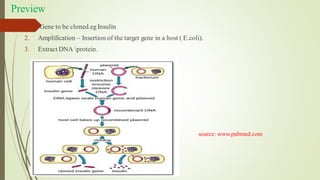
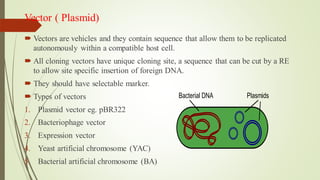
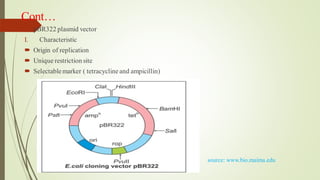
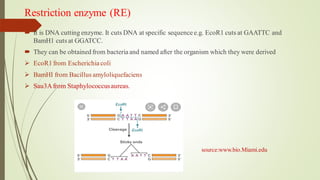
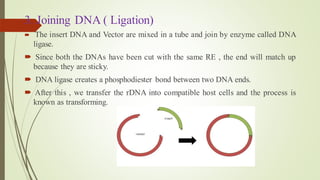
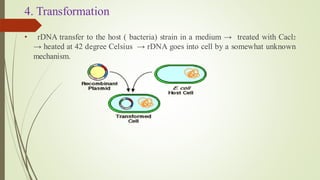
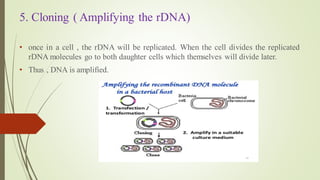
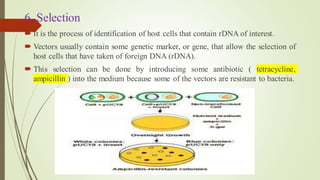
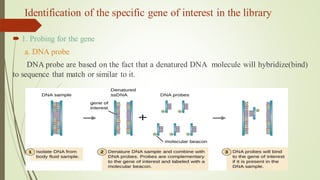
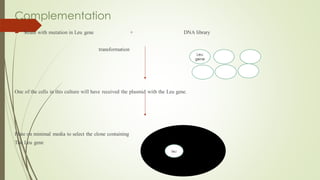
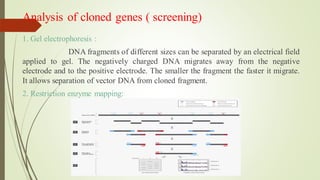
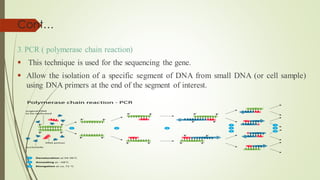
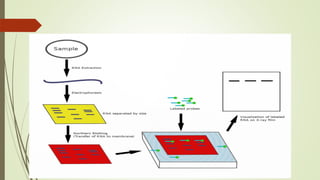
Recombinant DNA technology allows DNA to be artificially combined from different sources. It involves isolating the target DNA and vector, cutting them with restriction enzymes, joining them together with DNA ligase, transforming them into host cells, cloning the recombinant DNA by cell replication, and selecting cells containing the inserted gene. Recombinant DNA has applications in producing pharmaceuticals like insulin and vaccines, genetically modifying organisms, gene therapy, and more.