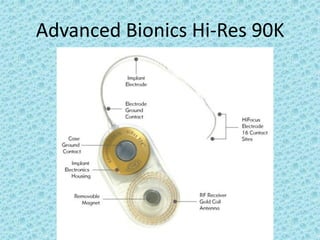
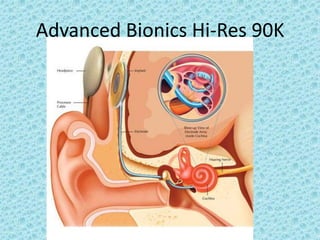
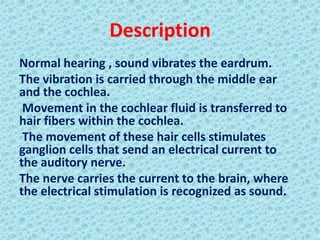
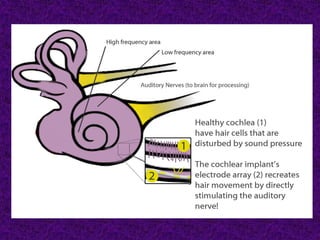
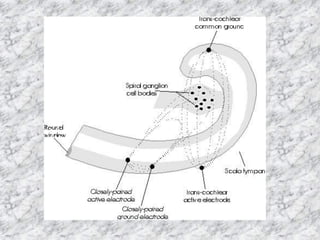
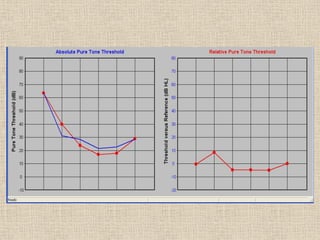
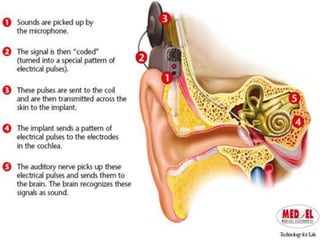
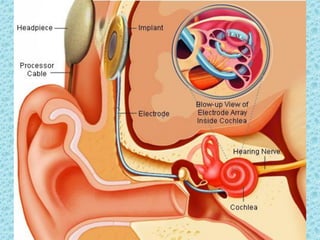
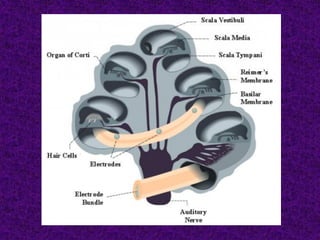
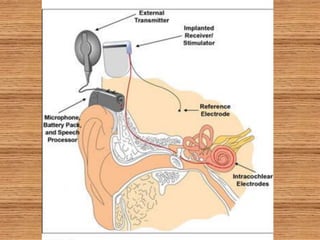
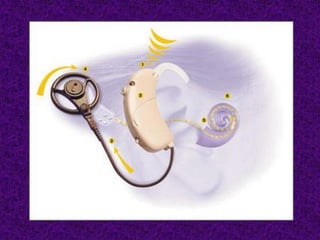
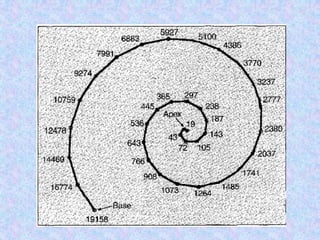
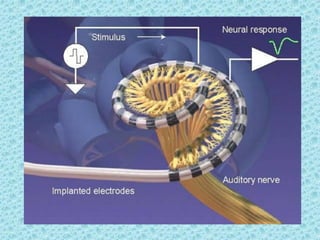
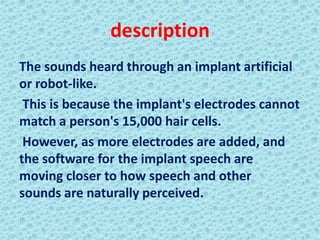
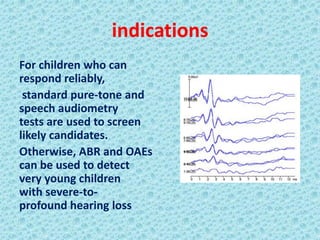
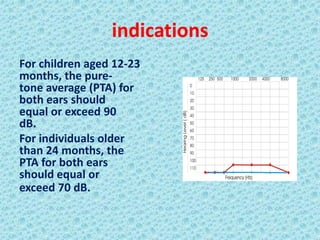
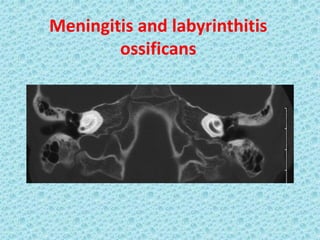
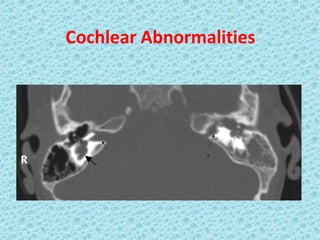
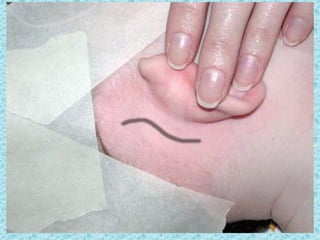
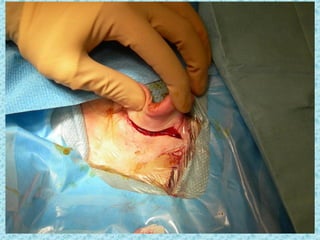
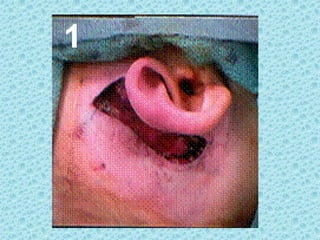
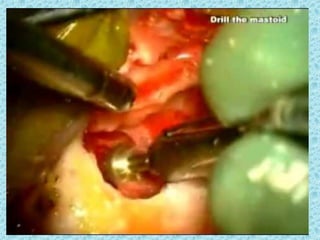
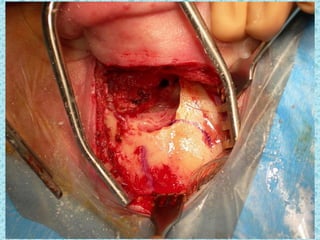
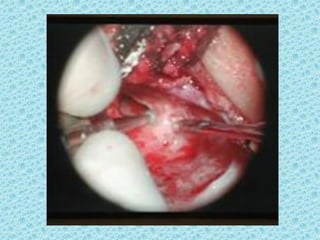
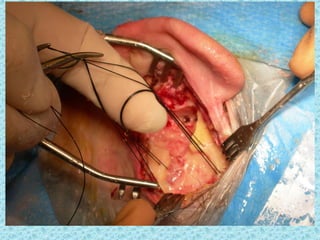
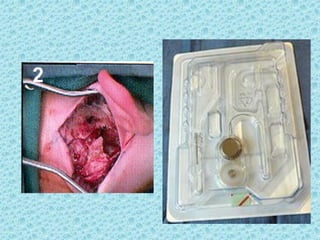
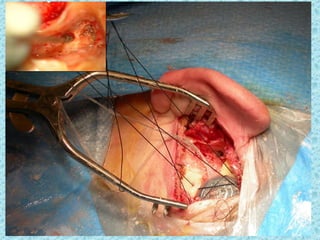
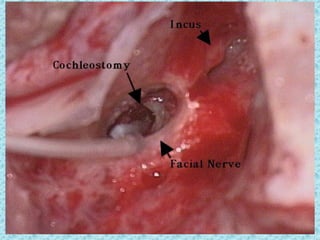
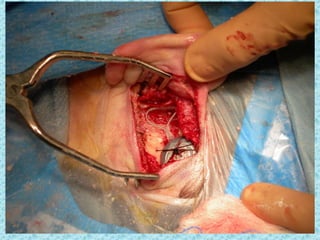
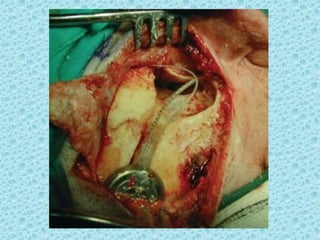
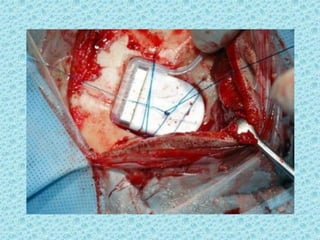
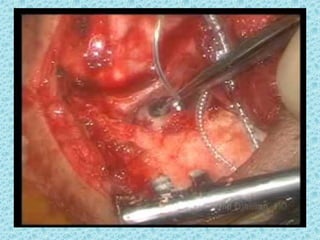
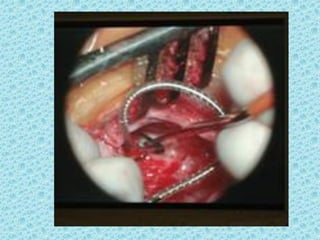
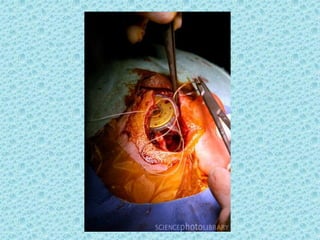
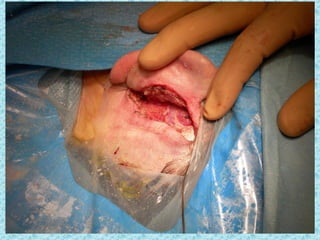
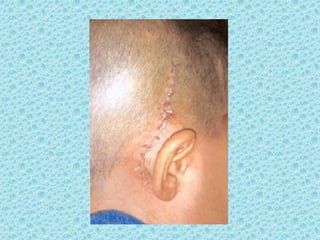
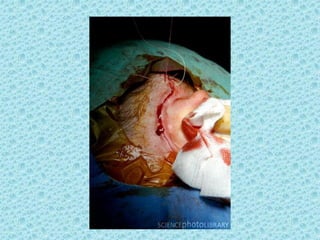
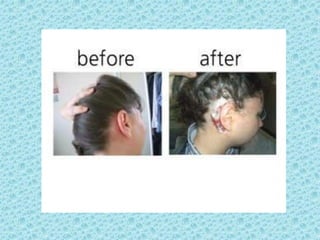
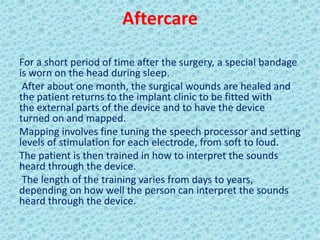
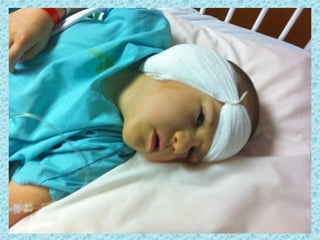
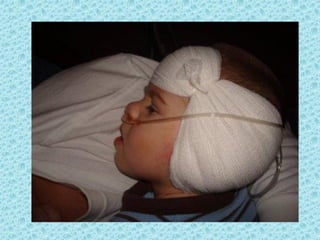
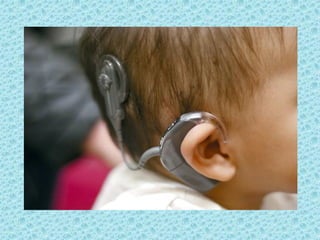
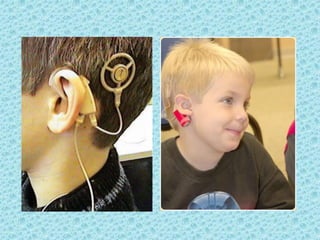
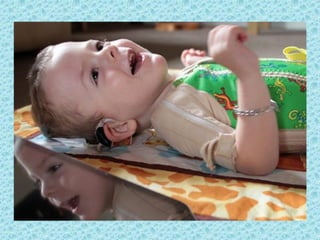
A cochlear implant is an electronic device surgically implanted to treat severe to profound hearing loss by stimulating the auditory nerve directly. The device has evolved since its initial development in the late 1960s, with significant advancements leading to multi-channel implants that improve sound perception. While cochlear implants improve communication for many patients, they come with risks, including surgical complications and potential device failure.