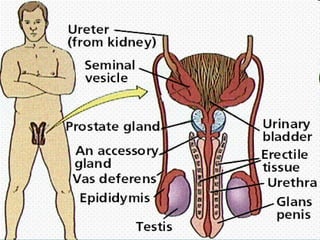
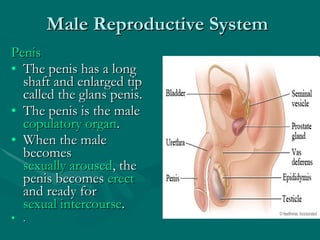
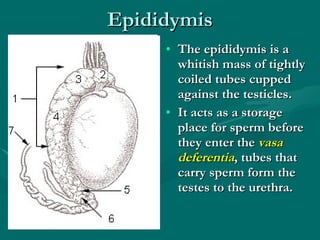
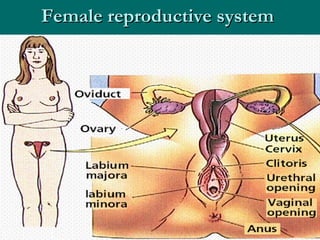
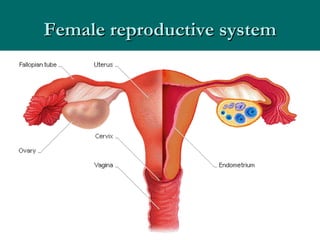
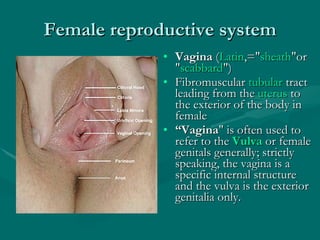
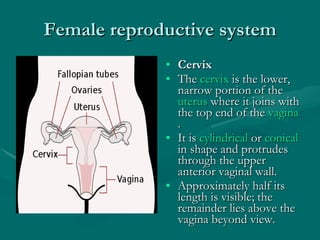
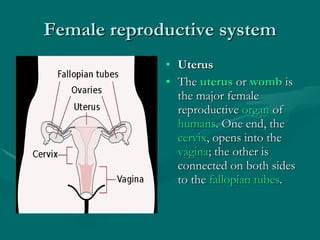
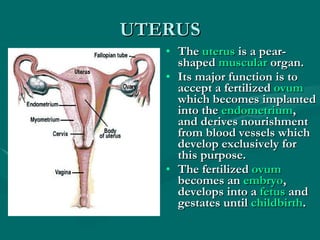
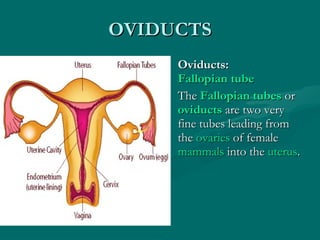
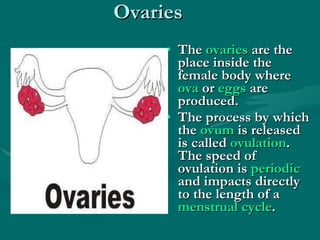
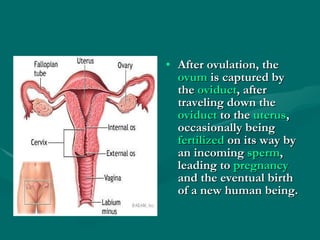
The document summarizes the key differences between the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the main organs in each system, including the penis, testicles, and epididymis in males, and the vagina, cervix, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes in females. It also outlines some of the main secondary sex characteristics that develop during puberty in males and females.













![Male Secondary Sex Characters Increased secretions of oil and sweat glands, often causing acne and body odor [3] Coarsening or rigidity of skin texture, due to less subcutaneous fat A prominent Adam's apple Fat deposits mainly around the abdomen and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanreproductivesystem-100424232629-phpapp02/85/Human-reproductive-system-27-320.jpg)
![Male Secondary Sex Characters Higher waist to hip ratio than prepubescent or adult females or prepubescent males, on average On average, larger hands and feet than prepubescent or adult females or prepubescent males[ citation needed ] Lower digit ratio , on average](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanreproductivesystem-100424232629-phpapp02/85/Human-reproductive-system-28-320.jpg)

![Female Secondary Sex Characters Decreased stature; adult females shorter stature than adult males, on average Widening of hips [5] ; lower waist to hip ratio than adult males, on average Upper arms approximately 1" longer, on average, for a given height [6] Changed distribution in weight and fat; more subcutaneous fat and fat deposits mainly around the buttocks , thighs and hips Higher digit ratio , on average](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanreproductivesystem-100424232629-phpapp02/85/Human-reproductive-system-30-320.jpg)
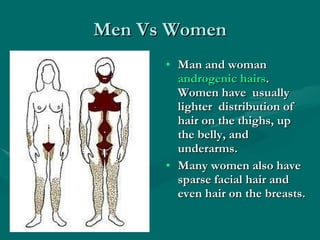
![Men Vs Women On average, men are taller than women [1] ( See sexual dimorphism ). On average, men have a larger waist in comparison to their hips (see waist-hip ratio ) than women. On average, men have longer canine teeth than women. On average, men have a greater capacity for cardiovascular endurance. This is due to the enlargement of the lungs of boys during puberty, characterized by a more prominent chest .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanreproductivesystem-100424232629-phpapp02/85/Human-reproductive-system-32-320.jpg)


![Men Vs Women Women have a larger hip section than men, probably an adaptation for giving birth to infants with large skulls. Men have a more pronounced 'Adam's Apple' or thyroid cartilage due to larger vocal cords (and deeper voices). [4] Studies examining the leg/trunk ratio between men and women have had conflicting results. In adolescents, there may be no significant gender difference](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humanreproductivesystem-100424232629-phpapp02/85/Human-reproductive-system-35-320.jpg)


