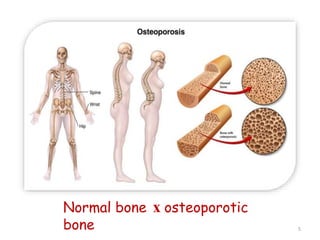
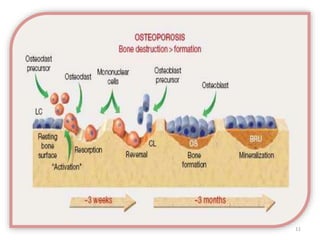
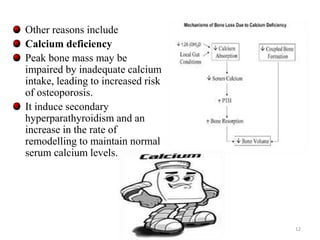
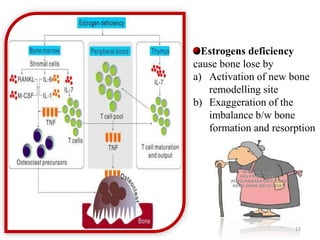
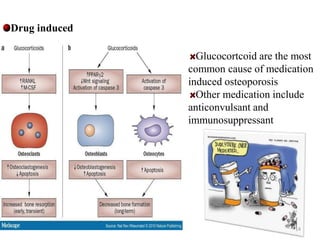
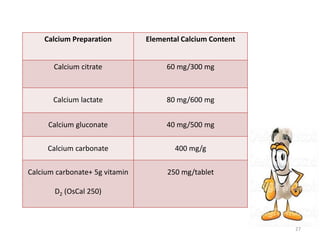
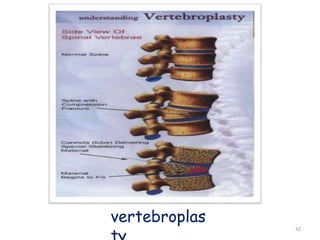
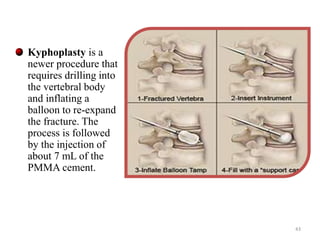
This document discusses osteoporosis, including its definitions, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment options. Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women, and can be caused by aging, genetics, lifestyle factors, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise and fall prevention as well as pharmacologic options like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and drugs that modify bone metabolism.