Embed presentation
Downloaded 31 times





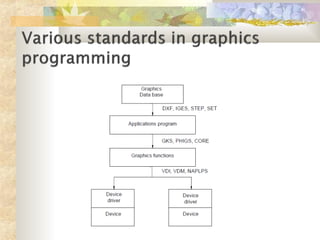

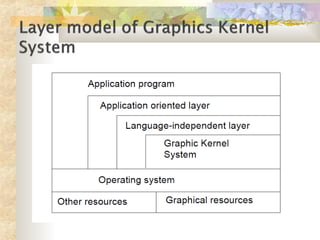



Graphics software acts as an intermediary between application programs and graphics hardware, supporting output primitives and interaction devices. There are two main types of graphics software: general programming packages that provide extensive graphics functions for use in languages like C and FORTRAN, including functions for shapes, colors, and transformations; and special-purpose applications packages that are designed for non-programmers to generate displays without programming knowledge, such as painting and CAD programs.










