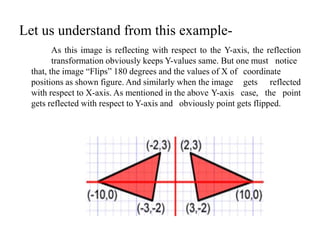
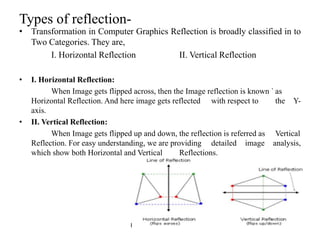
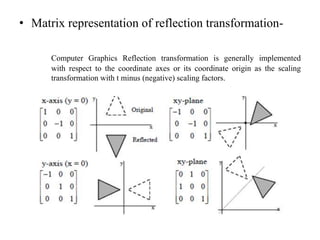
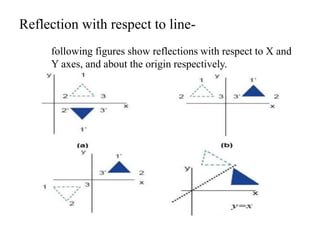
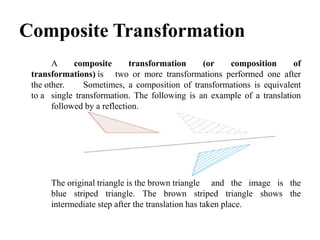
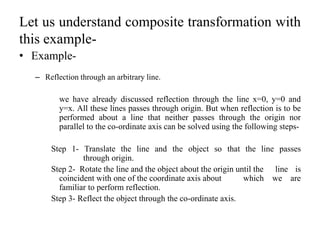
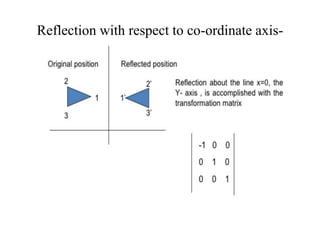
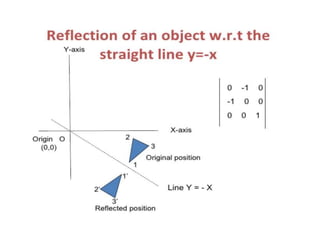
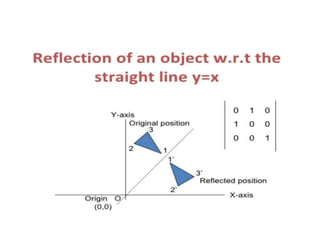
This document discusses reflection and composite transformations in computer graphics. Reflection is defined as a 180 degree rotation that produces a mirror image. There are two types of reflection: horizontal reflection across the y-axis and vertical reflection across the x-axis. A composite transformation performs two or more transformations sequentially, such as a translation followed by a reflection. Solving a composite transformation involves translating an object to rotate it around another point, applying the rotation, and translating back.


![Step 4- Apply the inverse rotation about the origin to shift the line
at translated position.
Step 5- Apply inverse translation to send back the object
(i.e., line) to its original position matrix rotation.
T = [TR ] * [Ro ] * [Rref] * [Ro
-1 ] * [Tr-1]
Where
TR - Translation matrix
Ro - Matrix for rotation by angle O
Rref – Reflection about any axis
R0
-1 - Inverse rotation
Tr
-1 - Inverse Translation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectiontransformation-180520071422/85/Reflection-transformation-9-320.jpg)

![• In matrix form, it can be shown as
[T] = [TR][RO][TR]-1
Where T
R = Translation matrix
R
O = Rotation matrix by an
angle 0
T
R
-1 = Inverse Translation
matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectiontransformation-180520071422/85/Reflection-transformation-14-320.jpg)