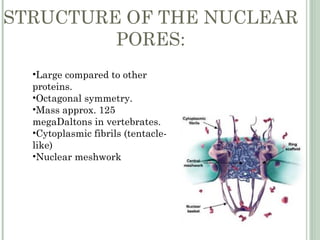
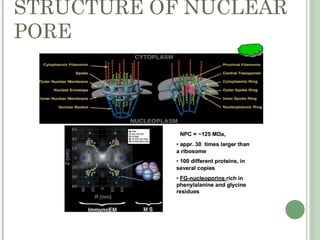
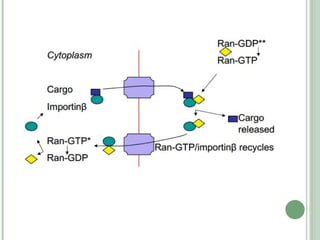
The nuclear envelope consists of an inner and outer nuclear membrane separated by the perinuclear space and punctuated by nuclear pore complexes. It encloses the nuclear DNA and separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The nuclear lamina, composed of lamin proteins and membrane proteins, lies underneath the inner nuclear membrane and provides mechanical support. Nuclear pore complexes have an octagonal symmetry and allow regulated transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm through import and export signals and adapter proteins.