Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times


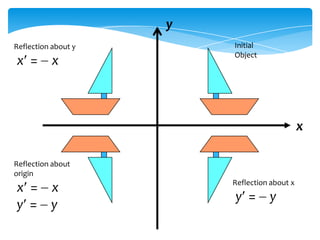
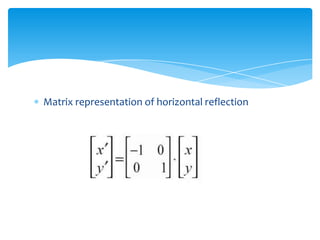
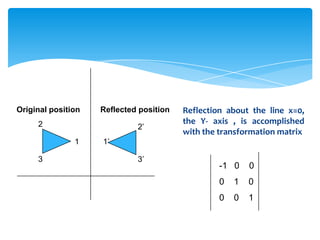
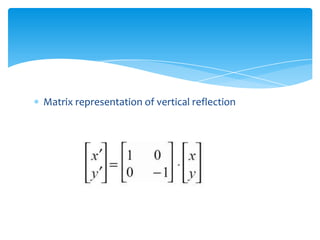
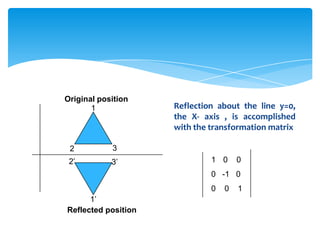



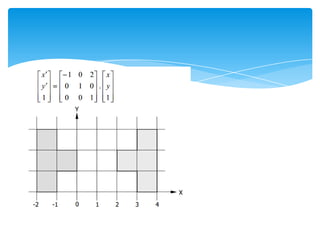


This document discusses reflections in 2-D spaces. It defines reflection as rotating an object 180 degrees around a reflection axis. It shows examples of reflecting objects about the y-axis and x-axis, as well as the transformation matrices used for horizontal and vertical reflections. It also provides an example of reflecting about a non-standard axis, in this case the line x=1, and shows the steps and resulting transformation.











