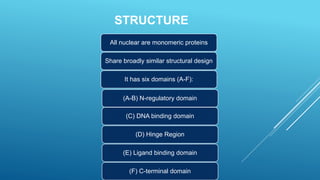
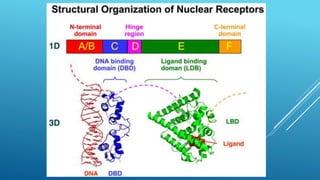
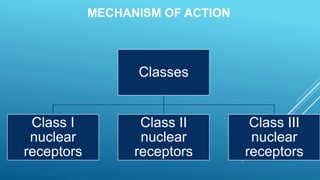
Nuclear receptors are a family of transcription factors that regulate gene expression in response to small lipophilic compounds like steroid hormones and lipids. They have a conserved structure of six domains including a ligand binding domain that activates gene expression when a ligand is present. Nuclear receptors function by binding to DNA as monomers or dimers and recruiting other proteins to regulate transcription. They are classified into three classes based on their ligand, subcellular localization, and mechanism of action.