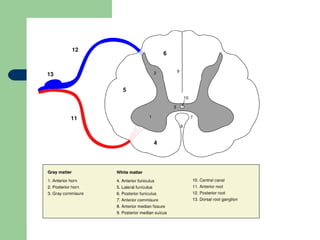
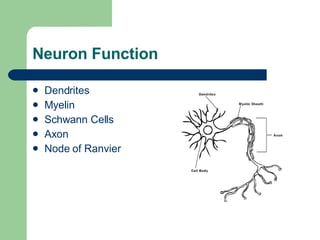
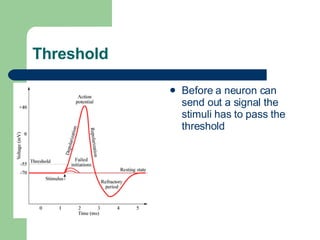
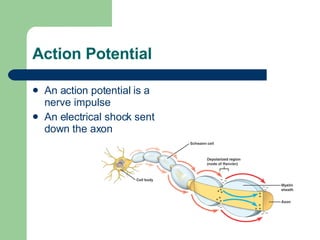
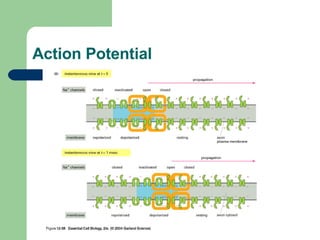
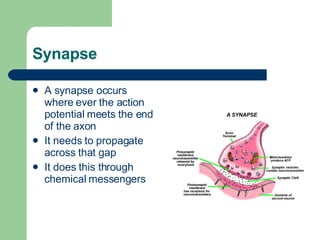
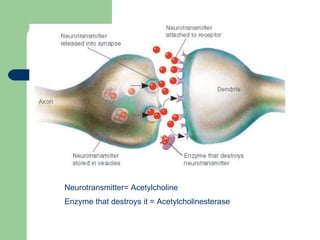
The endocrine and nervous systems work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. The endocrine system regulates processes like growth, metabolism, and mood through hormone secretion from glands like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, and adrenal glands. The nervous system is made up of the central and peripheral nervous systems and uses neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters like acetylcholine to transmit signals and coordinate responses to changes both internally and externally. Together these systems allow the body to detect changes, process information, and enact responses to maintain a stable internal state.