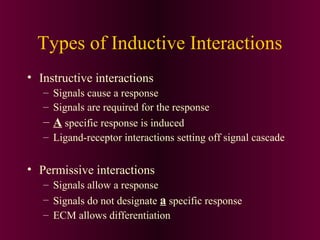
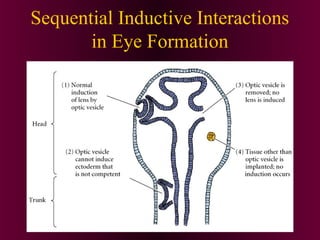
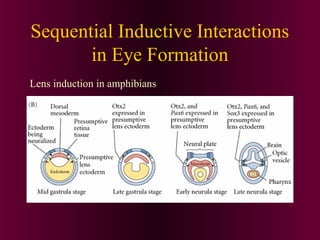
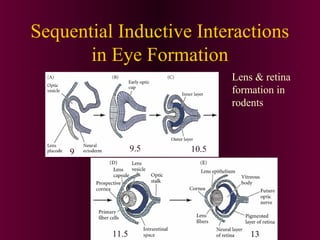
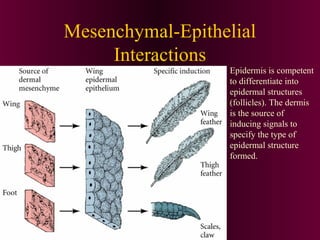
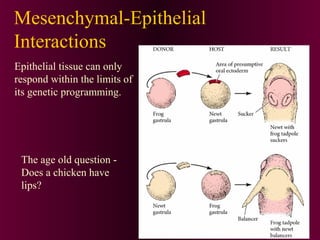
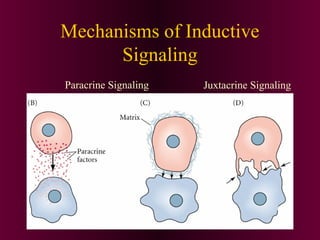
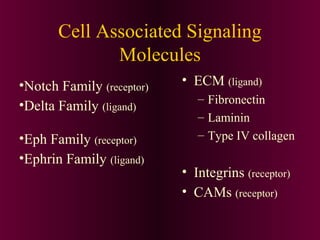
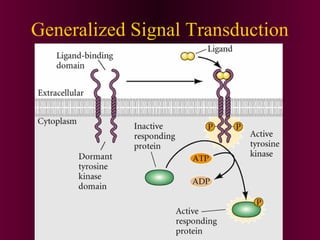
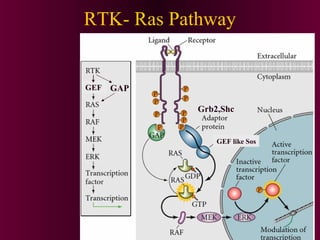
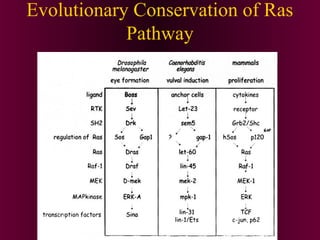
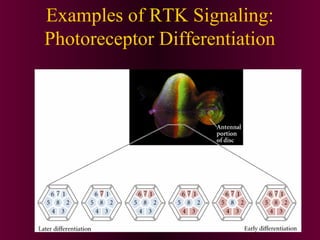
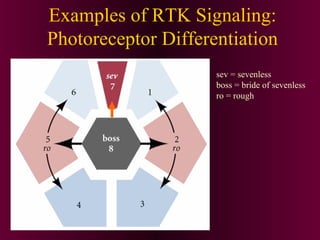
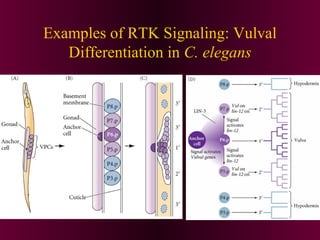
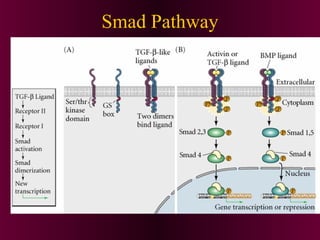
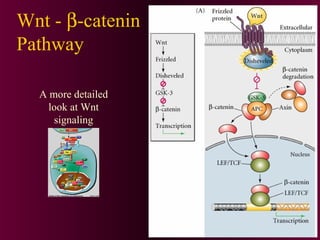
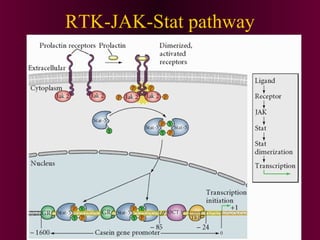
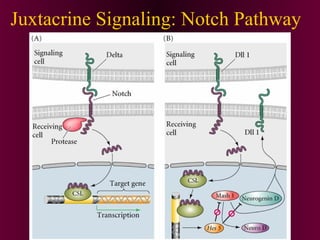
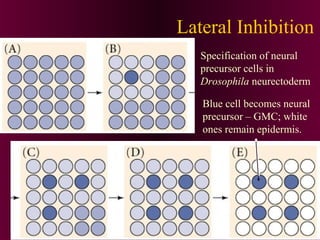
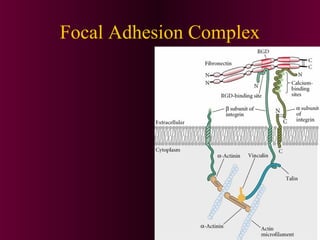
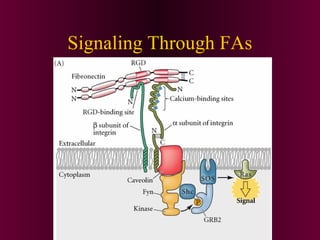
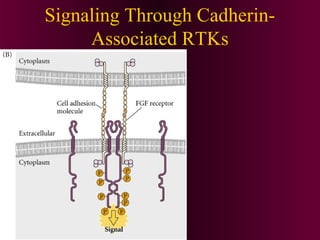
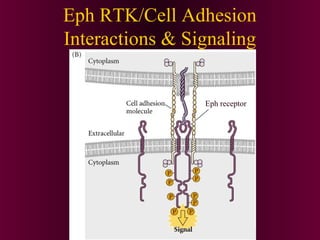
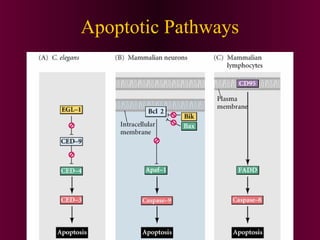
This document discusses cell-cell signaling through inductive interactions. It describes the key components of signaling including inducer cells that emit signals, responder cells that receive signals and change in response, and competence which is the ability of cells to respond. The main types of inductive interactions are instructive, where a specific response is induced, and permissive, where signals allow but do not determine the response. Examples of embryonic inductions are also provided. The mechanisms of inductive signaling include paracrine signaling through secreted factors and juxtacrine signaling through cell-associated proteins. Several key signaling pathways are then described in more detail such as RTK-Ras, Smad, Wnt-beta-catenin, JAK-