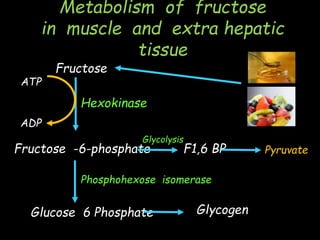
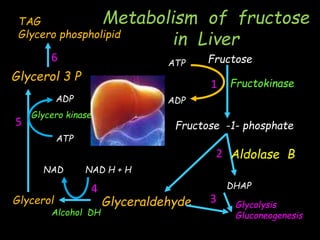
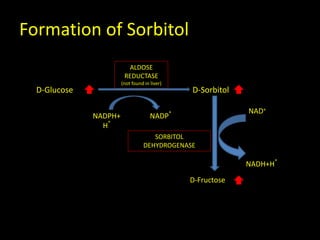
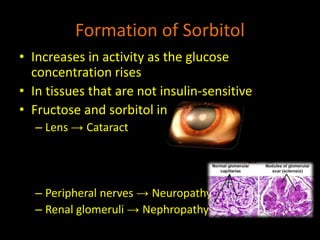
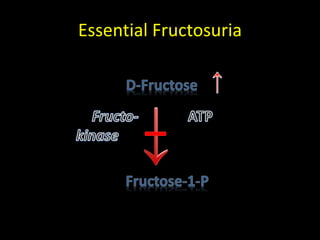
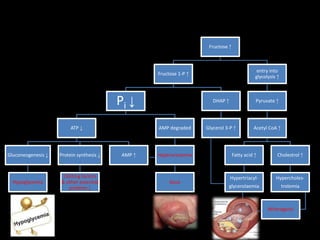
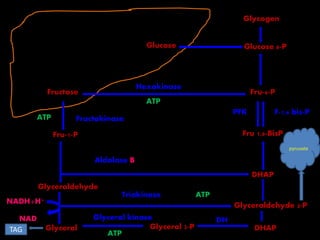
This document discusses fructose metabolism in the liver and extrahepatic tissues. It notes that fructose is metabolized to fructose-1-phosphate in the liver by fructokinase and can then enter pathways like glycolysis, glycogen synthesis, or lipogenesis. In extrahepatic tissues, fructose is first phosphorylated to fructose-6-phosphate by hexokinase and can then be converted to glucose-6-phosphate and enter glycolysis. Excessive fructose consumption can lead to hypoglycemia, hyperuricemia, and increased fatty acid and cholesterol levels due to increased flux through these metabolic pathways. Rare genetic defects like hereditary fructose int