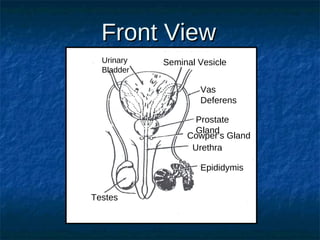
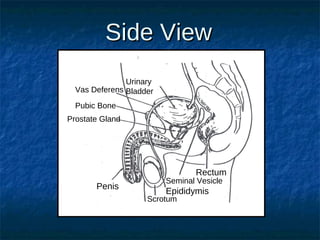
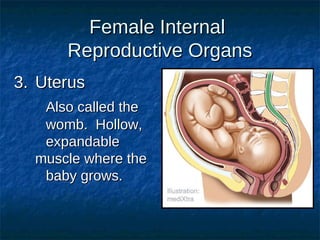
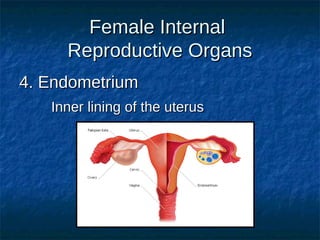
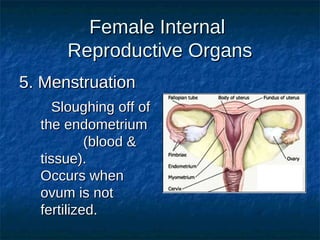
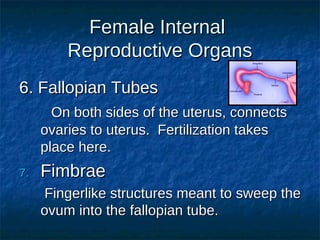
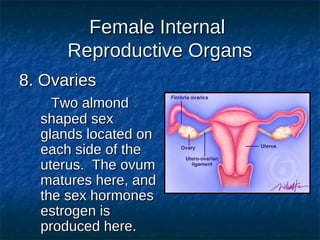
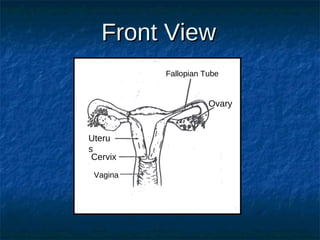
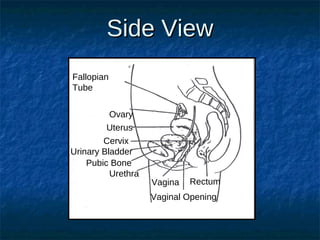
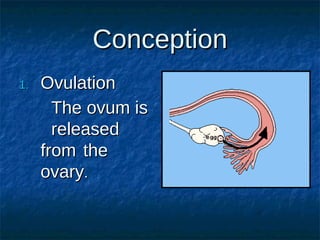
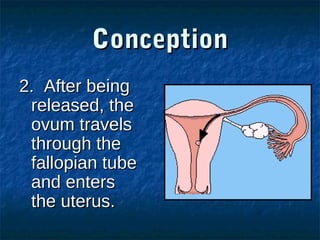
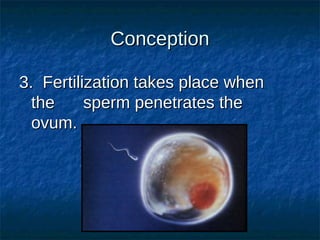
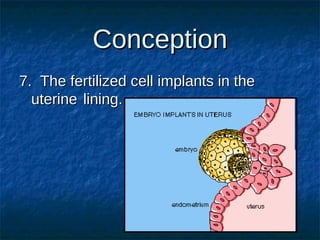
The male reproductive system contains both external and internal organs. The external organs include the penis and scrotum. The internal organs include the testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper's gland. Sperm and hormones are produced and stored in the testicles and related structures. The female reproductive system also contains external and internal organs. The external organs include the labia and vulva. The internal organs include the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The uterus is where a fetus develops during pregnancy. During ovulation, an egg is released from the ovaries and travels through the fallopian tubes where it may be fertilized by sperm