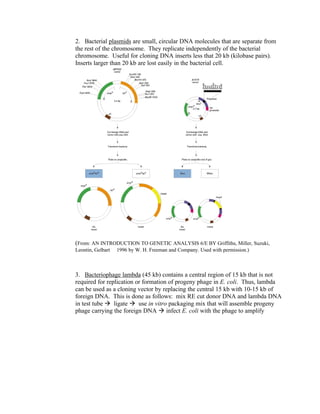
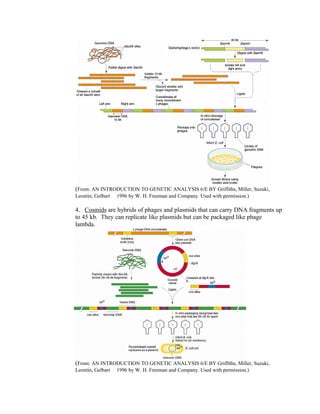
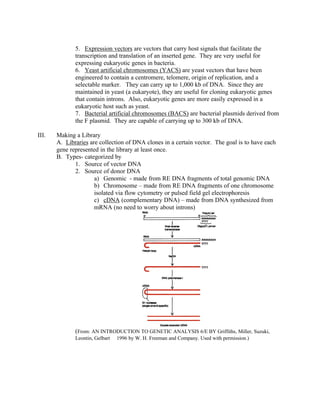
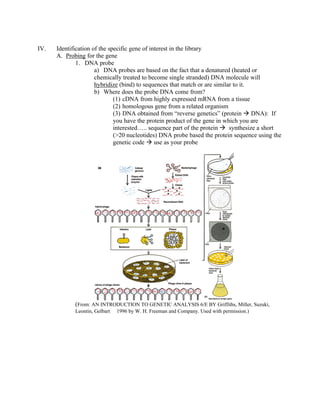
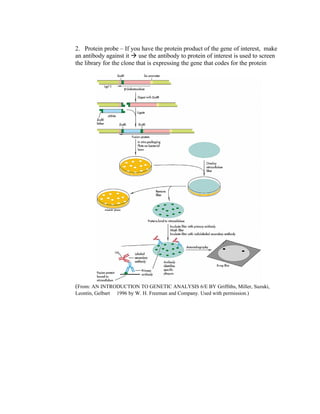
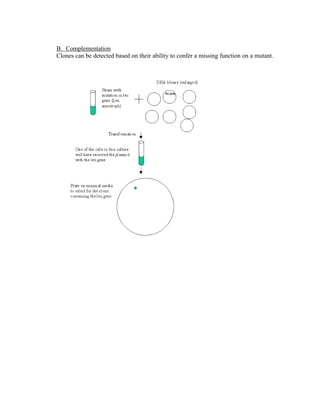
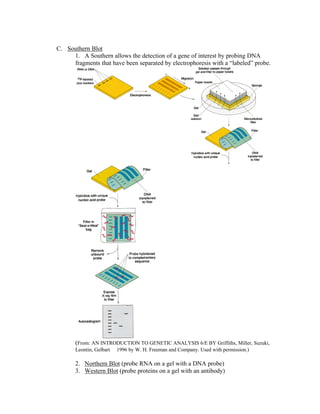
Recombinant DNA technology allows for the creation of new combinations of DNA segments not found in nature. DNA is isolated, cut with restriction enzymes, and ligated into cloning vectors which are then transformed into host cells. This amplifies the recombinant DNA. Vectors like plasmids and bacteriophages are used to clone DNA fragments. Libraries are collections of DNA clones that represent all genes. Specific genes of interest can be identified by probing the library with a DNA or protein probe based on known sequences.