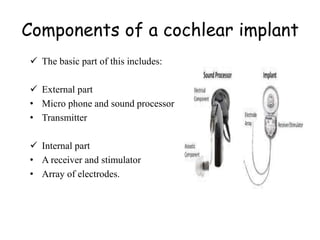
The Nucleus Hybrid L24 Cochlear Implant System is a device approved by the FDA to treat sensorineural hearing loss. It combines a cochlear implant and hearing aid to provide electrical stimulation for high frequencies and acoustic hearing for low frequencies. The internal implant converts sound to electrical signals that are transmitted to electrodes in the cochlea. This helps patients with good low-frequency hearing but poor high-frequency hearing by preserving natural hearing and improving sound perception. While it provides benefits over conventional hearing aids, limitations include inability to transmit rapid sounds and high medical costs.