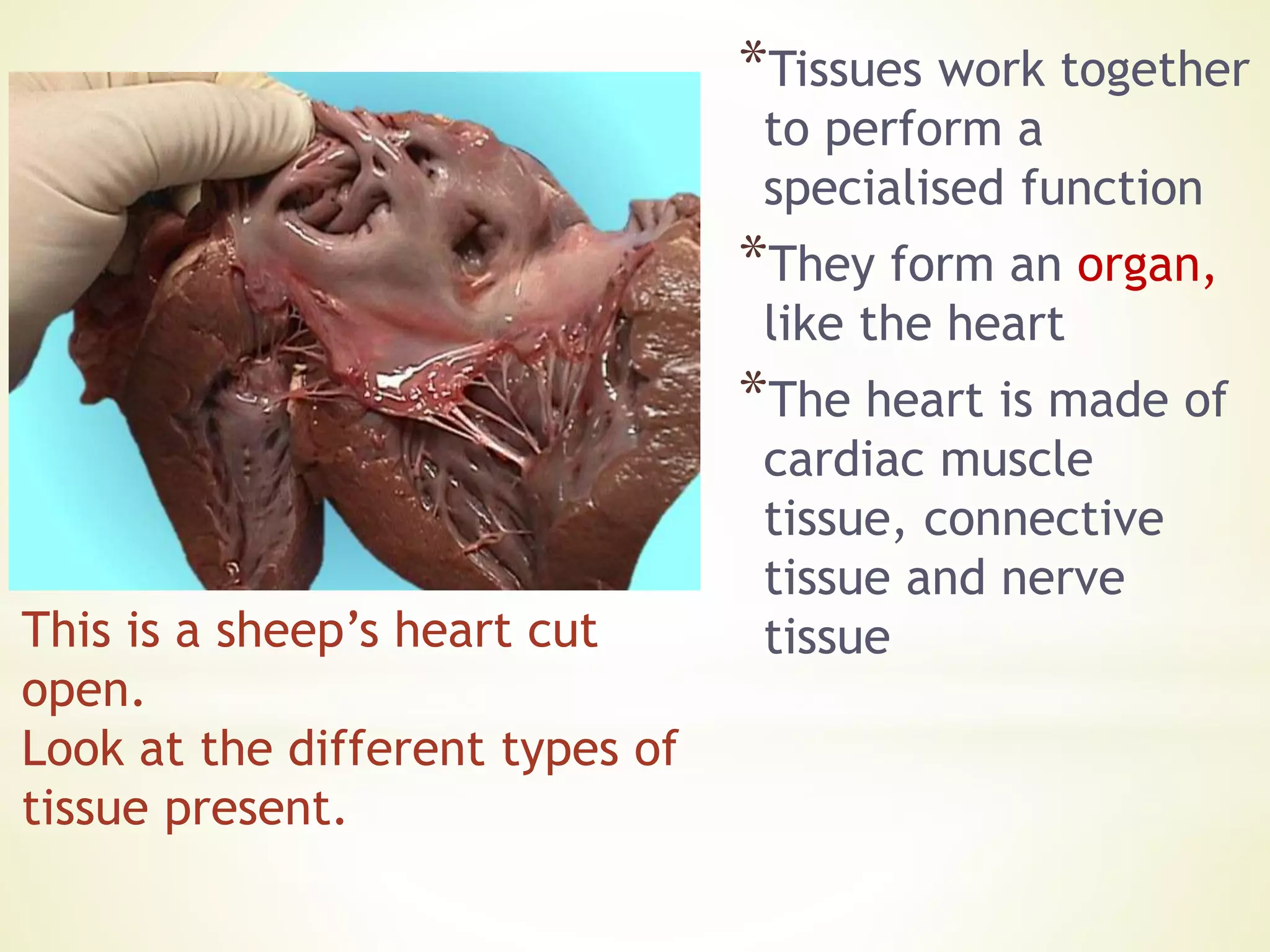
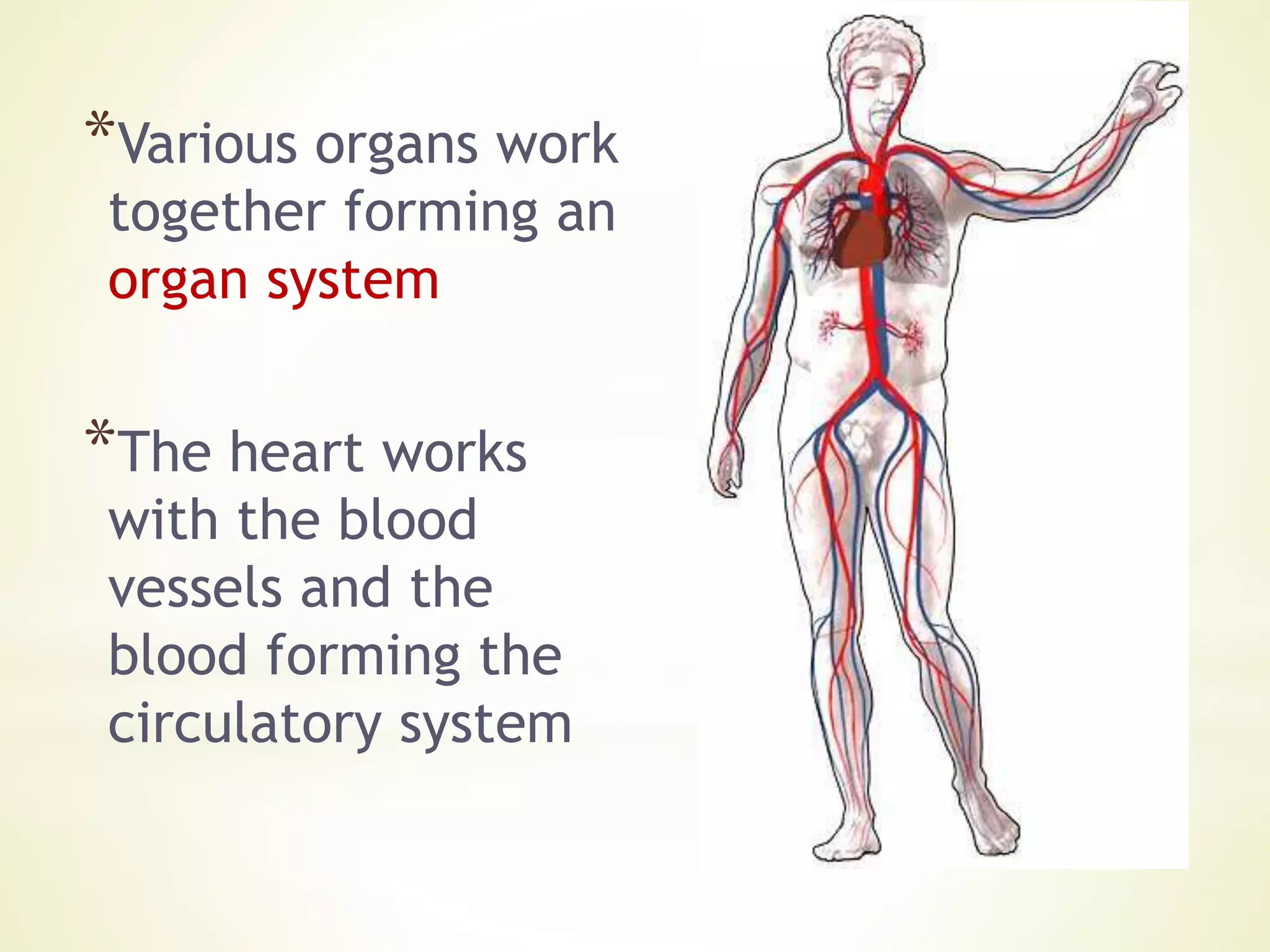
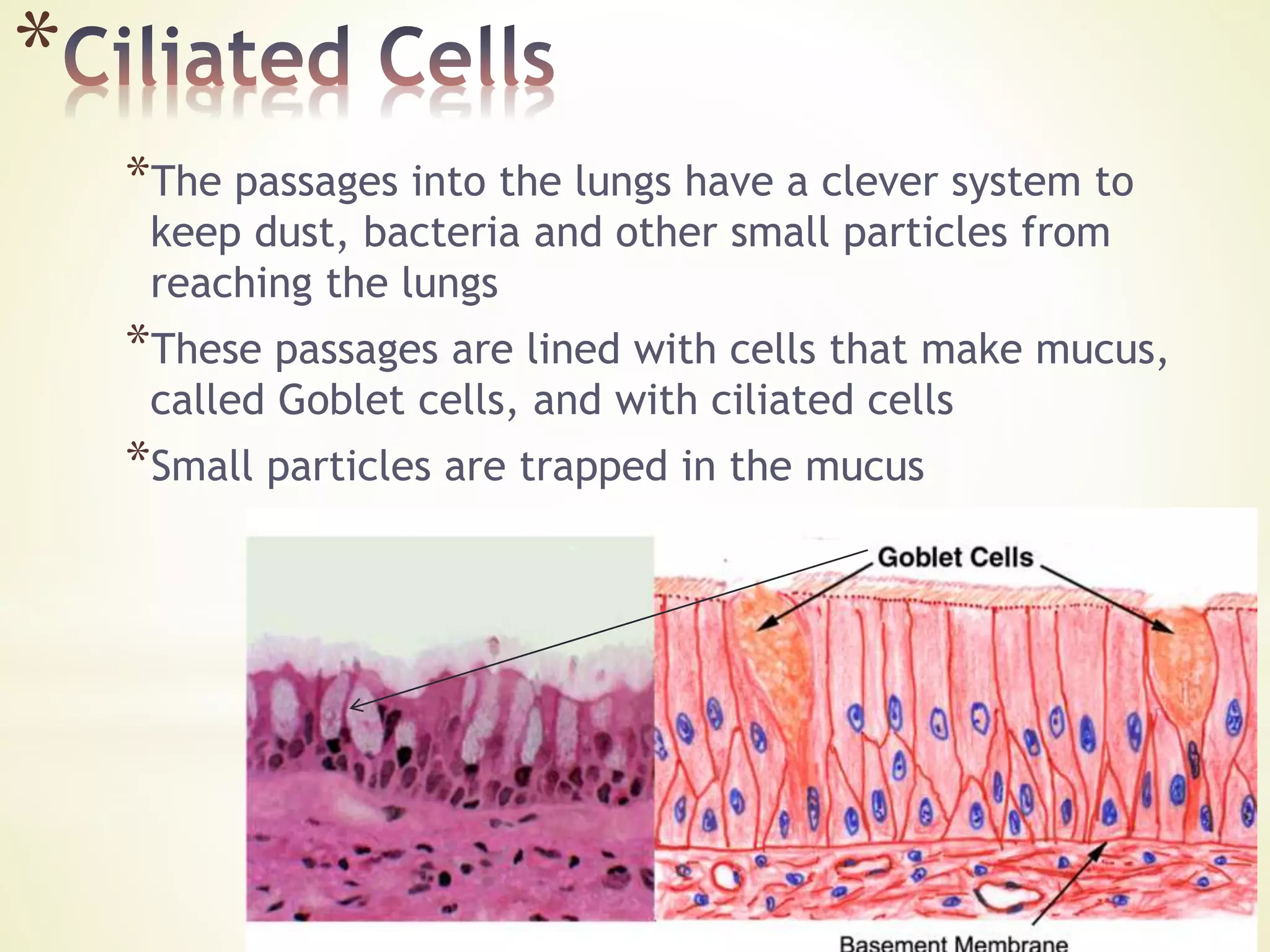
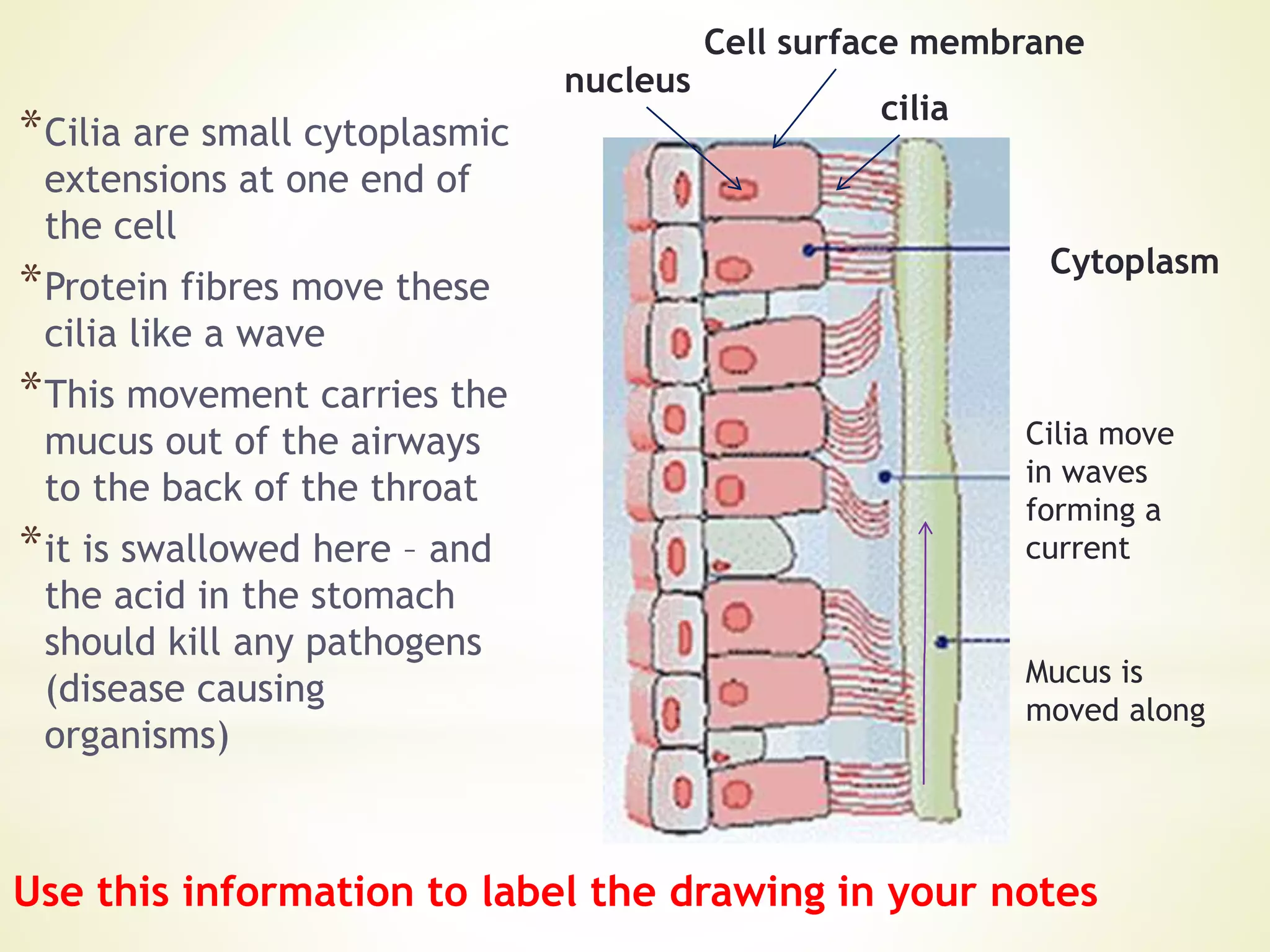
- Cells specialize to perform certain functions and tissues are formed when similar cells work together. Tissues combine to form organs which work together in organ systems.
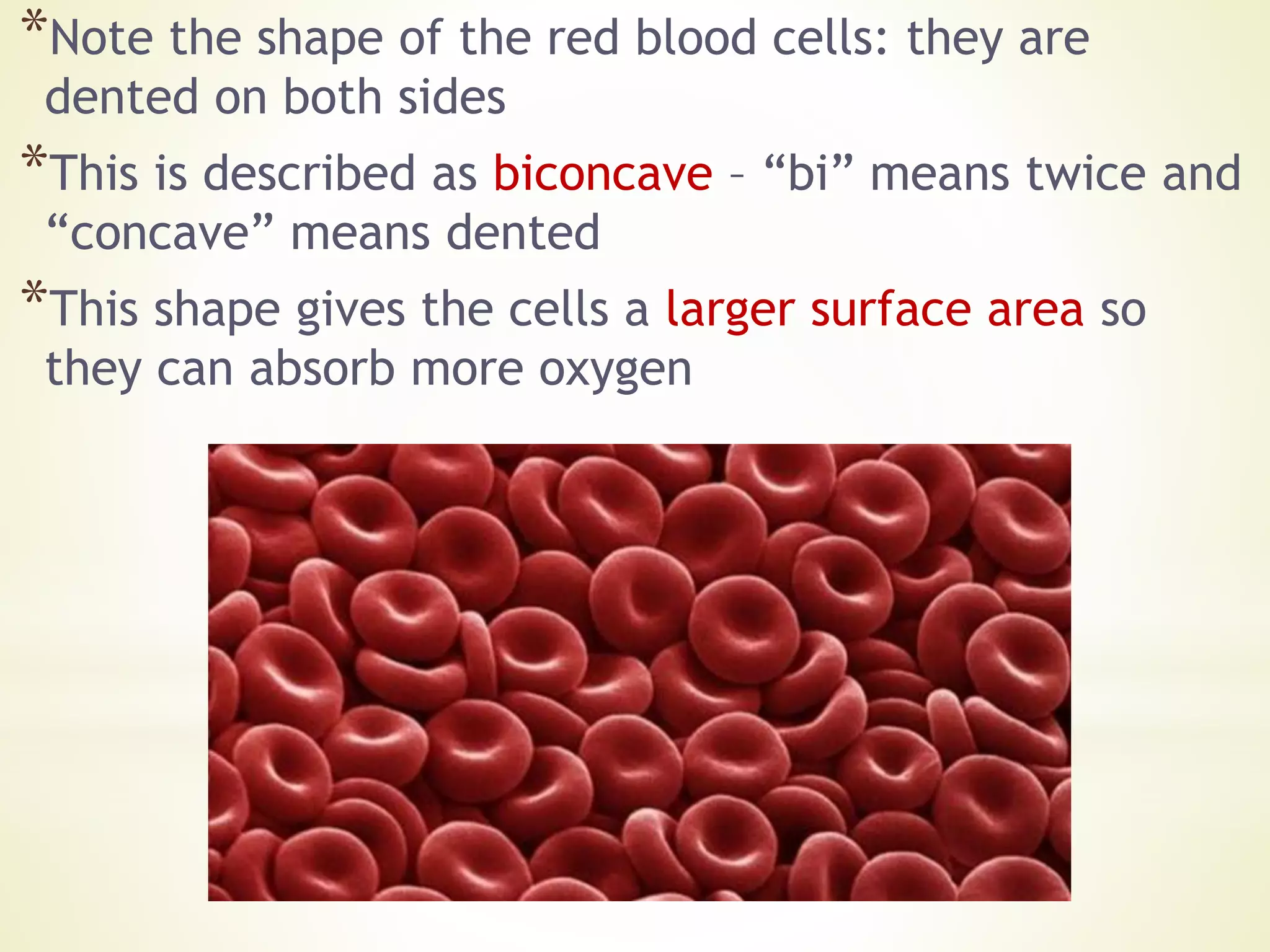
- The document discusses examples of specialized cells including ciliated epithelial cells, muscle cells, red blood cells, root hair cells, and xylem vessels. It provides details on the structure and function of these cell types.
- The levels of organization in multicellular organisms are discussed from cells to tissues to organs to organ systems.