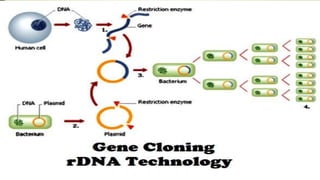
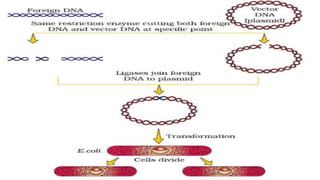
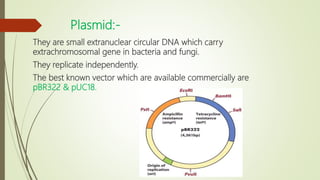
Recombinant DNA (r-DNA) technology, also known as genetic engineering, involves manipulating genetic material in vitro by cutting DNA into fragments and introducing them into host cells to alter phenotypes. There are three main tools used: enzymes, vector/vehicle DNA, and passenger DNA. Enzymes like endonucleases and ligases are used to cut and join DNA fragments. Vectors like plasmids are used to transfer passenger DNA, which can be cDNA, synthetic DNA, or random DNA fragments, into host cells. The goal is to alter organisms by genes or DNA sequences from other sources to suit human needs.